Polyethylene PET monofilament offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring high tension and minimal elongation. Multifilament PET, composed of numerous fine fibers twisted together, provides greater flexibility and abrasion resistance, suitable for uses where softness and knot security are essential. Selecting between monofilament and multifilament depends on the specific demands of the project, balancing toughness with pliability.
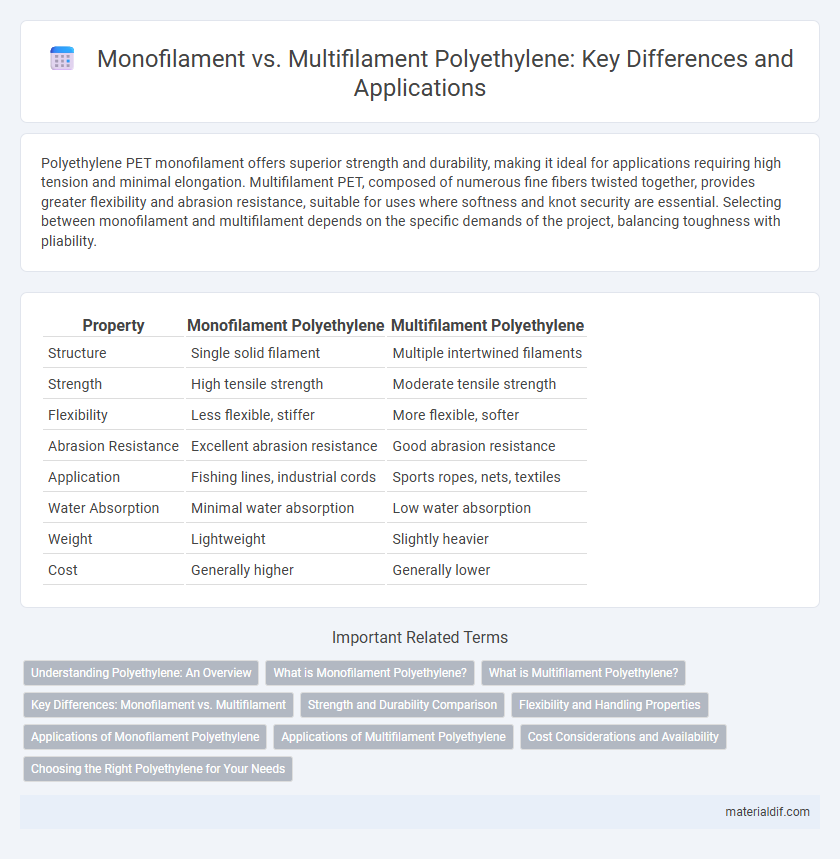
Table of Comparison
| Property | Monofilament Polyethylene | Multifilament Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single solid filament | Multiple intertwined filaments |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, stiffer | More flexible, softer |
| Abrasion Resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance | Good abrasion resistance |
| Application | Fishing lines, industrial cords | Sports ropes, nets, textiles |
| Water Absorption | Minimal water absorption | Low water absorption |
| Weight | Lightweight | Slightly heavier |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
Understanding Polyethylene: An Overview
Polyethylene monofilament offers high tensile strength and minimal water absorption, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and resistance to environmental factors. Multifilament polyethylene consists of multiple fine fibers woven together, providing superior flexibility and abrasion resistance, which is beneficial for ropes and fishing lines. Understanding the structural differences helps optimize polyethylene use in industries prioritizing either strength or flexibility.
What is Monofilament Polyethylene?
Monofilament polyethylene refers to a single, continuous strand of polyethylene fiber known for its high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to abrasion. It is commonly used in applications such as fishing lines, ropes, and industrial textiles where smoothness and uniform diameter are essential. Compared to multifilament polyethylene, monofilament offers lower elasticity and better resistance to UV degradation, making it ideal for long-term outdoor use.
What is Multifilament Polyethylene?
Multifilament polyethylene consists of numerous fine fibers braided or twisted together, enhancing flexibility, strength, and abrasion resistance compared to monofilament. It offers improved knot strength and is less prone to memory, making it ideal for applications like fishing lines, medical sutures, and high-performance textiles. Its structure provides better durability and smoother handling in demanding environments where superior tensile characteristics are critical.
Key Differences: Monofilament vs. Multifilament
Monofilament polyethylene consists of a single continuous strand, offering high tensile strength, low stretch, and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for durability and precision. Multifilament polyethylene is composed of multiple intertwined fibers, providing greater flexibility, softness, and better knot strength, which enhances handling and casting performance. The choice between monofilament and multifilament depends on the application requirements for strength, sensitivity, and manageability in fishing lines or industrial uses.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyethylene monofilament fibers offer superior tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring maximum durability. Multifilament polyethylene, composed of numerous smaller filaments twisted together, provides enhanced flexibility and better resistance to fatigue but generally exhibits lower overall strength compared to monofilament. The choice between monofilament and multifilament polyethylene depends on the balance needed between peak strength and flexibility for specific industrial or fishing uses.
Flexibility and Handling Properties
Polyethylene monofilament offers superior stiffness and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring high tensile strength and minimal stretch. Multifilament polyethylene fibers provide enhanced flexibility and softness, resulting in improved handling and knot security for fishing lines and textile uses. The choice between monofilament and multifilament depends on balancing the need for stiffness versus pliability in specific performance requirements.
Applications of Monofilament Polyethylene
Monofilament polyethylene is widely used in fishing lines due to its high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and low stretch properties, ensuring reliable performance in various aquatic environments. It is also favored in agricultural applications for crop support and trellis systems because of its durability and resistance to ultraviolet degradation. Furthermore, monofilament polyethylene finds usage in industrial sectors for filtration fabrics and sewing threads, leveraging its consistent diameter and robustness.
Applications of Multifilament Polyethylene
Multifilament polyethylene fibers are widely used in high-performance applications such as fishing lines, ropes, and protective textiles due to their superior strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance compared to monofilament. These fibers offer enhanced durability and knot strength, making them ideal for marine and industrial environments where reliability and toughness are critical. Multifilament structures also provide better contouring and shock absorption, which improves performance in sports equipment and medical sutures.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Monofilament polyethylene fibers typically incur lower manufacturing costs due to simpler extrusion processes, making them more affordable for high-volume applications. Multifilament variants require intricate twisting and weaving, increasing production expenses and limiting availability to specialized suppliers. Market demand favors monofilament for cost-sensitive uses, while multifilament remains preferred where enhanced durability justifies the premium price.
Choosing the Right Polyethylene for Your Needs
Monofilament polyethylene offers high tensile strength and superior abrasion resistance, ideal for applications requiring durability and minimal stretch, such as fishing lines and industrial cables. Multifilament polyethylene provides enhanced flexibility and softness, making it suitable for textiles, ropes, and sports equipment where comfort and flexibility are priorities. Selecting the right polyethylene depends on balancing strength, flexibility, and application-specific needs to achieve optimal performance and longevity.
Monofilament vs Multifilament Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com