Slip additives in polyethylene PET reduce surface friction, enhancing smoothness and processability during film extrusion and packaging applications. Antiblock additives prevent layers of PET film from sticking together by creating microscopic surface roughness, ensuring easy separation and improved handling. Both additives are essential for optimizing the performance and functionality of polyethylene PET films in industrial uses.
Table of Comparison
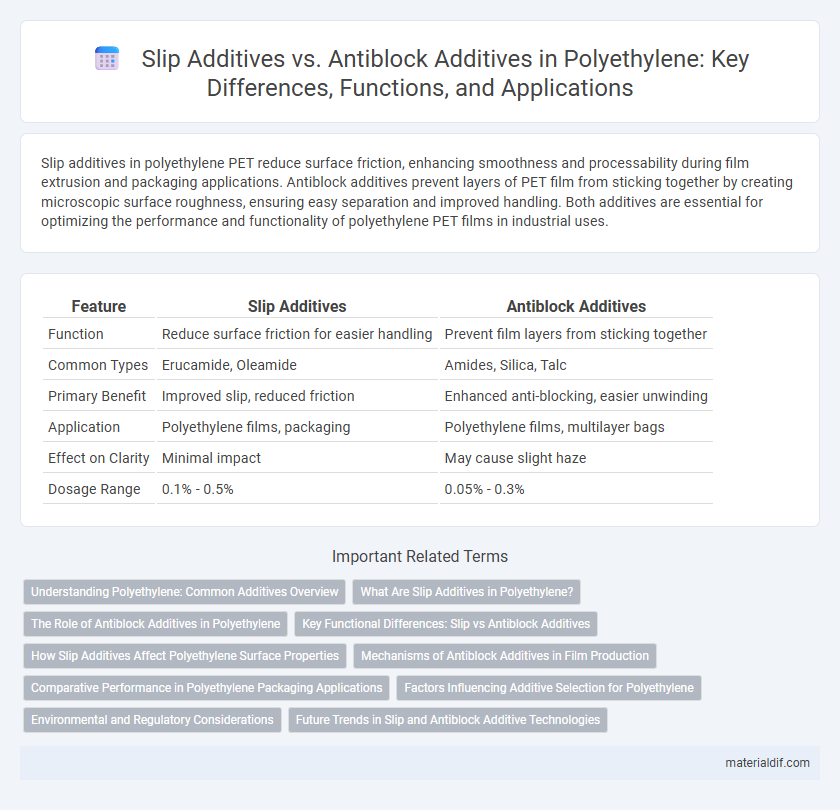
| Feature | Slip Additives | Antiblock Additives |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Reduce surface friction for easier handling | Prevent film layers from sticking together |
| Common Types | Erucamide, Oleamide | Amides, Silica, Talc |
| Primary Benefit | Improved slip, reduced friction | Enhanced anti-blocking, easier unwinding |
| Application | Polyethylene films, packaging | Polyethylene films, multilayer bags |
| Effect on Clarity | Minimal impact | May cause slight haze |
| Dosage Range | 0.1% - 0.5% | 0.05% - 0.3% |
Understanding Polyethylene: Common Additives Overview
Slip additives reduce friction on polyethylene surfaces, enhancing processability and improving handling during manufacturing and end-use applications. Antiblock additives create microscopic air gaps between polyethylene layers, preventing unwanted adhesion and facilitating sheet separation. Both additives optimize polyethylene film performance by addressing different surface interaction challenges essential for packaging and industrial uses.
What Are Slip Additives in Polyethylene?
Slip additives in polyethylene are specialized compounds incorporated to reduce surface friction, enhancing the material's ability to slide smoothly during processing and end-use applications. These additives migrate to the polymer's surface, forming a lubricating layer that minimizes blockiness and improves handling characteristics such as unwind force and machinability. Common slip additives include fatty acid amides like erucamide and oleamide, which are crucial for packaging films and flexible polyethylene products.
The Role of Antiblock Additives in Polyethylene
Antiblock additives in polyethylene are crucial for enhancing surface slip resistance by preventing layer adhesion during film processing and packaging applications. These additives create microscopic surface roughness, reducing blocking and facilitating smoother unwind and handling. Optimizing antiblock concentrations directly improves film clarity, mechanical properties, and processing efficiency in polyethylene manufacturing.
Key Functional Differences: Slip vs Antiblock Additives
Slip additives enhance the surface lubricity of polyethylene films, reducing friction and preventing film-to-film sticking during processing and handling. Antiblock additives, typically fine inorganic particles like silica or talc, create microscopic surface roughness that minimizes the contact area between film layers to improve clarity and ease of separation. The key functional difference lies in slip additives primarily lowering coefficient of friction, while antiblock additives focus on maintaining optical clarity and preventing blocking through surface texture modification.
How Slip Additives Affect Polyethylene Surface Properties
Slip additives in polyethylene enhance surface lubricity by migrating to the polymer-air interface, reducing the coefficient of friction and improving processability during film extrusion. These additives create a slippery surface that prevents blocking, enables smooth unwinding, and reduces abrasion in packaging applications. Compared to antiblock additives that primarily increase surface roughness to prevent film sticking, slip additives modify the surface energy and frictional properties for superior handling and clarity.
Mechanisms of Antiblock Additives in Film Production
Antiblock additives in polyethylene film production create micro-roughness on the film surface, preventing layers from sticking together during winding and handling. These additives typically consist of inorganic particles such as silica or talc, which protrude from the film surface to reduce contact area and improve slip performance. Proper dispersion and concentration of antiblock agents are crucial to maintain optical clarity and mechanical properties while ensuring efficient film separation.
Comparative Performance in Polyethylene Packaging Applications
Slip additives in polyethylene packaging primarily reduce surface friction, enhancing machinability and ease of handling by promoting smooth film release during processing. In contrast, antiblock additives improve clarity and prevent film layers from sticking together by creating micro-roughness on the surface, which maintains transparency and stacking quality. Comparative performance shows slip additives excel in high-speed packaging lines requiring rapid movement, while antiblock additives are superior in applications focused on film clarity and preventing blocking during storage.
Factors Influencing Additive Selection for Polyethylene
Slip additives and antiblock additives are selected based on factors such as the desired surface properties, processing conditions, and end-use requirements of polyethylene films. Slip additives enhance surface lubrication to reduce friction, improving machinability and handling, while antiblock additives create microscopic surface roughness to prevent film layers from sticking together. The compatibility with polyethylene matrix, additive migration rate, and impact on optical clarity are critical considerations in optimizing the performance of polyethylene packaging applications.
Environmental and Regulatory Considerations
Slip additives in polyethylene films reduce surface friction, improving processing and handling but may include components like erucamide, whose environmental persistence and potential bioaccumulation are under increasing regulatory scrutiny. Antiblock additives, typically silica or synthetic waxes, prevent film blocking without significant migration concerns, generally exhibiting lower environmental impact and facing fewer regulatory restrictions. Choosing between slip and antiblock additives requires balancing performance benefits with compliance to evolving global environmental regulations such as REACH and TSCA.
Future Trends in Slip and Antiblock Additive Technologies
Future trends in slip and antiblock additive technologies for polyethylene emphasize the development of sustainable, bio-based additives that improve film processing and surface properties while reducing environmental impact. Advances in nanotechnology enable enhanced slip performance and antiblocking efficiency at lower additive concentrations, contributing to thinner, lighter films with superior clarity and durability. Increased integration of multifunctional additives combining slip, antiblock, and antimicrobial properties is driving innovation in packaging solutions to meet evolving consumer demands and regulatory standards.
Slip Additives vs Antiblock Additives Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com