High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) offers excellent strength-to-density ratio and chemical resistance, making it ideal for containers and pipes. Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) provides superior abrasion resistance and impact strength, suited for industrial applications like conveyor belts and medical devices. Both materials deliver durability, but UHMWPE excels in heavy-duty and wear-intensive environments compared to HDPE.
Table of Comparison
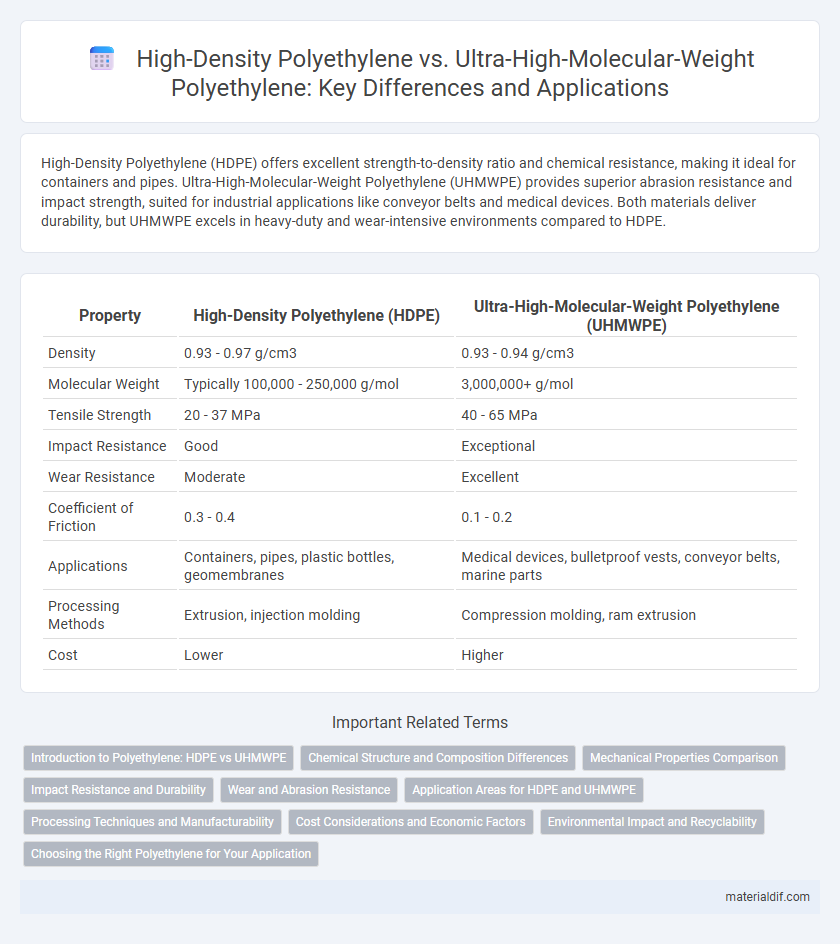
| Property | High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.93 - 0.97 g/cm3 | 0.93 - 0.94 g/cm3 |
| Molecular Weight | Typically 100,000 - 250,000 g/mol | 3,000,000+ g/mol |
| Tensile Strength | 20 - 37 MPa | 40 - 65 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Good | Exceptional |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.3 - 0.4 | 0.1 - 0.2 |
| Applications | Containers, pipes, plastic bottles, geomembranes | Medical devices, bulletproof vests, conveyor belts, marine parts |
| Processing Methods | Extrusion, injection molding | Compression molding, ram extrusion |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Polyethylene: HDPE vs UHMWPE
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) are two significant types of polyethylene distinguished by their molecular weight and density. HDPE has a density range of 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm3, offering high strength-to-density ratio and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for containers and piping. UHMWPE features extremely long molecular chains with a molecular weight typically between 3.5 to 7.5 million g/mol, resulting in superior abrasion resistance, low friction, and high impact strength used in applications like medical implants and industrial parts.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) consists of long linear chains with minimal branching, resulting in a dense, crystalline structure that provides high tensile strength and stiffness. Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) features exceptionally long polymer chains with very high molecular weight, enhancing its impact resistance and wear properties due to increased chain entanglement and crystallinity. The key compositional difference lies in UHMWPE's far greater molecular weight, which directly influences its superior mechanical performance compared to HDPE.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) offers excellent tensile strength ranging from 0.2 to 0.4 GPa and demonstrates good impact resistance, making it suitable for containers and piping. Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) surpasses HDPE with tensile strength up to 3 GPa and exceptional abrasion resistance, ideal for demanding applications such as medical implants and ballistic protection. The superior molecular weight of UHMWPE accounts for its enhanced mechanical properties, including higher impact strength and greater wear resistance compared to HDPE.
Impact Resistance and Durability
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) offers excellent impact resistance suitable for general-purpose applications, with a tensile strength of approximately 0.2-0.4 GPa and moderate durability under varying environmental conditions. Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) demonstrates superior impact resistance due to its extremely long polymer chains, delivering tensile strength up to 3.1 GPa and exceptional abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-wear applications. The molecular weight difference significantly enhances UHMWPE's durability, resulting in greater resistance to cracking, wear, and chemical exposure compared to HDPE.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) demonstrates strong wear resistance suitable for general applications involving moderate abrasion. Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) surpasses HDPE in abrasion resistance due to its significantly higher molecular weight, resulting in superior durability and performance in heavy wear environments. Industries requiring extreme wear resistance, such as mining and medical implants, often prefer UHMWPE for its exceptional toughness and low friction properties.
Application Areas for HDPE and UHMWPE
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is widely used in packaging, piping systems, and plastic containers due to its strength, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) excels in applications requiring extreme wear resistance, such as medical devices, ballistic armor, and industrial liners. The distinct molecular structure of UHMWPE provides superior impact strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-performance engineering applications.
Processing Techniques and Manufacturability
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is processed primarily through conventional techniques such as injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding, offering ease of manufacturability with high throughput and lower energy requirements. Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) requires specialized processing methods like compression molding and ram extrusion due to its extremely high molecular weight, which results in high viscosity and challenges in melt flow. The choice between HDPE and UHMWPE in manufacturing depends on the required mechanical properties and processing capabilities, with HDPE favored for mass production and UHMWPE used in applications demanding superior wear resistance and impact strength.
Cost Considerations and Economic Factors
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) due to lower raw material and processing expenses. UHMWPE, characterized by exceptional abrasion resistance and impact strength, commands a higher price driven by its specialized applications in medical implants and high-performance industrial components. Economic factors influencing selection include production volume, required durability, and lifecycle cost efficiency, where HDPE suits large-scale, cost-sensitive projects and UHMWPE justifies investment in critical, high-stress environments.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) exhibits strong recyclability due to its widespread use and established recycling infrastructure, contributing to reduced environmental impact through reuse and reduced landfill waste. Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), while offering superior abrasion resistance and strength, is less commonly recycled because of its specialized applications and complex processing requirements. Both polymers derive from non-renewable fossil fuels, but HDPE's extensive recyclability offers a more sustainable lifecycle compared to UHMWPE's limited recycling options and longer degradation timeline.
Choosing the Right Polyethylene for Your Application
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) offers excellent strength-to-density ratio, chemical resistance, and ease of fabrication, making it ideal for containers, pipes, and geomembranes. Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) provides superior abrasion resistance, impact strength, and low friction, which suits applications in heavy-duty industrial components and medical devices. Selecting the right polyethylene depends on specific requirements such as mechanical load, wear resistance, and environmental exposure to optimize performance and longevity.
High-Density Polyethylene vs Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com