Extrusion grade polyethylene PET is designed for continuous processing, offering consistent melt flow and excellent surface finish ideal for films and sheets. Rotomolding grade polyethylene PET features higher molecular weight for enhanced impact resistance and thermal stability, ensuring durability in molded hollow products. Selecting the appropriate grade optimizes performance and product quality based on the manufacturing technique.
Table of Comparison
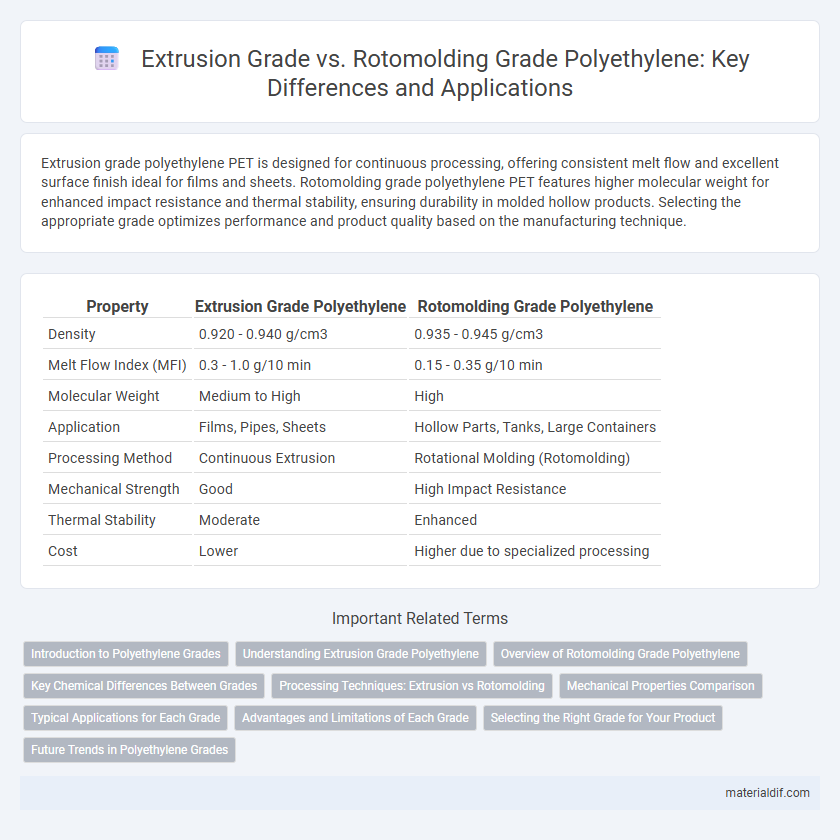
| Property | Extrusion Grade Polyethylene | Rotomolding Grade Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.920 - 0.940 g/cm3 | 0.935 - 0.945 g/cm3 |
| Melt Flow Index (MFI) | 0.3 - 1.0 g/10 min | 0.15 - 0.35 g/10 min |
| Molecular Weight | Medium to High | High |
| Application | Films, Pipes, Sheets | Hollow Parts, Tanks, Large Containers |
| Processing Method | Continuous Extrusion | Rotational Molding (Rotomolding) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good | High Impact Resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate | Enhanced |
| Cost | Lower | Higher due to specialized processing |
Introduction to Polyethylene Grades
Polyethylene grades vary primarily by their molecular weight and density, influencing their processing methods and applications. Extrusion grade polyethylene is formulated for continuous processes like film and pipe production, offering balanced melt flow and strength properties. Rotomolding grade polyethylene features a higher molecular weight and lower melt flow index, optimizing it for slow cooling in rotational molding applications, resulting in durable and impact-resistant products.
Understanding Extrusion Grade Polyethylene
Extrusion grade polyethylene is specifically formulated for processing methods that involve melting and forcing the polymer through a shaped die to form continuous profiles, such as pipes, sheets, and films. This grade typically features a narrow molecular weight distribution and optimized melt flow index, enabling consistent flow behavior and improved mechanical properties during extrusion. Understanding extrusion grade polyethylene is crucial for selecting materials that deliver high dimensional stability, excellent surface finish, and enhanced strength in applications requiring precise, uniform shapes.
Overview of Rotomolding Grade Polyethylene
Rotomolding grade polyethylene is specifically engineered for rotational molding processes, characterized by its low density and enhanced impact resistance to produce seamless, hollow products with uniform wall thickness. This grade exhibits a slower melt flow index compared to extrusion grade, ensuring better material distribution and superior mechanical properties. Its molecular structure offers excellent stress crack resistance and durability, making it ideal for manufacturing tanks, containers, and recreational equipment.
Key Chemical Differences Between Grades
Extrusion grade polyethylene typically contains higher molecular weight polymers with narrow molecular weight distribution, optimizing melt strength and flow for continuous shaping processes. Rotomolding grade polyethylene features lower density and broader molecular weight distribution to enhance stress relaxation and impact resistance during slow rotational molding cycles. Chemical additives and branching levels differ, with extrusion grades favoring linear structures for strength and rotomolding grades incorporating more long-chain branching to improve material flexibility and mold release.
Processing Techniques: Extrusion vs Rotomolding
Extrusion grade polyethylene is specifically formulated for the extrusion process, where melted resin is continuously forced through a die to create consistent, uniform shapes such as pipes, sheets, and films. Rotomolding grade polyethylene is optimized for rotational molding, involving heating the resin inside a rotating mold to produce hollow, seamless parts with uniform wall thickness, ideal for tanks and containers. The molecular weight and density of polyethylene differ between grades to accommodate the shear forces and cooling rates inherent to each processing technique, ensuring optimal material flow and final product properties.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Extrusion grade polyethylene typically exhibits higher tensile strength and stiffness due to its molecular structure optimized for continuous shaping processes, enhancing durability in applications requiring rigid forms. Rotomolding grade polyethylene, characterized by its lower density and molecular weight, offers superior impact resistance and ductility, making it ideal for complex hollow shapes that undergo repeated stress. Mechanical properties such as elongation at break and hardness vary significantly, with extrusion grades favoring rigidity and rotomolding grades prioritizing flexibility and impact endurance.
Typical Applications for Each Grade
Extrusion grade polyethylene is typically used for manufacturing thin films, pipes, and sheets due to its high melt flow and excellent processability. Rotomolding grade polyethylene excels in producing hollow and large seamless products such as tanks, playground equipment, and containers, benefiting from its lower density and better impact resistance. Each grade's distinct molecular structure optimizes performance for specific applications in packaging, construction, and industrial sectors.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Grade
Extrusion grade polyethylene offers high melt strength and excellent flow properties, making it ideal for producing thin films and complex profiles with superior surface finish, but it may suffer from lower impact resistance compared to rotomolding grade. Rotomolding grade polyethylene provides enhanced stress crack resistance and uniform wall thickness, which is advantageous for manufacturing hollow, seamless products like tanks and containers, though it generally exhibits slower production rates and higher material costs. Selecting between extrusion and rotomolding grades depends on the required mechanical properties, product geometry, and manufacturing efficiency.
Selecting the Right Grade for Your Product
Choosing the right grade of polyethylene depends on the manufacturing process and the mechanical properties required for the product. Extrusion grade polyethylene offers high melt flow index and is ideal for continuous profiles, films, and sheets, ensuring uniform thickness and strength. Rotomolding grade polyethylene features lower density and higher impact resistance, making it suitable for hollow, seamless items like tanks and containers that require durability and flexibility.
Future Trends in Polyethylene Grades
Future trends in polyethylene grades emphasize enhanced molecular weight distribution and improved thermal stability for both extrusion and rotomolding applications. Innovations in catalyst technology will enable the production of specialized polymers with tailored mechanical properties, increasing efficiency in manufacturing flexible packaging and large hollow parts. Sustainability drives the development of bio-based and recyclable extrusion and rotomolding grades, aligning with circular economy goals in the plastics industry.
Extrusion Grade vs Rotomolding Grade Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com