HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) offers greater tensile strength, chemical resistance, and rigidity, making it ideal for heavy-duty containers and piping. MDPE (Medium-Density Polyethylene) provides more flexibility and impact resistance, suited for gas pipes and packaging films. Selecting between HDPE and MDPE depends on the specific application requirements related to durability and flexibility.
Table of Comparison
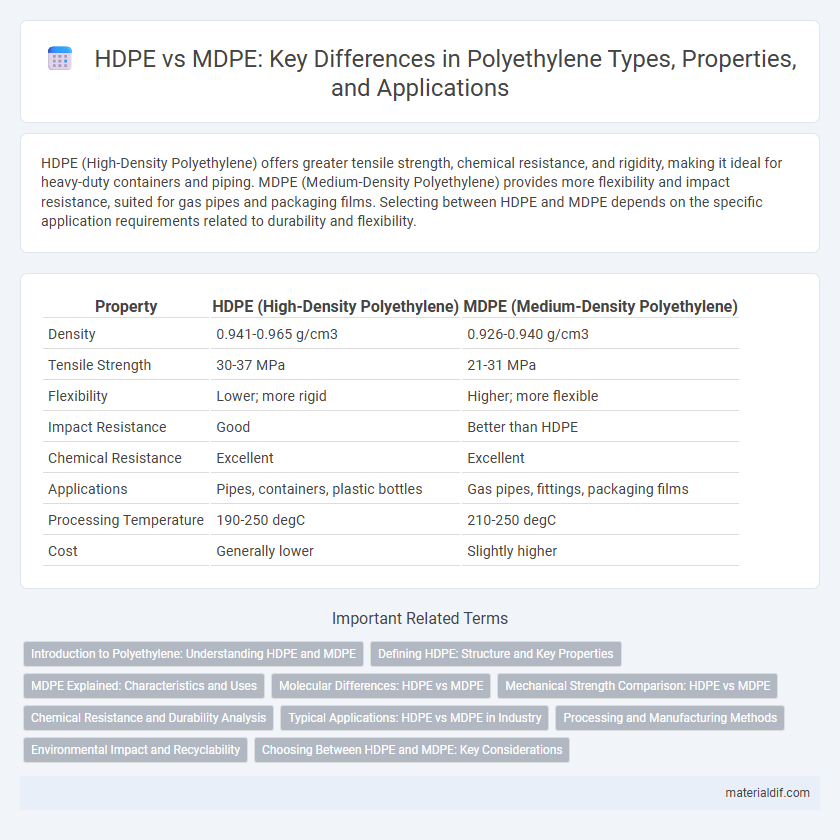
| Property | HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) | MDPE (Medium-Density Polyethylene) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.941-0.965 g/cm3 | 0.926-0.940 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 30-37 MPa | 21-31 MPa |
| Flexibility | Lower; more rigid | Higher; more flexible |
| Impact Resistance | Good | Better than HDPE |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Applications | Pipes, containers, plastic bottles | Gas pipes, fittings, packaging films |
| Processing Temperature | 190-250 degC | 210-250 degC |
| Cost | Generally lower | Slightly higher |
Introduction to Polyethylene: Understanding HDPE and MDPE
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Medium-Density Polyethylene (MDPE) are two key types of polyethylene polymers distinguished by their density and molecular structure. HDPE typically has a density range of 0.941 to 0.966 g/cm3, making it more rigid and suitable for applications like piping, containers, and plastic bottles, whereas MDPE's density ranges from 0.926 to 0.940 g/cm3, providing greater flexibility and impact resistance ideal for gas pipes and packaging films. Understanding the differences in crystallinity and mechanical properties between HDPE and MDPE is essential for selecting the appropriate material for specific industrial uses.
Defining HDPE: Structure and Key Properties
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) is characterized by a linear polymer structure with minimal branching, resulting in high tensile strength, rigidity, and resistance to impact and chemicals. Its density typically ranges from 0.94 to 0.97 g/cm3, providing enhanced mechanical properties compared to MDPE (Medium-Density Polyethylene). HDPE's crystalline structure contributes to its superior hardness and melting point, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and environmental stress crack resistance.
MDPE Explained: Characteristics and Uses
MDPE (Medium-Density Polyethylene) features a density ranging from 0.926 to 0.940 g/cm3, offering improved stress cracking resistance and flexibility compared to HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene). It is commonly used in applications such as gas pipes, fittings, and packaging materials where moderate strength and toughness are essential. Enhanced impact resistance and good chemical stability make MDPE ideal for corrosion-resistant containers and industrial piping systems.
Molecular Differences: HDPE vs MDPE
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) features a linear polymer structure with minimal branching, resulting in higher crystallinity and density ranging from 0.941 to 0.965 g/cm3. Medium-Density Polyethylene (MDPE) contains more short-chain branching, causing lower crystallinity and density between 0.926 and 0.940 g/cm3. These molecular differences impact mechanical properties, with HDPE exhibiting greater tensile strength and rigidity compared to the more flexible MDPE.
Mechanical Strength Comparison: HDPE vs MDPE
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) exhibits higher mechanical strength and tensile modulus compared to MDPE (Medium-Density Polyethylene), making it more suitable for applications requiring robust load-bearing capacity. MDPE offers greater flexibility and impact resistance due to its lower density and branched structure, which enhances toughness under stress. The superior rigidity of HDPE contrasts with the improved ductility of MDPE, influencing their respective uses in piping, packaging, and structural components.
Chemical Resistance and Durability Analysis
HDPE exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to MDPE, effectively resisting acids, bases, and alcohols, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments. MDPE offers greater impact resistance and flexibility, enhancing durability in applications subject to mechanical stress or temperature fluctuations. Both polymers demonstrate excellent long-term environmental stress crack resistance, with HDPE slightly outperforming MDPE in high-stress scenarios.
Typical Applications: HDPE vs MDPE in Industry
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) is widely used in the manufacturing of rigid containers, pipes, and geomembranes due to its high tensile strength and chemical resistance. MDPE (Medium-Density Polyethylene) finds applications in gas pipes, packaging films, and electrical cable insulation, balancing flexibility with strength. Both materials serve essential roles in the industry, with HDPE preferred for durability and MDPE for impact resistance and easier processing.
Processing and Manufacturing Methods
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) is processed primarily through methods such as injection molding, blow molding, and extrusion, allowing for the creation of rigid, high-strength products. MDPE (Medium-Density Polyethylene) is commonly manufactured via blow molding and rotational molding techniques, producing more flexible and impact-resistant items. Differences in polymer chain branching affect processing temperatures and cooling rates, with HDPE requiring higher temperatures and slower cooling for optimal crystallinity compared to MDPE.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) offers superior recyclability compared to medium-density polyethylene (MDPE) due to its more uniform molecular structure, facilitating easier processing in recycling plants. HDPE's enhanced environmental impact profile is attributed to its higher strength-to-density ratio, resulting in reduced material usage and lower carbon footprint during production. MDPE, while less commonly recycled, still supports circular economy goals but often requires more energy-intensive processes, increasing its overall environmental burden.
Choosing Between HDPE and MDPE: Key Considerations
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) offers superior tensile strength and chemical resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications like industrial containers and piping. Medium-Density Polyethylene (MDPE) provides greater flexibility and impact resistance, suitable for gas pipelines and protective film coatings. When choosing between HDPE and MDPE, consider the specific requirements for durability, pressure resistance, and environmental stress.
HDPE vs MDPE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com