Opaque polyethylene offers superior UV protection and light-blocking properties, making it ideal for packaging products sensitive to light exposure. Transparent polyethylene provides clarity and visibility of the contents while maintaining flexibility and moisture resistance. Choosing between opaque and transparent polyethylene depends on the need for product visibility versus protection from environmental factors.
Table of Comparison
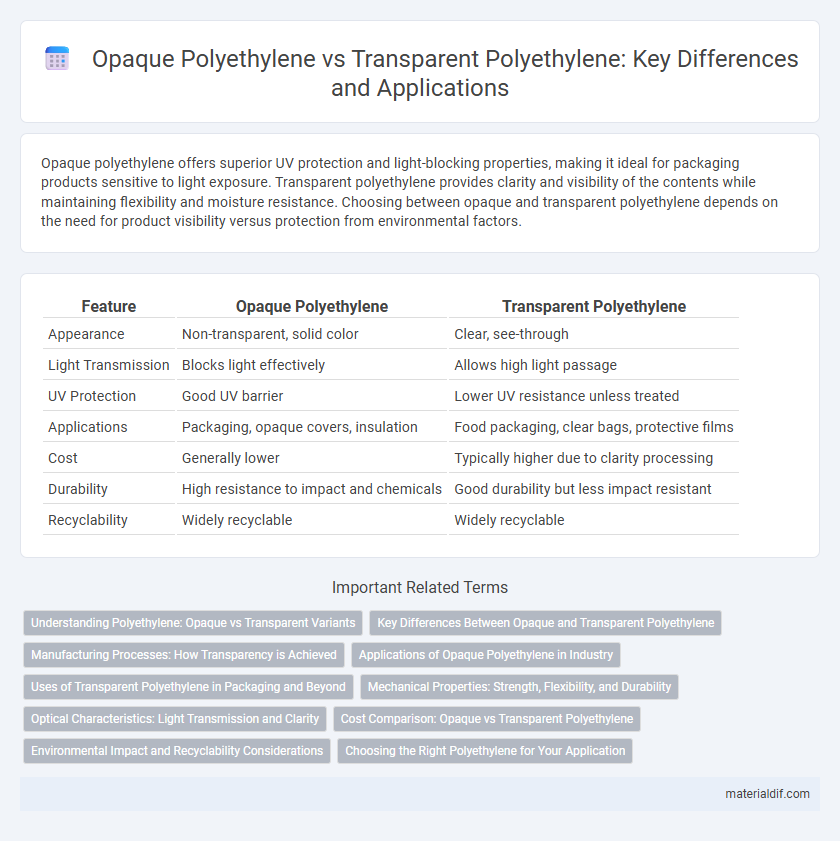
| Feature | Opaque Polyethylene | Transparent Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Non-transparent, solid color | Clear, see-through |
| Light Transmission | Blocks light effectively | Allows high light passage |
| UV Protection | Good UV barrier | Lower UV resistance unless treated |
| Applications | Packaging, opaque covers, insulation | Food packaging, clear bags, protective films |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher due to clarity processing |
| Durability | High resistance to impact and chemicals | Good durability but less impact resistant |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable | Widely recyclable |
Understanding Polyethylene: Opaque vs Transparent Variants
Opaque polyethylene is characterized by the addition of fillers or pigments, which block light transmission and enhance UV resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring light protection and privacy. Transparent polyethylene, on the other hand, maintains clarity by minimizing additives, offering excellent visibility and flexibility for packaging and protective coverings. Understanding the structural differences between these variants helps in selecting the right polyethylene type for tailored performance in industrial and consumer products.
Key Differences Between Opaque and Transparent Polyethylene
Opaque polyethylene features a high concentration of additives or pigments that block light transmission, resulting in a solid, non-see-through appearance, which is ideal for applications requiring UV protection and content privacy. Transparent polyethylene lacks these additives, allowing for clear visibility through the material, making it suitable for packaging that displays product contents. The differences in light transmission affect mechanical properties such as tensile strength and flexibility, with opaque variants often exhibiting enhanced durability but reduced clarity.
Manufacturing Processes: How Transparency is Achieved
Opaque polyethylene is produced by incorporating additives like titanium dioxide or calcium carbonate during the polymerization or extrusion process, scattering light and preventing it from passing through. Transparent polyethylene is achieved by controlling the polymer's crystallinity and molecular weight distribution, resulting in fewer light-scattering crystals and a clearer, more uniform structure. The manufacturing process for transparent polyethylene often involves adjusting cooling rates and employing advanced catalyst systems to optimize clarity without compromising material strength.
Applications of Opaque Polyethylene in Industry
Opaque polyethylene is extensively used in packaging industries for producing containers, bottles, and lids that require UV resistance and protection from light-sensitive contents. It is favored in agricultural films and geomembranes due to its ability to block sunlight, preventing weed growth and soil degradation. Additionally, opaque polyethylene plays a critical role in manufacturing household products and automotive parts that demand durability and reduced glare.
Uses of Transparent Polyethylene in Packaging and Beyond
Transparent polyethylene is widely utilized in packaging applications such as food wrap, clear bags, and protective covers due to its excellent clarity and moisture barrier properties. Beyond packaging, it serves in agricultural films, greenhouse covers, and flexible containers where visibility and durability are essential. Its adaptability and clarity make it a preferred choice for products requiring both protection and visual inspection.
Mechanical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Opaque polyethylene exhibits higher tensile strength and enhanced impact resistance compared to transparent polyethylene, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Transparent polyethylene offers greater flexibility and elongation at break, allowing for better formability and adaptability in packaging uses. Both types demonstrate excellent chemical resistance and durability, though opaque variants generally provide superior UV protection and long-term environmental stability.
Optical Characteristics: Light Transmission and Clarity
Opaque polyethylene exhibits low light transmission due to the presence of additives or fillers that scatter and absorb light, resulting in reduced clarity and a matte finish. Transparent polyethylene allows high light transmission, offering excellent clarity with minimal light scattering, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility through the material. The optical characteristics of polyethylene directly influence its use in packaging, with opaque variants providing protection from light-sensitive contents and transparent forms enabling product visibility.
Cost Comparison: Opaque vs Transparent Polyethylene
Opaque polyethylene typically incurs lower production costs than transparent polyethylene due to the simpler manufacturing processes and fewer purity requirements. Transparent polyethylene demands higher-grade raw materials and specialized extrusion techniques, which increase its overall expense. The price differential can significantly impact packaging and product design decisions in industries prioritizing cost-efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability Considerations
Opaque polyethylene, often pigmented with additives such as titanium dioxide, tends to complicate recycling processes due to color contamination in recycled streams, reducing material purity and recyclability. Transparent polyethylene, lacking colorants, offers higher recyclability and better compatibility with mechanical recycling systems, promoting a circular economy. Both forms impact the environment, but transparent polyethylene's improved recyclability generally results in lower environmental footprints through enhanced material recovery and reduced landfill reliance.
Choosing the Right Polyethylene for Your Application
Opaque polyethylene offers superior UV resistance and is ideal for products requiring light protection, such as food packaging and agricultural films. Transparent polyethylene provides excellent clarity and is preferred for applications where product visibility is essential, including retail packaging and protective coverings. Selecting the right polyethylene depends on factors like durability, clarity requirements, and exposure conditions to optimize performance and cost-efficiency.
Opaque Polyethylene vs Transparent Polyethylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com