Food-grade polyethylene is specifically manufactured to meet strict safety and hygiene standards, ensuring it is non-toxic and suitable for direct contact with food products. Industrial-grade polyethylene, while durable and cost-effective, may contain additives or contaminants that make it unsuitable for food applications. Choosing food-grade polyethylene is essential for preventing chemical leaching and maintaining the purity and safety of consumables.
Table of Comparison
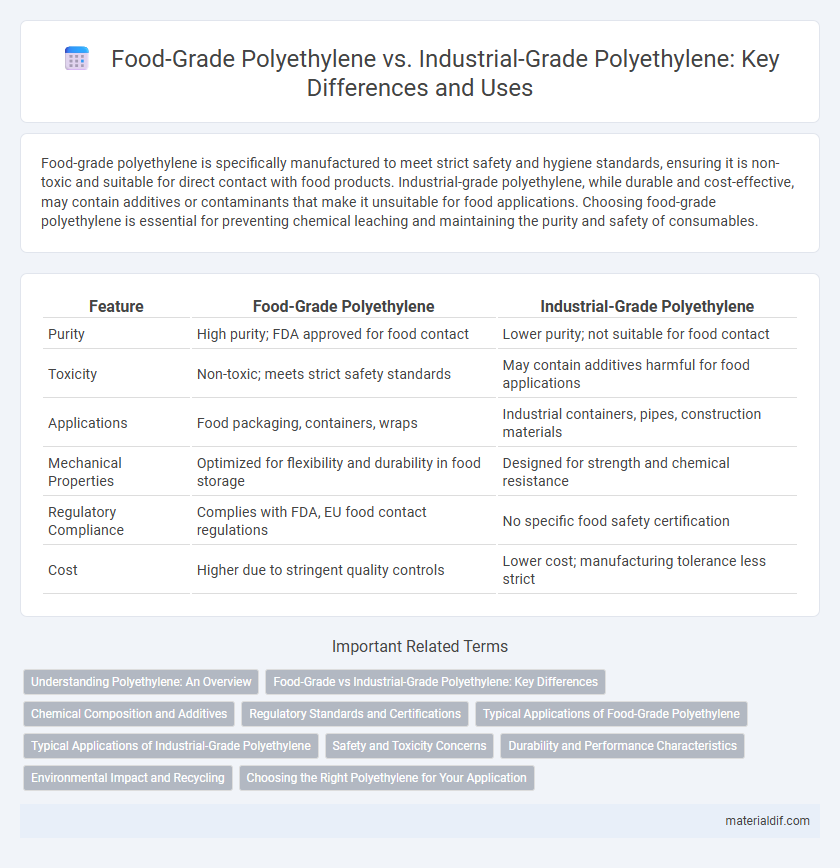
| Feature | Food-Grade Polyethylene | Industrial-Grade Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | High purity; FDA approved for food contact | Lower purity; not suitable for food contact |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic; meets strict safety standards | May contain additives harmful for food applications |
| Applications | Food packaging, containers, wraps | Industrial containers, pipes, construction materials |
| Mechanical Properties | Optimized for flexibility and durability in food storage | Designed for strength and chemical resistance |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complies with FDA, EU food contact regulations | No specific food safety certification |
| Cost | Higher due to stringent quality controls | Lower cost; manufacturing tolerance less strict |
Understanding Polyethylene: An Overview
Food-grade polyethylene complies with FDA and EU regulations, ensuring it is safe for direct contact with consumables due to its high purity and non-toxic additives. Industrial-grade polyethylene often contains additives that improve durability and chemical resistance but are unsuitable for food applications. Understanding the distinct chemical compositions and certification standards is crucial for selecting the appropriate polyethylene type in manufacturing processes.
Food-Grade vs Industrial-Grade Polyethylene: Key Differences
Food-grade polyethylene meets strict FDA and EU regulations for safety, ensuring it is non-toxic, odorless, and resistant to contamination, making it ideal for packaging and storing consumables. Industrial-grade polyethylene, while durable and cost-effective, lacks these certifications and may contain additives or impurities unsuitable for direct food contact. The key differences lie in chemical purity, regulatory compliance, and intended applications, with food-grade material prioritizing health safety and industrial-grade focusing on robustness and economic efficiency.
Chemical Composition and Additives
Food-grade polyethylene is formulated with high-purity polymers and stringent additive controls ensuring no harmful chemicals or heavy metals are present, making it safe for direct contact with food. Industrial-grade polyethylene contains a broader range of additives like antioxidants, UV stabilizers, and processing aids that enhance durability but may include substances unsuitable for food applications. The chemical composition in food-grade variants emphasizes compliance with FDA and EU regulations, specifically avoiding contaminants and ensuring minimal migratory residues.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Food-grade polyethylene complies with strict regulatory standards such as FDA 21 CFR 177.1520 and EU Regulation No. 10/2011, ensuring safety for direct contact with consumables through rigorous testing for chemical migration and purity. Industrial-grade polyethylene lacks these certifications, as it is produced for applications where food safety is not a concern, and may contain additives unsuitable for food contact. Compliance with standardized certifications like NSF and FDA is critical for food-grade polyethylene to guarantee non-toxicity and prevent contamination in packaging and processing environments.
Typical Applications of Food-Grade Polyethylene
Food-grade polyethylene is extensively used in packaging materials, such as food containers, plastic wraps, and grocery bags, due to its non-toxic and chemically inert properties. It is commonly found in applications requiring direct contact with consumables, including milk bottles, water pouches, and edible oil containers. This grade meets stringent FDA and EU standards, ensuring safe usage in the food and beverage industry.
Typical Applications of Industrial-Grade Polyethylene
Industrial-grade polyethylene is primarily utilized in heavy-duty applications such as manufacturing pipes, automotive parts, and construction materials due to its enhanced durability and resistance to chemicals. It is commonly found in packaging for industrial products, geomembranes for landfills, and containers for hazardous chemicals. This grade is preferred for environments requiring high mechanical strength and thermal stability rather than food safety compliance.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns
Food-grade polyethylene complies with strict FDA regulations ensuring it is free from harmful chemicals and safe for direct contact with food products. Industrial-grade polyethylene may contain additives or contaminants that pose toxicity risks, rendering it unsuitable for food applications. Safety concerns emphasize the importance of selecting food-grade materials to prevent chemical leaching and ensure consumer health protection.
Durability and Performance Characteristics
Food-grade polyethylene exhibits higher purity standards and enhanced chemical resistance, ensuring safety for direct food contact and preventing contamination. Industrial-grade polyethylene offers superior mechanical strength and greater resistance to extreme environmental conditions, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications and prolonged outdoor exposure. Durability in food-grade variants prioritizes non-toxicity and regulatory compliance, whereas industrial-grade materials emphasize robustness and long-term performance under stress.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Food-grade polyethylene is manufactured under stringent regulations to ensure safety, resulting in purer material with fewer additives that simplifies recycling processes and reduces environmental contaminants. Industrial-grade polyethylene often contains additives and fillers that complicate recycling, leading to increased environmental impact due to limited reuse options and potential release of harmful substances. Effective segregation of food-grade and industrial-grade polyethylene enhances recycling efficiency and minimizes pollution, supporting sustainable waste management efforts.
Choosing the Right Polyethylene for Your Application
Food-grade polyethylene meets strict FDA and FDA-equivalent regulatory standards, ensuring it is non-toxic, odorless, and safe for direct contact with food products. Industrial-grade polyethylene offers enhanced durability and chemical resistance, suitable for applications requiring structural strength or exposure to harsh environments. Selecting the appropriate polyethylene depends on factors such as safety requirements, mechanical properties, and environmental exposure specific to your application.
Food-grade polyethylene vs Industrial-grade polyethylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com