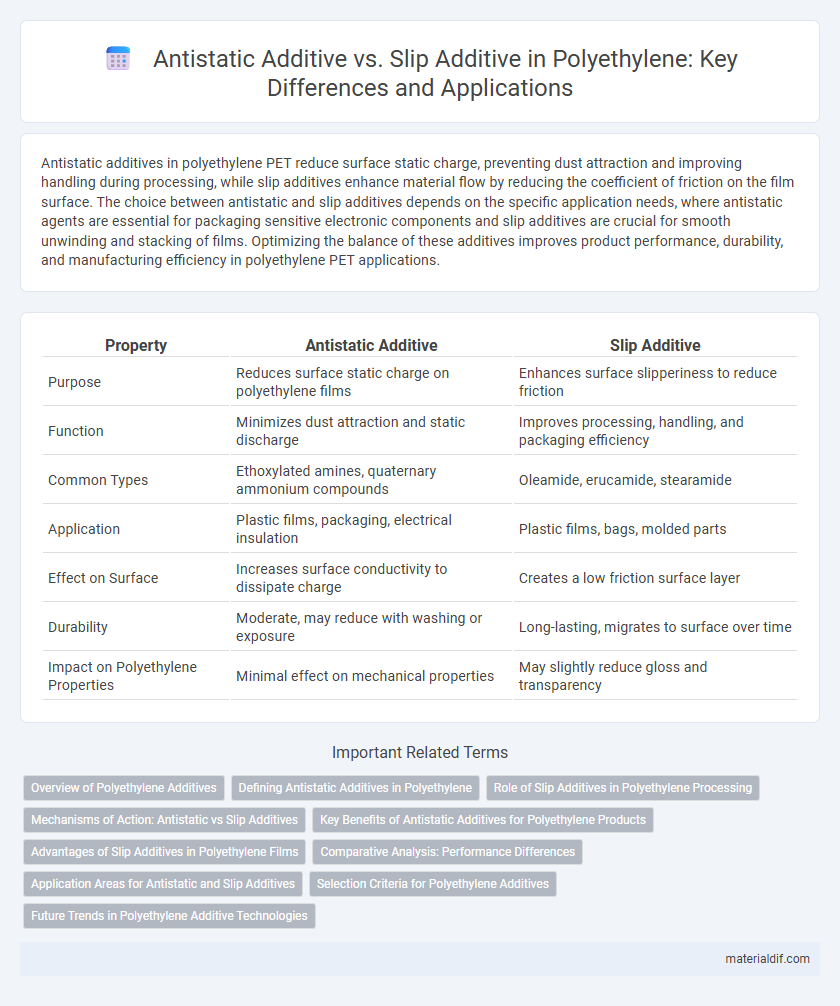
Antistatic additives in polyethylene PET reduce surface static charge, preventing dust attraction and improving handling during processing, while slip additives enhance material flow by reducing the coefficient of friction on the film surface. The choice between antistatic and slip additives depends on the specific application needs, where antistatic agents are essential for packaging sensitive electronic components and slip additives are crucial for smooth unwinding and stacking of films. Optimizing the balance of these additives improves product performance, durability, and manufacturing efficiency in polyethylene PET applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Antistatic Additive | Slip Additive |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces surface static charge on polyethylene films | Enhances surface slipperiness to reduce friction |
| Function | Minimizes dust attraction and static discharge | Improves processing, handling, and packaging efficiency |
| Common Types | Ethoxylated amines, quaternary ammonium compounds | Oleamide, erucamide, stearamide |
| Application | Plastic films, packaging, electrical insulation | Plastic films, bags, molded parts |
| Effect on Surface | Increases surface conductivity to dissipate charge | Creates a low friction surface layer |
| Durability | Moderate, may reduce with washing or exposure | Long-lasting, migrates to surface over time |
| Impact on Polyethylene Properties | Minimal effect on mechanical properties | May slightly reduce gloss and transparency |
Overview of Polyethylene Additives
Polyethylene additives enhance material performance by targeting specific properties such as static control and surface friction. Antistatic additives reduce static electricity buildup in polyethylene, ensuring safer handling and improved processing, while slip additives lower the coefficient of friction, facilitating easier film handling and packaging operations. Selecting the appropriate additive depends on the desired application balance between static dissipation and surface slip characteristics.
Defining Antistatic Additives in Polyethylene
Antistatic additives in polyethylene reduce surface resistivity by attracting moisture, preventing static electricity buildup that can damage electronic components or attract dust. These additives are chemically designed to migrate to the polymer surface, forming a conductive layer that dissipates static charges efficiently. In contrast, slip additives primarily improve polymer processing and surface lubrication without affecting the static dissipative properties essential for sensitive applications.
Role of Slip Additives in Polyethylene Processing
Slip additives in polyethylene processing reduce surface friction, improving material flow and preventing defects during extrusion and film formation. Unlike antistatic additives, which primarily minimize static charge buildup, slip additives enhance the polymer's flexibility and enable smoother handling by creating a lubricating layer on the surface. This lubrication effect facilitates faster production speeds and improves overall film quality in polyethylene applications.
Mechanisms of Action: Antistatic vs Slip Additives
Antistatic additives in polyethylene function by increasing the surface conductivity, allowing static charges to dissipate and preventing dust attraction or electric discharge. Slip additives reduce the coefficient of friction on the polyethylene surface by migrating to the surface and forming a lubricating layer, facilitating easier handling and processing. These mechanisms differ fundamentally, with antistatic additives targeting electrical properties while slip additives modify the physical surface characteristics.
Key Benefits of Antistatic Additives for Polyethylene Products
Antistatic additives enhance polyethylene products by reducing surface electrical charges, preventing dust attraction and improving printability and processing consistency. Unlike slip additives that primarily reduce friction and improve film mobility, antistatic agents maintain product clarity and avoid interference with mechanical properties. This ensures enhanced product performance in packaging, electronics, and medical applications, where static buildup can compromise quality and safety.
Advantages of Slip Additives in Polyethylene Films
Slip additives in polyethylene films improve processing by reducing surface friction, enabling faster manufacturing speeds and preventing film blocking. These additives enhance film clarity and gloss without compromising mechanical properties, unlike some antistatic agents that may alter surface tension. Slip additives also provide long-lasting lubrication, ensuring better performance in packaging applications where smooth handling and reduced equipment wear are critical.
Comparative Analysis: Performance Differences
Antistatic additives in polyethylene reduce surface resistivity, preventing static charge buildup and enhancing material handling safety, whereas slip additives primarily improve the polymer's surface lubrication, reducing friction and preventing blocking during processing. Antistatic agents function by attracting moisture to create a conductive surface layer, while slip additives migrate to the surface to form a lubricating film that facilitates smoother film extrusion and winding. The key performance difference lies in their functional contributions: antistatic additives focus on electrical properties, while slip additives optimize mechanical processing and surface handling.
Application Areas for Antistatic and Slip Additives
Antistatic additives in polyethylene are primarily used in electronic packaging, medical device housings, and automotive components to prevent static electricity buildup and ensure safety and functionality. Slip additives are commonly applied in polyethylene films for packaging, agricultural covers, and industrial liners to reduce surface friction, improve processing efficiency, and enhance product handling. Both additives optimize polyethylene performance by addressing specific application challenges in diverse industrial and consumer markets.
Selection Criteria for Polyethylene Additives
Selection criteria for polyethylene additives depend on the desired performance characteristics; antistatic additives are chosen to reduce surface electrical charge and improve handling safety, especially in packaging applications sensitive to static buildup. Slip additives are selected to lower the coefficient of friction, enhancing processing efficiency and preventing surface scratches or blockages during film extrusion and converting. Optimal selection considers processing conditions, end-use requirements, environmental impact, and compatibility with polyethylene resin to balance functionality and cost-effectiveness.
Future Trends in Polyethylene Additive Technologies
Future trends in polyethylene additive technologies emphasize the development of multifunctional additives that combine antistatic and slip properties to enhance material performance while reducing processing complexity. Advances in nanotechnology and bio-based additives are driving innovations that improve durability, environmental sustainability, and cost-effectiveness in polyethylene applications. Integration of smart additives capable of responding to environmental stimuli is expected to revolutionize packaging and film production, improving product lifespan and functionality.
Antistatic additive vs Slip additive Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com