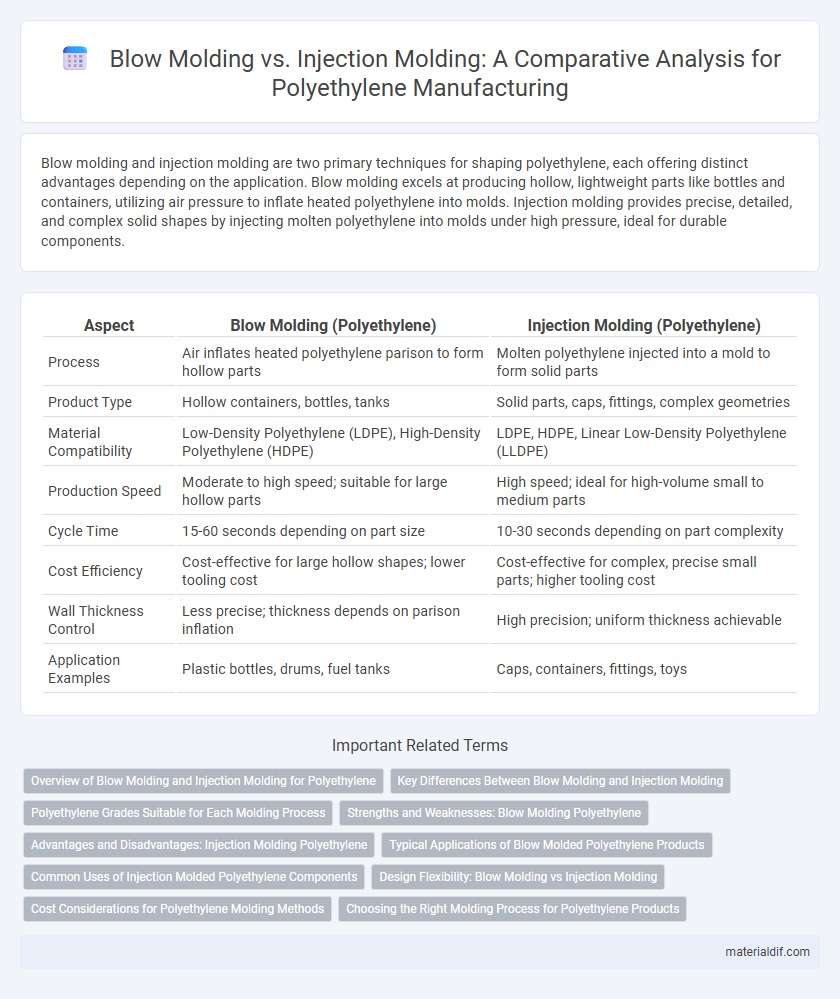
Blow molding and injection molding are two primary techniques for shaping polyethylene, each offering distinct advantages depending on the application. Blow molding excels at producing hollow, lightweight parts like bottles and containers, utilizing air pressure to inflate heated polyethylene into molds. Injection molding provides precise, detailed, and complex solid shapes by injecting molten polyethylene into molds under high pressure, ideal for durable components.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Blow Molding (Polyethylene) | Injection Molding (Polyethylene) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Air inflates heated polyethylene parison to form hollow parts | Molten polyethylene injected into a mold to form solid parts |
| Product Type | Hollow containers, bottles, tanks | Solid parts, caps, fittings, complex geometries |
| Material Compatibility | Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | LDPE, HDPE, Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) |
| Production Speed | Moderate to high speed; suitable for large hollow parts | High speed; ideal for high-volume small to medium parts |
| Cycle Time | 15-60 seconds depending on part size | 10-30 seconds depending on part complexity |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for large hollow shapes; lower tooling cost | Cost-effective for complex, precise small parts; higher tooling cost |
| Wall Thickness Control | Less precise; thickness depends on parison inflation | High precision; uniform thickness achievable |
| Application Examples | Plastic bottles, drums, fuel tanks | Caps, containers, fittings, toys |
Overview of Blow Molding and Injection Molding for Polyethylene
Blow molding for polyethylene primarily involves heating the polymer and inflating it into a mold cavity to create hollow parts like bottles and containers, offering excellent wall thickness distribution and cost efficiency for large-volume production. Injection molding melts polyethylene pellets and injects the polymer into a closed mold, producing precise, complex, and solid parts with high dimensional accuracy and surface finish. Both methods leverage polyethylene's thermoplastic properties but differ in application, production speed, and product design capabilities.
Key Differences Between Blow Molding and Injection Molding
Blow molding and injection molding differ primarily in their process and applications for polyethylene products; blow molding inflates heated polyethylene into a mold to form hollow objects like bottles, while injection molding injects molten polyethylene into a mold for solid parts such as containers or caps. Blow molding excels in producing lightweight, hollow parts with uniform wall thickness, whereas injection molding offers greater precision and complexity for detailed polyethylene components. The choice between these methods depends on product design, volume requirements, and the desired mechanical properties of the polyethylene item.
Polyethylene Grades Suitable for Each Molding Process
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) are commonly preferred for blow molding due to their excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and ability to form hollow shapes. Injection molding primarily utilizes high molecular weight polyethylene (HMWPE) and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) grades, which provide superior strength, rigidity, and wear resistance essential for precise, solid components. Selecting the appropriate polyethylene grade ensures optimal processing performance and mechanical properties tailored to the requirements of blow or injection molding applications.
Strengths and Weaknesses: Blow Molding Polyethylene
Blow molding polyethylene excels in producing hollow, lightweight, and seamless containers with excellent impact resistance and uniform wall thickness, making it ideal for bottles and large containers. Its main weakness lies in limited design complexity and surface detail compared to injection molding, restricting intricate shapes and tighter tolerances. Blow molding typically offers faster cycle times and lower material waste for hollow products, but it struggles with precision and small, solid parts production.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Injection Molding Polyethylene
Injection molding polyethylene offers precise control over complex geometries and high production efficiency, making it ideal for detailed and intricate parts. However, it has limitations in processing large hollow items compared to blow molding, and the initial tooling costs can be higher. The process provides excellent surface finish and material strength but may result in longer cycle times for thick-walled components.
Typical Applications of Blow Molded Polyethylene Products
Blow molded polyethylene products are typically used for manufacturing hollow containers such as bottles, fuel tanks, and large drums due to their excellent flexibility and chemical resistance. This process is ideal for packaging applications that require lightweight, durable, and airtight solutions, including detergents, motor oils, and edible oils containers. The versatility of blow molding supports the creation of complex shapes with uniform wall thickness, making it the preferred method for producing polyethylene products intended for liquid storage and distribution.
Common Uses of Injection Molded Polyethylene Components
Injection molded polyethylene components are commonly used in packaging applications such as caps, closures, and containers due to their precise dimensions and smooth finishes. These components also serve critical roles in automotive parts, including fuel tanks and interior trims, where durability and chemical resistance are essential. Additionally, injection molding enables the production of complex, high-strength medical devices and consumer goods requiring tight tolerances and consistent quality.
Design Flexibility: Blow Molding vs Injection Molding
Blow molding offers superior design flexibility for creating hollow polyethylene products with complex shapes and varying wall thicknesses, ideal for containers and bottles. Injection molding excels in producing detailed, precise polyethylene components with intricate features and tight tolerances, suitable for small, solid parts. The choice between blow molding and injection molding depends on the part geometry and functional requirements of the polyethylene product.
Cost Considerations for Polyethylene Molding Methods
Blow molding of polyethylene typically incurs lower tooling costs compared to injection molding, making it more cost-effective for high-volume production of hollow parts like bottles and containers. Injection molding, while having higher upfront mold expenses due to complex tooling, offers greater precision and faster cycle times for creating detailed, solid polyethylene components. Evaluating production volume, part complexity, and desired material properties is crucial in determining the most cost-efficient polyethylene molding method.
Choosing the Right Molding Process for Polyethylene Products
Blow molding excels in producing hollow polyethylene products such as bottles and containers, offering efficient material usage and lightweight design. Injection molding provides precise dimensional control for complex, solid polyethylene parts like caps and automotive components, ensuring high strength and surface quality. Selecting the right molding process depends on the product's shape, wall thickness, and production volume requirements to optimize cost and performance.
Blow Molding vs Injection Molding (Polyethylene) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com