Polyethylene pipe offers excellent flexibility, durability, and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for plumbing, irrigation, and industrial fluid transport. In contrast, polyethylene sheet provides a versatile, lightweight solution for packaging, protective coverings, and barrier applications due to its flat, uniform surface. Both materials benefit from polyethylene's chemical resistance and low moisture absorption but cater to different structural and functional requirements.
Table of Comparison
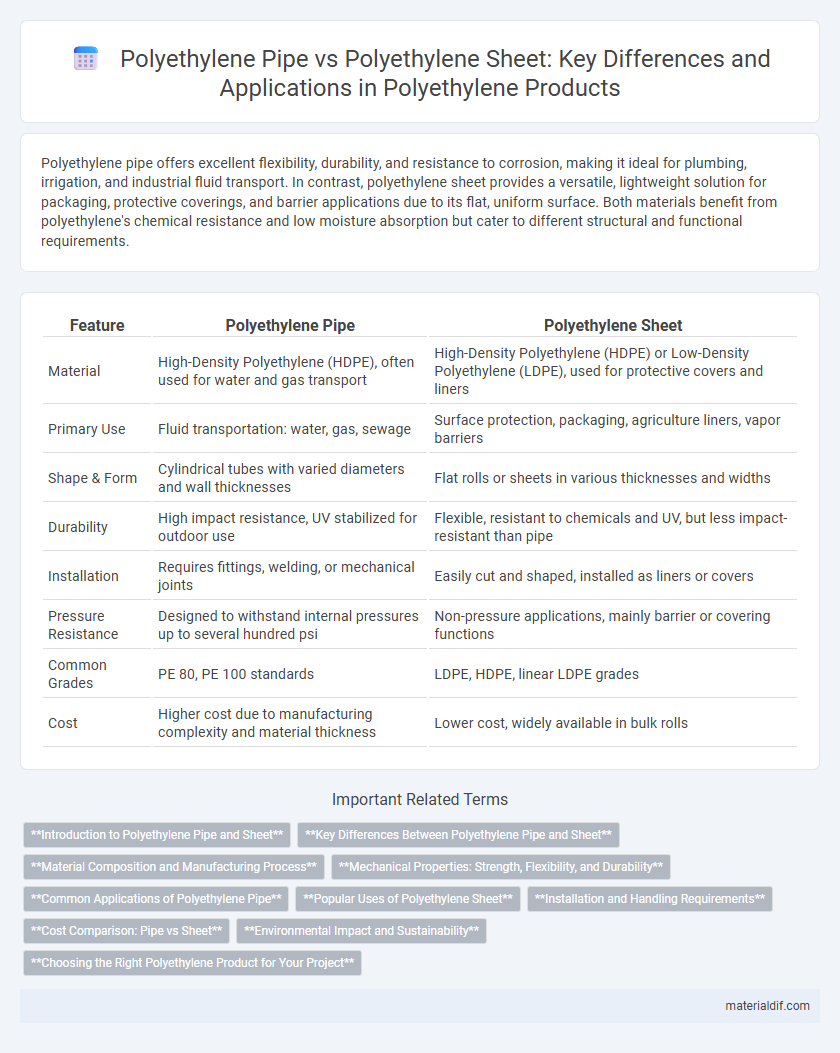
| Feature | Polyethylene Pipe | Polyethylene Sheet |
|---|---|---|
| Material | High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), often used for water and gas transport | High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) or Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), used for protective covers and liners |
| Primary Use | Fluid transportation: water, gas, sewage | Surface protection, packaging, agriculture liners, vapor barriers |
| Shape & Form | Cylindrical tubes with varied diameters and wall thicknesses | Flat rolls or sheets in various thicknesses and widths |
| Durability | High impact resistance, UV stabilized for outdoor use | Flexible, resistant to chemicals and UV, but less impact-resistant than pipe |
| Installation | Requires fittings, welding, or mechanical joints | Easily cut and shaped, installed as liners or covers |
| Pressure Resistance | Designed to withstand internal pressures up to several hundred psi | Non-pressure applications, mainly barrier or covering functions |
| Common Grades | PE 80, PE 100 standards | LDPE, HDPE, linear LDPE grades |
| Cost | Higher cost due to manufacturing complexity and material thickness | Lower cost, widely available in bulk rolls |
Introduction to Polyethylene Pipe and Sheet
Polyethylene pipe is engineered for fluid transport in applications such as water supply, gas distribution, and irrigation, characterized by high durability and flexibility. Polyethylene sheets, typically used in packaging, geomembranes, and construction, offer excellent chemical resistance and tensile strength for barrier and protective purposes. Both forms leverage polyethylene's lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, tailored to distinct industrial and commercial functions.
Key Differences Between Polyethylene Pipe and Sheet
Polyethylene pipe is engineered for durability and flexibility in fluid transport applications, featuring a hollow cylindrical design that withstands high pressure and environmental stress. Polyethylene sheet, however, is a flat, solid form primarily used for barriers, liners, and protective covers, offering versatility in thickness and size for diverse industrial and construction uses. The key differences lie in their structural design, intended function, and mechanical properties tailored to specific applications such as piping systems versus surface protection or containment.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Polyethylene pipe and polyethylene sheet both utilize high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyethylene resins, but their material composition varies slightly to suit specific applications: polyethylene pipe often incorporates additives for enhanced flexibility and impact resistance, while polyethylene sheet focuses on stiffness and surface finish. The manufacturing process for polyethylene pipe typically involves extrusion with precise diameter control and often includes fusion welding methods for joint integrity, whereas polyethylene sheets are produced through calendaring or flat extrusion to achieve uniform thickness and smooth surfaces. These differences in composition and processing ensure that polyethylene pipes provide durability and pressure resistance for fluid transport, while sheets deliver versatility in packaging, lining, and industrial fabrication.
Mechanical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Polyethylene pipe exhibits superior mechanical strength and pressure resistance, making it ideal for fluid transport applications requiring high durability under stress. In contrast, polyethylene sheet offers greater flexibility and impact resistance, suitable for packaging and protective coverings where adaptability is crucial. Both materials demonstrate excellent chemical resistance and environmental stress crack resistance, but pipe forms prioritize tensile strength while sheets emphasize flexibility and toughness.
Common Applications of Polyethylene Pipe
Polyethylene pipe is extensively used in water supply systems, natural gas distribution, and agricultural irrigation due to its flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability under varying pressures. Its ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions and resist corrosion makes it ideal for underground and industrial piping applications. Common installations include municipal water mains, gas service lines, and wastewater management systems, where longevity and leak resistance are critical.
Popular Uses of Polyethylene Sheet
Polyethylene sheets are widely used in packaging, construction, and industrial applications due to their durability, flexibility, and moisture resistance. Common uses include protective coverings, vapor barriers, and liners for tanks and ponds. These sheets also serve as insulation material and in manufacturing components for automotive and consumer goods.
Installation and Handling Requirements
Polyethylene pipe requires specialized fittings and careful fusion welding techniques to ensure secure joints, while polyethylene sheets are typically installed using heat welding or mechanical fastening, which demands precise temperature control and alignment. Handling polyethylene pipes involves attention to bending radius and support spacing to prevent deformation, whereas sheets require flat storage and careful handling to avoid creases or tears. Both forms necessitate proper surface preparation to achieve optimal bonding and maintain material integrity during installation.
Cost Comparison: Pipe vs Sheet
Polyethylene pipes typically cost more per unit length than polyethylene sheets due to their specialized manufacturing process and pressure-rating specifications. Sheets offer a lower initial material cost and greater versatility for cutting and fabrication but may incur higher labor expenses for applications requiring piping solutions. Evaluating total project expenses involves comparing the upfront cost difference with installation efficiency and performance requirements of polyethylene pipe versus sheet.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene pipes often offer improved sustainability due to their long lifespan and recyclability compared to polyethylene sheets, which tend to have shorter usage cycles and higher rates of single-use waste. The manufacturing of polyethylene pipes generally consumes less energy and produces fewer emissions per unit of functional use, contributing to a reduced carbon footprint. Recyclability and durability of polyethylene pipes enhance resource efficiency, making them more environmentally favorable in applications requiring longevity and robustness.
Choosing the Right Polyethylene Product for Your Project
Polyethylene pipe offers superior flexibility and durability, making it ideal for water supply, irrigation, and industrial applications where pressure resistance is crucial. Polyethylene sheets provide excellent chemical resistance and are preferred for lining, flooring, and protective barriers in construction and environmental projects. Selecting the right polyethylene product depends on project requirements such as load conditions, exposure to chemicals, and the need for structural integrity or chemical protection.
Polyethylene Pipe vs Polyethylene Sheet Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com