Opaque polyethylene (PE) offers superior light-blocking properties, making it ideal for packaging sensitive products requiring protection from UV rays and light exposure. Transparent PE provides excellent clarity and visibility, enhancing product presentation in retail environments while maintaining flexibility and durability. Choosing between opaque and transparent PE depends on the specific application needs, balancing protection with aesthetic appeal.
Table of Comparison
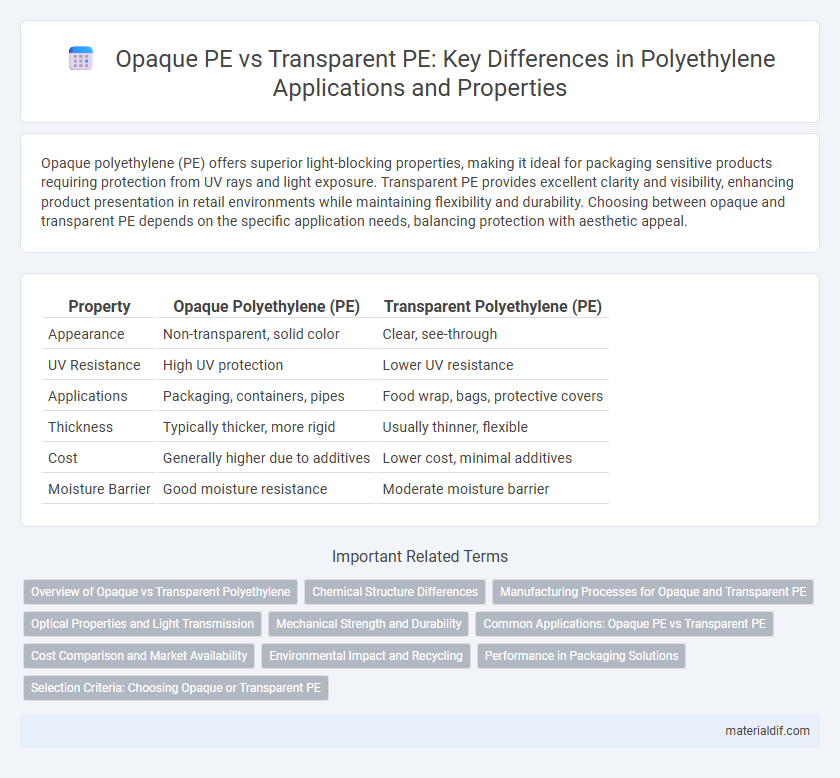
| Property | Opaque Polyethylene (PE) | Transparent Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Non-transparent, solid color | Clear, see-through |
| UV Resistance | High UV protection | Lower UV resistance |
| Applications | Packaging, containers, pipes | Food wrap, bags, protective covers |
| Thickness | Typically thicker, more rigid | Usually thinner, flexible |
| Cost | Generally higher due to additives | Lower cost, minimal additives |
| Moisture Barrier | Good moisture resistance | Moderate moisture barrier |
Overview of Opaque vs Transparent Polyethylene
Opaque polyethylene contains additives such as titanium dioxide that block light transmission, resulting in a material with enhanced UV resistance and improved protection for light-sensitive products. Transparent polyethylene, typically low-density or linear low-density PE, offers high clarity and flexibility, making it ideal for packaging applications where product visibility is essential. The choice between opaque and transparent polyethylene depends on the balance between protecting contents from light exposure and the need for visual presentation.
Chemical Structure Differences
Opaque polyethylene contains a higher concentration of branching and short-chain branches that disrupt the polymer chain packing, resulting in a more amorphous structure with increased light scattering. Transparent polyethylene, characterized by a linear or minimally branched molecular structure, allows tighter chain packing and higher crystallinity, enabling greater light transmission. The chemical structure differences directly influence the optical properties, with opaque PE typically having more comonomers like 1-butene or 1-hexene incorporated to introduce irregularities, while transparent PE maintains a more uniform polyethylene backbone.
Manufacturing Processes for Opaque and Transparent PE
Opaque polyethylene (PE) typically undergoes polymerization with additives such as titanium dioxide or other opacifiers during the extrusion or molding processes to achieve its non-transparent properties. Transparent PE is produced using high-purity catalysts and controlled polymerization parameters, minimizing impurities and crystallinity variations to enhance clarity. Manufacturing methods for transparent PE often involve advanced degassing and filtration techniques to reduce haze and improve optical performance.
Optical Properties and Light Transmission
Opaque polyethylene (PE) exhibits low light transmission due to its high concentration of fillers and additives, scattering light and preventing visibility through the material. In contrast, transparent PE has minimal impurities and a more crystalline structure, allowing higher optical clarity and light transmission rates, often exceeding 85%. These optical properties critically influence applications such as packaging, where transparency is essential for product visibility, while opacity provides UV protection and privacy.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Opaque polyethylene (PE) typically exhibits higher mechanical strength and enhanced durability due to the inclusion of additives like titanium dioxide that increase resistance to UV degradation and impact. Transparent PE, while offering superior clarity and flexibility, generally has lower tensile strength and is more susceptible to environmental stress cracking over time. The choice between opaque and transparent PE depends on the application's need for robustness versus visual transparency.
Common Applications: Opaque PE vs Transparent PE
Opaque polyethylene (PE) is commonly used in packaging for products that require UV protection and light blocking, such as detergent bottles, agricultural films, and milk jugs. Transparent PE finds applications in food wrap, grocery bags, and clear packaging, where product visibility is essential for consumer appeal. Both types serve distinct markets, with opaque PE enhancing durability and protection, while transparent PE offers clarity and flexibility for display purposes.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Opaque polyethylene (PE) typically incurs higher production costs due to the addition of opacifying agents like titanium dioxide, making it more expensive than transparent PE. Transparent PE offers greater market availability because of its wide use in packaging and low manufacturing costs, driving high demand globally. Cost differences influence product selection, with opaque PE preferred for applications requiring UV protection or concealment, while transparent PE dominates sectors emphasizing clarity and cost efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Opaque polyethylene typically contains additives such as titanium dioxide that hinder recyclability by contaminating clear PE recycling streams, leading to lower recycling rates and increased landfill waste. Transparent polyethylene, often used in films and packaging, allows easier sorting and recycling due to its purity and compatibility with existing recycling processes, reducing environmental impact by promoting circular use. Choosing transparent PE supports enhanced material recovery and minimizes environmental burdens associated with opaque PE disposal.
Performance in Packaging Solutions
Opaque polyethylene offers superior light-blocking properties, protecting contents from UV degradation and preserving product integrity in packaging solutions. Transparent polyethylene excels in clarity and visual appeal, allowing consumers to see the product while maintaining adequate moisture and gas barrier performance. Both materials provide excellent sealability and durability, but the choice depends on the specific packaging requirements related to product visibility and protection.
Selection Criteria: Choosing Opaque or Transparent PE
Selection criteria for choosing between opaque and transparent polyethylene (PE) primarily depend on product visibility, UV protection, and application requirements. Opaque PE offers superior UV resistance and concealment for products needing protection from light degradation, while transparent PE enables clear visibility of contents, enhancing consumer appeal and product identification. Mechanical strength and barrier properties should also be evaluated based on specific packaging or manufacturing needs.
Opaque PE vs Transparent PE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com