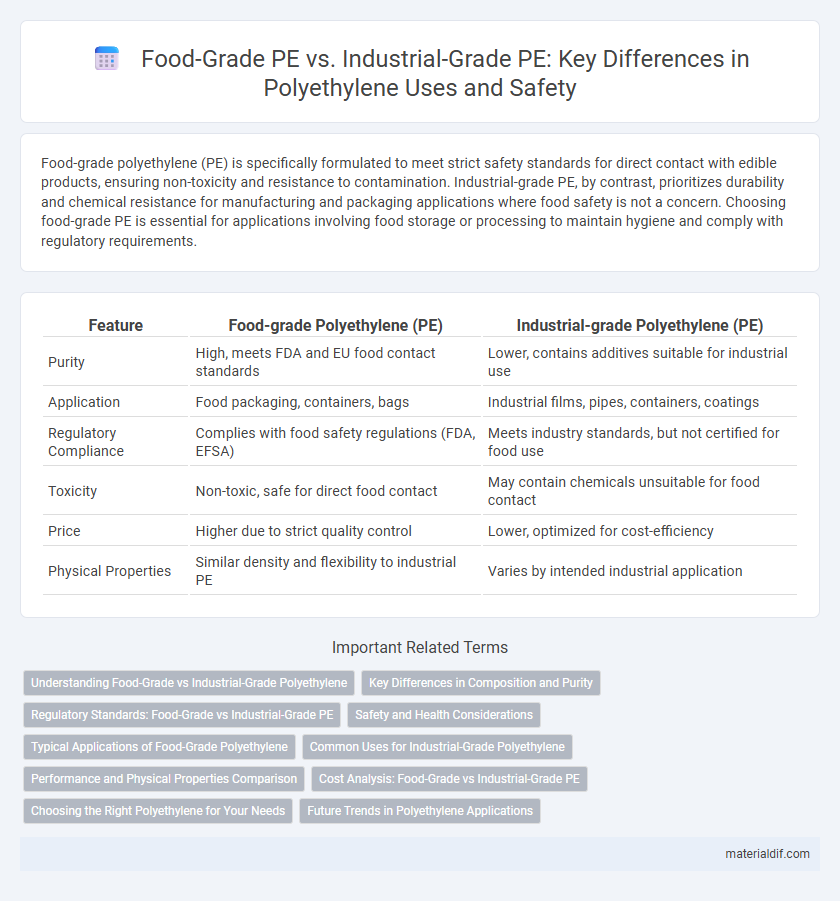
Food-grade polyethylene (PE) is specifically formulated to meet strict safety standards for direct contact with edible products, ensuring non-toxicity and resistance to contamination. Industrial-grade PE, by contrast, prioritizes durability and chemical resistance for manufacturing and packaging applications where food safety is not a concern. Choosing food-grade PE is essential for applications involving food storage or processing to maintain hygiene and comply with regulatory requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Food-grade Polyethylene (PE) | Industrial-grade Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | High, meets FDA and EU food contact standards | Lower, contains additives suitable for industrial use |
| Application | Food packaging, containers, bags | Industrial films, pipes, containers, coatings |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complies with food safety regulations (FDA, EFSA) | Meets industry standards, but not certified for food use |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, safe for direct food contact | May contain chemicals unsuitable for food contact |
| Price | Higher due to strict quality control | Lower, optimized for cost-efficiency |
| Physical Properties | Similar density and flexibility to industrial PE | Varies by intended industrial application |
Understanding Food-Grade vs Industrial-Grade Polyethylene
Food-grade polyethylene complies with strict FDA regulations ensuring it is non-toxic, odorless, and safe for direct contact with food products, making it ideal for packaging and storage applications. Industrial-grade polyethylene lacks these certifications and may contain additives or impurities unsuitable for food contact but offers enhanced durability and chemical resistance for heavy-duty uses. Understanding the distinctions in purity, regulatory compliance, and intended application is critical when selecting polyethylene for either food-related or industrial purposes.
Key Differences in Composition and Purity
Food-grade polyethylene (PE) is produced under strict regulatory standards ensuring high purity and the absence of harmful additives, making it safe for direct contact with consumables. Industrial-grade PE contains a broader range of additives and impurities tailored for enhanced mechanical properties or chemical resistance but lacks certification for food safety. The primary compositional difference lies in the controlled molecular weight distribution and minimal residual catalysts in food-grade PE, optimizing it for applications like packaging and containers.
Regulatory Standards: Food-Grade vs Industrial-Grade PE
Food-grade polyethylene (PE) complies with stringent regulatory standards established by agencies such as the FDA and EFSA, ensuring it is safe for direct contact with food and does not release harmful substances. Industrial-grade PE lacks these certifications and may contain additives or impurities unsuitable for food applications, making it restricted to non-food industries. Regulatory standards for food-grade PE mandate rigorous testing for chemical migration, purity, and overall safety, which are not required for industrial-grade variants.
Safety and Health Considerations
Food-grade polyethylene (PE) complies with strict regulatory standards set by agencies like the FDA and EFSA, ensuring it is non-toxic, odorless, and free from harmful additives, making it safe for direct contact with consumables. Industrial-grade PE lacks these certifications and may contain impurities or chemicals unsuitable for food contact, posing potential health risks such as contamination and chemical migration. Selecting food-grade PE is critical for maintaining safety and hygiene in food packaging, processing, and storage applications.
Typical Applications of Food-Grade Polyethylene
Food-grade polyethylene (PE) is primarily used in applications that require strict compliance with food safety standards, including packaging materials such as plastic films, containers, and bags for storing dairy products, meats, fruits, and vegetables. It is also common in manufacturing food storage tanks, conveyor belts, and cutting boards where non-toxic and odorless properties are essential to prevent contamination. Industrial-grade PE, by contrast, is typically utilized in products like pipes, automotive parts, and heavy-duty containers where food safety regulations do not apply.
Common Uses for Industrial-Grade Polyethylene
Industrial-grade polyethylene is extensively used in applications requiring high durability and chemical resistance, such as manufacturing pipes, geomembranes, and heavy-duty containers. Its robust properties make it ideal for construction materials, automotive parts, and agricultural films. Unlike food-grade polyethylene, which meets strict safety standards for direct contact with consumables, industrial-grade PE prioritizes mechanical strength and environmental resistance over food safety compliance.
Performance and Physical Properties Comparison
Food-grade polyethylene (PE) exhibits higher purity levels and enhanced resistance to chemicals, making it suitable for packaging applications requiring strict safety standards. Industrial-grade PE typically offers greater tensile strength and impact resistance, optimized for durability in harsh environments but lacks the stringent regulatory compliance of food-grade variants. The molecular weight distribution in food-grade PE ensures improved clarity and flexibility, whereas industrial-grade PE prioritizes thermal stability and abrasion resistance for heavy-duty uses.
Cost Analysis: Food-Grade vs Industrial-Grade PE
Food-grade polyethylene (PE) typically incurs higher production and certification costs due to stringent FDA compliance and purity standards compared to industrial-grade PE, which is manufactured with fewer restrictions. The enhanced quality control and additives required for food safety elevate food-grade PE's price, making it 20-40% more expensive per kilogram than industrial-grade PE in bulk procurement. Industrial-grade PE, optimized for durability and resistance rather than purity, offers a cost-efficient solution for applications where contamination risks are minimal and regulatory compliance is less rigorous.
Choosing the Right Polyethylene for Your Needs
Food-grade polyethylene (PE) is specifically formulated to meet strict FDA and EFSA regulations, ensuring it is safe for direct contact with consumables, making it ideal for packaging, containers, and kitchenware. Industrial-grade PE offers enhanced durability and chemical resistance, tailored for applications like piping, automotive parts, and heavy-duty packaging where performance under stress is critical. Selecting the right polyethylene depends on compliance requirements, intended use, and environmental exposure to optimize safety and functionality.
Future Trends in Polyethylene Applications
Food-grade polyethylene (PE) is formulated to meet strict safety and regulatory standards for direct contact with consumables, ensuring non-toxicity and high purity, while industrial-grade PE emphasizes mechanical strength and chemical resistance for robust engineering uses. Future trends indicate increasing demand for bio-based and recyclable food-grade PE to address sustainability goals and reduce environmental impact, alongside advancements in high-performance industrial PE blends that enhance durability and temperature resistance. Innovations in nanocomposite additives and smart packaging technologies are expected to drive the evolution of polyethylene applications across both food-grade and industrial sectors.
Food-grade PE vs Industrial-grade PE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com