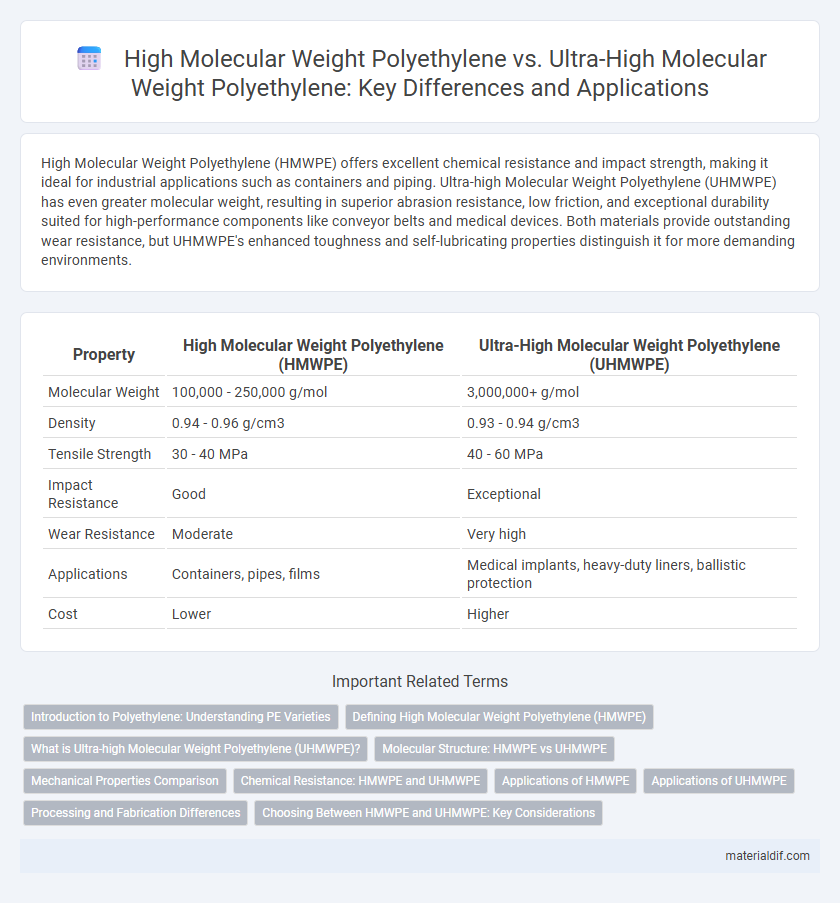
High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (HMWPE) offers excellent chemical resistance and impact strength, making it ideal for industrial applications such as containers and piping. Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) has even greater molecular weight, resulting in superior abrasion resistance, low friction, and exceptional durability suited for high-performance components like conveyor belts and medical devices. Both materials provide outstanding wear resistance, but UHMWPE's enhanced toughness and self-lubricating properties distinguish it for more demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (HMWPE) | Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 100,000 - 250,000 g/mol | 3,000,000+ g/mol |
| Density | 0.94 - 0.96 g/cm3 | 0.93 - 0.94 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 30 - 40 MPa | 40 - 60 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Good | Exceptional |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | Very high |
| Applications | Containers, pipes, films | Medical implants, heavy-duty liners, ballistic protection |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Polyethylene: Understanding PE Varieties
High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (HMWPE) features a molecular weight typically ranging from 200,000 to 500,000 g/mol, offering enhanced strength and resistance compared to Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE). Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) surpasses this with molecular weights in the range of 3.1 to 5.67 million g/mol, resulting in exceptional toughness, abrasion resistance, and impact strength. These differences in molecular weight define their applications, with HMWPE used in containers and pipes, while UHMWPE is preferred for high-performance materials in medical devices and ballistic protection.
Defining High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (HMWPE)
High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (HMWPE) features a polymer chain length longer than conventional polyethylene, typically with a molecular weight between 100,000 to 250,000 g/mol, which enhances its mechanical strength and abrasion resistance. It differs from Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), which possesses molecular weights exceeding 1,000,000 g/mol, resulting in superior toughness and impact resistance. HMWPE is widely used in applications requiring enhanced durability while maintaining processability, such as piping systems and industrial components.
What is Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE)?
Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) is a subset of polyethylene characterized by extremely long polymer chains, with molecular weights typically exceeding 3.1 million g/mol, significantly higher than high molecular weight polyethylene (HMWPE). This structural difference imparts exceptional mechanical properties to UHMWPE, including superior abrasion resistance, high impact strength, and outstanding chemical resistance, making it ideal for demanding applications such as biomedical implants and industrial components. Its ultra-long chains enable a low coefficient of friction and enhanced wear resistance compared to conventional HMWPE.
Molecular Structure: HMWPE vs UHMWPE
High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (HMWPE) features long polymer chains with a molecular weight ranging from 100,000 to 500,000 g/mol, offering enhanced tensile strength and chemical resistance. Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) possesses significantly longer chains exceeding 3 million g/mol, creating a highly entangled molecular network that provides superior abrasion resistance and impact strength. The extended chain length in UHMWPE results in a denser molecular structure, contributing to its exceptional durability compared to HMWPE.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (HMWPE) exhibits excellent impact resistance and tensile strength, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and moderate hardness. Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) surpasses HMWPE with superior tensile strength, enhanced abrasion resistance, and exceptional impact toughness due to its longer polymer chains and higher molecular mass. The increased crystallinity and molecular alignment in UHMWPE result in mechanical properties ideal for high-performance industrial components, bulletproof vests, and medical implants.
Chemical Resistance: HMWPE and UHMWPE
High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (HMWPE) exhibits excellent chemical resistance against acids, bases, and a wide range of solvents, making it ideal for applications requiring moderate durability in harsh environments. Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) surpasses HMWPE in chemical resistance due to its higher molecular weight and increased chain entanglement, resulting in superior resistance to corrosive chemicals, abrasion, and wear. Both HMWPE and UHMWPE resist stress cracking and environmental stress factors, with UHMWPE preferred for extreme chemical and mechanical conditions in industries such as chemical processing and medical devices.
Applications of HMWPE
High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (HMWPE) is widely utilized in applications requiring enhanced durability and chemical resistance, such as conveyor belts, marine components, and industrial liners. Its high impact strength and low friction coefficient make it ideal for manufacturing gears, bearings, and wear strips in heavy machinery. Unlike Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), which is preferred for extreme wear resistance and biomedical implants, HMWPE balances cost and performance for general industrial uses.
Applications of UHMWPE
Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) is widely used in demanding applications such as medical implants, ballistic protection, and industrial components due to its exceptional abrasion resistance, high impact strength, and low coefficient of friction. Compared to high molecular weight polyethylene (HMWPE), UHMWPE provides superior durability and wear resistance, making it ideal for joint replacements, bulletproof vests, and conveyor belts. Its biocompatibility and ability to absorb energy also enable its use in prosthetics, surgical devices, and high-performance fibers in aerospace and military industries.
Processing and Fabrication Differences
High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (HMWPE) exhibits better melt processability, allowing for conventional techniques such as extrusion and injection molding, while Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) has extremely high viscosity, making it unsuitable for standard melt processing and instead requiring methods like compression molding or ram extrusion. UHMWPE's long polymer chains provide superior mechanical strength and wear resistance but pose challenges in fabrication due to limited flow properties, necessitating specialized processing equipment. The choice between HMWPE and UHMWPE depends on the application demands for strength versus ease of manufacturing complexity.
Choosing Between HMWPE and UHMWPE: Key Considerations
High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (HMWPE) offers excellent abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it suitable for applications demanding durability and moderate impact resistance. Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) provides superior impact strength and enhanced wear resistance due to its higher molecular weight, ideal for high-performance uses like medical implants and heavy-duty industrial equipment. When choosing between HMWPE and UHMWPE, consider factors such as required mechanical strength, impact resistance, and application-specific durability to ensure optimal material performance.
High Molecular Weight PE vs Ultra-high Molecular Weight PE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com