Anti-block additives in polyethylene PET prevent film layers from sticking together by creating a microscopic rough surface, enhancing handling and processing efficiency. Slip additives reduce the coefficient of friction on the film surface, improving machinability and reducing surface scratches during high-speed operations. Both additives optimize PET film performance but target different functional challenges in packaging and industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
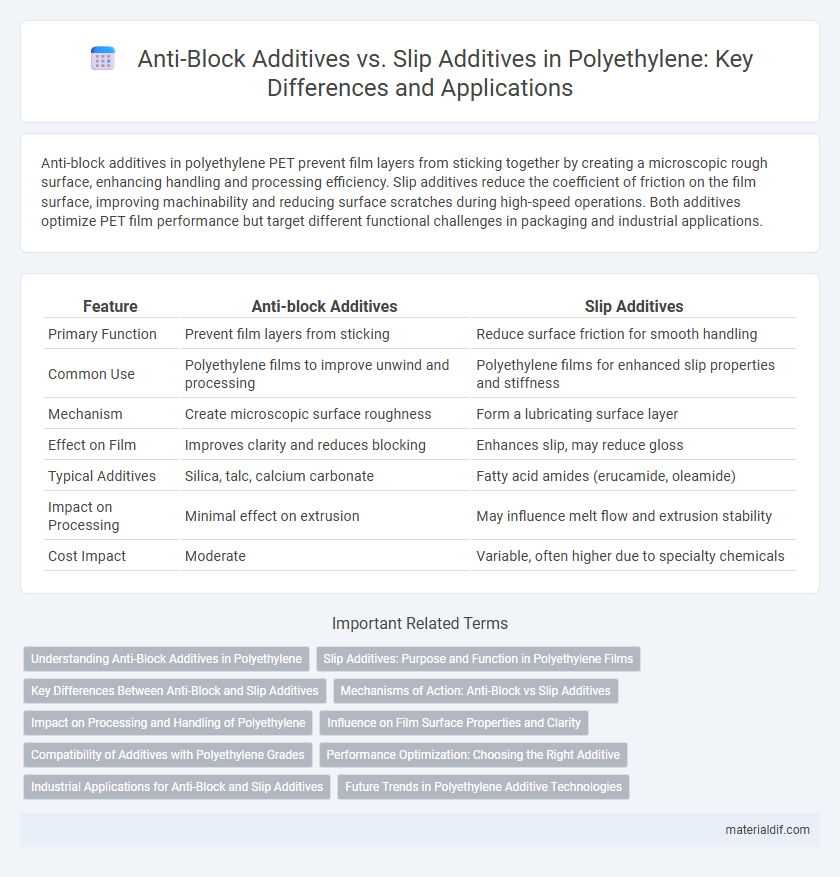
| Feature | Anti-block Additives | Slip Additives |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Prevent film layers from sticking | Reduce surface friction for smooth handling |
| Common Use | Polyethylene films to improve unwind and processing | Polyethylene films for enhanced slip properties and stiffness |
| Mechanism | Create microscopic surface roughness | Form a lubricating surface layer |
| Effect on Film | Improves clarity and reduces blocking | Enhances slip, may reduce gloss |
| Typical Additives | Silica, talc, calcium carbonate | Fatty acid amides (erucamide, oleamide) |
| Impact on Processing | Minimal effect on extrusion | May influence melt flow and extrusion stability |
| Cost Impact | Moderate | Variable, often higher due to specialty chemicals |
Understanding Anti-Block Additives in Polyethylene
Anti-block additives in polyethylene are fine particles that prevent film layers from sticking together by creating microscopic surface gaps, enhancing unwind and processing efficiency. These additives improve film clarity and reduce defects without compromising mechanical properties, making them essential in packaging applications. Unlike slip additives, which reduce surface friction for better machinability, anti-block agents specifically target adhesion issues between polymer layers.
Slip Additives: Purpose and Function in Polyethylene Films
Slip additives in polyethylene films reduce the coefficient of friction, enhancing surface smoothness and preventing film blocking during processing and end-use. These additives migrate to the film surface, forming a lubricating layer that facilitates handling, winding, and packaging performance. Compared to anti-block additives that create micro-roughness to prevent adhesion, slip additives improve film clarity and surface slip without compromising transparency.
Key Differences Between Anti-Block and Slip Additives
Anti-block additives in polyethylene films prevent layers from sticking together by creating microscopic particles that increase surface roughness, enhancing film separability and reducing blocking issues during processing. Slip additives, conversely, migrate to the film surface to lower the coefficient of friction, improving the film's glide and handling properties without affecting clarity or strength. The key differences lie in their functionality: anti-block additives focus on anti-adhesion properties while slip additives prioritize surface lubrication for easier film movement.
Mechanisms of Action: Anti-Block vs Slip Additives
Anti-block additives in polyethylene function by creating microscopic surface irregularities that reduce the adhesive forces between film layers, preventing them from sticking together. Slip additives work by migrating to the film surface and forming a lubricating layer that lowers the coefficient of friction, enhancing the material's slip properties. Both types of additives modify surface interactions but target different surface phenomena--anti-block additives reduce blocking by increasing surface roughness, while slip additives improve glide by decreasing surface friction.
Impact on Processing and Handling of Polyethylene
Anti-block additives in polyethylene prevent film layers from sticking together, improving handling and unwinding during processing, while slip additives reduce surface friction, enhancing downstream processing speed and efficiency. The presence of anti-block agents ensures easier film separation without affecting clarity, whereas slip agents minimize abrasions and static buildup, facilitating smoother transport and packaging. Both additives optimize the processing performance but address distinct challenges related to surface interaction and material flow.
Influence on Film Surface Properties and Clarity
Anti-block additives in polyethylene films enhance surface separation and reduce tackiness by creating micro-roughness, which can slightly decrease film clarity due to light diffusion. Slip additives improve surface lubrication, lowering coefficient of friction and enabling smoother film handling with minimal impact on transparency. Optimal selection and concentration of these additives balance desired surface properties with maintaining high optical clarity in polyethylene packaging films.
Compatibility of Additives with Polyethylene Grades
Anti-block additives and slip additives serve distinct functions in polyethylene films, with anti-blocks preventing film layers from sticking and slips reducing surface friction for smooth processing. Compatibility of these additives varies with polyethylene grades such as LDPE, LLDPE, and HDPE, where factors like molecular weight and density influence additive dispersion and effectiveness. Selecting appropriate additive types and concentrations tailored to specific polyethylene grades is crucial to maintain film clarity, mechanical properties, and processing efficiency.
Performance Optimization: Choosing the Right Additive
Anti-block additives enhance polyethylene's surface friction to prevent film layers from sticking together, improving processing efficiency and reducing defects. Slip additives lower the coefficient of friction between film layers, facilitating smooth handling and improved machinability during converting operations. Selecting the appropriate additive depends on balancing film clarity, production speed, and end-use performance requirements for optimized polyethylene product quality.
Industrial Applications for Anti-Block and Slip Additives
Anti-block additives in polyethylene prevent film layers from sticking together, enhancing processing efficiency and product handling in industrial applications such as packaging and agricultural films. Slip additives reduce the coefficient of friction on polyethylene surfaces, improving machinability and transport speed in high-speed converting operations like bag making and lamination. Both additives optimize polyethylene performance by addressing surface friction properties crucial for film production and end-use durability.
Future Trends in Polyethylene Additive Technologies
Future trends in polyethylene additive technologies emphasize enhanced anti-block additives that improve film clarity and surface smoothness while minimizing friction without compromising transparency. Innovations in slip additives focus on creating more sustainable, bio-based materials that reduce environmental impact and improve processing efficiency. Advances in nanotechnology and smart additives are expected to deliver multifunctional properties, combining anti-block and slip functions for optimized polyethylene performance in packaging and industrial applications.
Anti-block additives vs Slip additives Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com