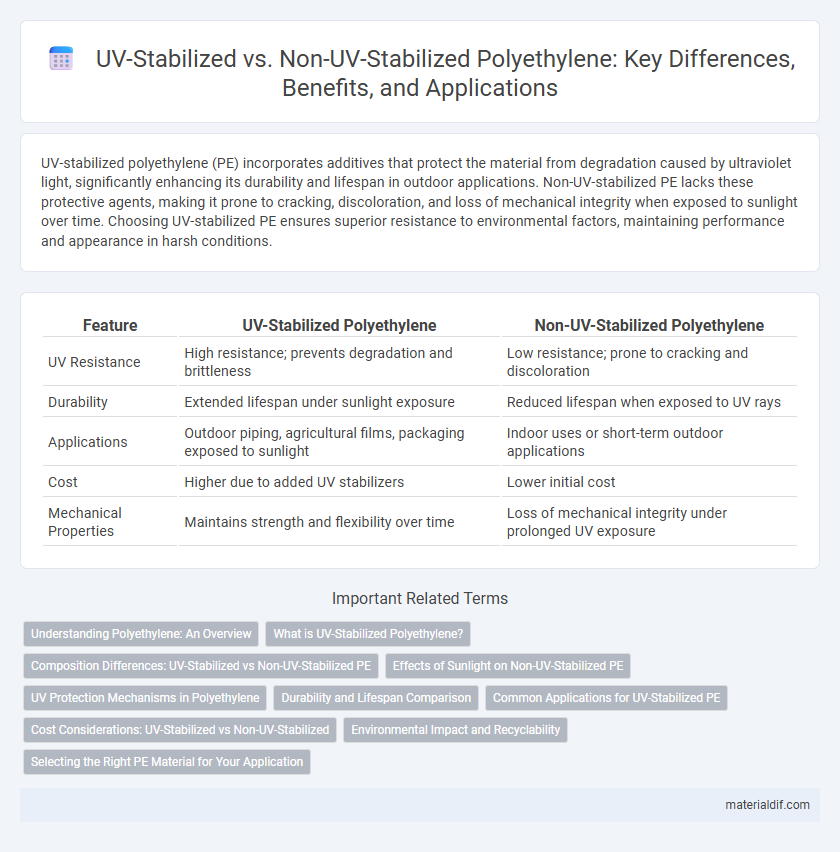
UV-stabilized polyethylene (PE) incorporates additives that protect the material from degradation caused by ultraviolet light, significantly enhancing its durability and lifespan in outdoor applications. Non-UV-stabilized PE lacks these protective agents, making it prone to cracking, discoloration, and loss of mechanical integrity when exposed to sunlight over time. Choosing UV-stabilized PE ensures superior resistance to environmental factors, maintaining performance and appearance in harsh conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | UV-Stabilized Polyethylene | Non-UV-Stabilized Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|
| UV Resistance | High resistance; prevents degradation and brittleness | Low resistance; prone to cracking and discoloration |
| Durability | Extended lifespan under sunlight exposure | Reduced lifespan when exposed to UV rays |
| Applications | Outdoor piping, agricultural films, packaging exposed to sunlight | Indoor uses or short-term outdoor applications |
| Cost | Higher due to added UV stabilizers | Lower initial cost |
| Mechanical Properties | Maintains strength and flexibility over time | Loss of mechanical integrity under prolonged UV exposure |
Understanding Polyethylene: An Overview
UV-stabilized polyethylene incorporates additives that protect the polymer chains from degradation caused by ultraviolet radiation, significantly extending the material's lifespan in outdoor applications. Non-UV-stabilized polyethylene lacks these additives, resulting in faster brittleness, discoloration, and mechanical failure when exposed to sunlight. Understanding the differences between UV-stabilized and non-UV-stabilized polyethylene is crucial for selecting the right type for environmental durability and long-term performance.
What is UV-Stabilized Polyethylene?
UV-stabilized polyethylene is a type of polyethylene that contains additives or coatings designed to protect it from degradation caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure. These stabilizers prevent the breakdown of polymer chains, thereby enhancing the material's durability and lifespan when used outdoors or in environments with high UV exposure. Non-UV-stabilized polyethylene lacks such protection, leading to brittleness, discoloration, and reduced mechanical properties over time.
Composition Differences: UV-Stabilized vs Non-UV-Stabilized PE
UV-stabilized polyethylene contains additives such as UV absorbers and hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) that protect the polymer chains from photodegradation caused by ultraviolet radiation. Non-UV-stabilized polyethylene lacks these additives, making it more susceptible to brittleness, discoloration, and loss of mechanical properties when exposed to sunlight. The inclusion of UV stabilizers enhances the polymer's durability and extends its service life in outdoor applications.
Effects of Sunlight on Non-UV-Stabilized PE
Non-UV-stabilized polyethylene degrades rapidly when exposed to sunlight due to the breakdown of polymer chains by ultraviolet radiation. This photodegradation causes discoloration, brittleness, and loss of mechanical strength, significantly reducing the material's lifespan. Prolonged exposure leads to surface cracking and polymer embrittlement, which compromise the integrity of PE products used in outdoor applications.
UV Protection Mechanisms in Polyethylene
UV-stabilized polyethylene incorporates additives such as UV absorbers and hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) to effectively block or absorb harmful ultraviolet radiation, preventing polymer chain degradation. Non-UV-stabilized polyethylene lacks these protective compounds, making it more susceptible to photo-oxidation, leading to brittleness, discoloration, and loss of mechanical properties over time. The incorporation of UV protection mechanisms significantly extends the useful lifespan and performance reliability of polyethylene in outdoor applications.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
UV-stabilized polyethylene (PE) significantly enhances durability by incorporating additives that protect against ultraviolet radiation, preventing chain scission and surface degradation, which extend the material's lifespan to over 10 years even in harsh sunlight exposure. Non-UV-stabilized PE tends to suffer from brittleness, discoloration, and cracking within 1 to 3 years when exposed to UV rays, drastically reducing its functional lifespan. This difference makes UV-stabilized PE ideal for outdoor applications requiring long-term performance and resistance to environmental stressors.
Common Applications for UV-Stabilized PE
UV-stabilized polyethylene (PE) is essential in outdoor applications such as agricultural films, geomembranes, and packaging materials where prolonged UV exposure can cause degradation and loss of mechanical properties. Its enhanced resistance to ultraviolet radiation prolongs the material's lifespan and maintains flexibility, making it ideal for greenhouse covers, irrigation pipes, and outdoor furniture components. Non-UV-stabilized PE is typically confined to indoor or short-term use where UV exposure is minimal to prevent premature aging and brittleness.
Cost Considerations: UV-Stabilized vs Non-UV-Stabilized
UV-stabilized polyethylene typically incurs higher initial costs due to added UV inhibitors and specialized manufacturing processes, which enhance durability and lifespan under sunlight exposure. Non-UV-stabilized polyethylene offers lower upfront expenses but may require more frequent replacement or maintenance when used outdoors, increasing long-term costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including product longevity and performance in UV-exposed environments, is essential for optimal material selection.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
UV-stabilized polyethylene (PE) contains additives that protect the material from degradation caused by ultraviolet radiation, significantly slowing its breakdown and reducing the release of microplastics into the environment compared to non-UV-stabilized PE. The enhanced durability of UV-stabilized PE often leads to longer product lifespans, decreasing the frequency of replacement and associated waste. Both types of PE are recyclable, but UV-stabilized PE may require specialized recycling processes to separate additives, potentially complicating recycling but helping to maintain material quality for reuse.
Selecting the Right PE Material for Your Application
Selecting the right polyethylene (PE) material depends on exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation; UV-stabilized PE incorporates additives such as carbon black or UV absorbers that prevent degradation and extend lifespan in outdoor applications. Non-UV-stabilized PE is suitable for indoor or low UV exposure environments where cost efficiency is prioritized over long-term durability. Evaluating factors like environmental exposure, durability requirements, and cost considerations ensures optimal performance and longevity of PE products.
UV-stabilized PE vs Non-UV-stabilized PE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com