UV-treated polycarbonate offers enhanced durability and resistance to yellowing or degradation from prolonged sun exposure compared to non-UV polycarbonate. This treatment extends the lifespan of polycarbonate products, maintaining their clarity and strength in outdoor applications. Non-UV polycarbonate, while strong and impact-resistant, tends to become brittle and discolored when exposed to ultraviolet rays over time.
Table of Comparison
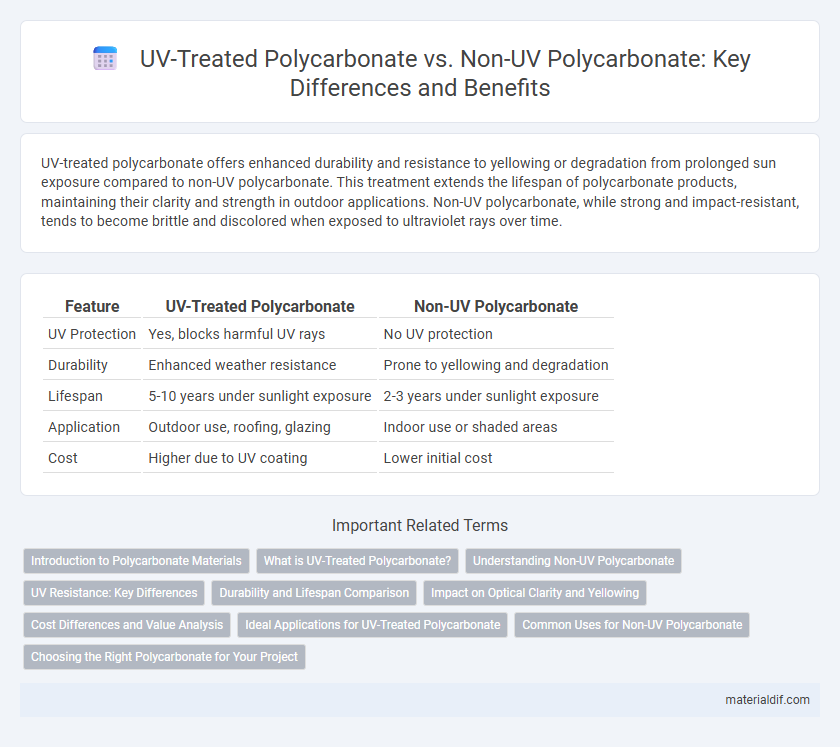
| Feature | UV-Treated Polycarbonate | Non-UV Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| UV Protection | Yes, blocks harmful UV rays | No UV protection |
| Durability | Enhanced weather resistance | Prone to yellowing and degradation |
| Lifespan | 5-10 years under sunlight exposure | 2-3 years under sunlight exposure |
| Application | Outdoor use, roofing, glazing | Indoor use or shaded areas |
| Cost | Higher due to UV coating | Lower initial cost |
Introduction to Polycarbonate Materials
Polycarbonate materials are widely utilized for their high impact resistance and optical clarity, making them ideal for various applications in construction, automotive, and electronics. UV-treated polycarbonate includes a protective coating that significantly enhances its resistance to ultraviolet radiation, preventing yellowing and degradation over time. Non-UV polycarbonate lacks this protective layer, leading to faster deterioration when exposed to sunlight, limiting its durability and performance in outdoor environments.
What is UV-Treated Polycarbonate?
UV-treated polycarbonate is a type of polycarbonate material coated or formulated with ultraviolet (UV) inhibitors that protect it from the harmful effects of UV radiation, such as yellowing, brittleness, and degradation over time. This treatment significantly enhances the material's durability and longevity when exposed to direct sunlight, making it ideal for outdoor applications like glazing, roofing, and protective shields. In contrast, non-UV polycarbonate lacks this protective layer and tends to deteriorate faster under UV exposure, limiting its performance and lifespan in environments with strong sunlight.
Understanding Non-UV Polycarbonate
Non-UV polycarbonate, unlike its UV-treated counterpart, lacks a protective coating that shields it from ultraviolet radiation, making it more susceptible to yellowing and degradation over time when exposed to sunlight. This material is often chosen for indoor applications where UV exposure is minimal, ensuring durability without the added cost of UV stabilization. Understanding the limitations of non-UV polycarbonate is crucial for selecting the right material for applications requiring long-term clarity and strength in outdoor environments.
UV Resistance: Key Differences
UV-treated polycarbonate offers superior UV resistance compared to non-UV polycarbonate by incorporating stabilizers that absorb and dissipate harmful ultraviolet rays, significantly reducing yellowing and material degradation over time. Non-UV polycarbonate lacks these additives, resulting in faster discoloration, brittleness, and loss of impact strength when exposed to prolonged sunlight. This difference makes UV-treated polycarbonate ideal for outdoor applications requiring long-term durability and clarity.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
UV-treated polycarbonate offers significantly enhanced durability by resisting discoloration, cracking, and surface degradation caused by prolonged sun exposure, extending its lifespan up to 10-15 years or more. Non-UV polycarbonate tends to yellow, become brittle, and lose structural integrity within 3-5 years under direct UV radiation. The inclusion of UV stabilizers in treated polycarbonate ensures long-term performance in outdoor applications, making it the preferred choice for roofing, glazing, and protective covers.
Impact on Optical Clarity and Yellowing
UV-treated polycarbonate significantly enhances optical clarity by resisting yellowing caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light. Non-UV polycarbonate tends to degrade faster, exhibiting noticeable yellowing that reduces light transmission and clarity over time. The UV stabilization process incorporates additives that absorb harmful UV rays, maintaining the material's transparency and durability in outdoor applications.
Cost Differences and Value Analysis
UV-treated polycarbonate typically costs 15-30% more than non-UV polycarbonate due to the added protective coatings that enhance durability and prevent yellowing from sun exposure. The value analysis shows that while the initial expense is higher, UV-treated polycarbonate significantly extends product lifespan and reduces maintenance, leading to lower long-term costs. Non-UV polycarbonate may be suitable for indoor or low-exposure applications, but it often incurs replacement and performance degradation costs over time.
Ideal Applications for UV-Treated Polycarbonate
UV-treated polycarbonate offers superior resistance to yellowing and degradation caused by prolonged sun exposure, making it ideal for outdoor applications such as skylights, greenhouse panels, and protective eyewear lenses. Its enhanced UV stability ensures longevity and maintains clarity, crucial for architectural glazing, automotive components, and outdoor signage. Non-UV polycarbonate, while strong and impact-resistant, is better suited for indoor uses where UV exposure is minimal, as it lacks the protective coating needed for sustained outdoor durability.
Common Uses for Non-UV Polycarbonate
Non-UV polycarbonate is commonly used in indoor applications where exposure to sunlight is minimal, such as interior glazing, machine guards, and electronic housings. Its high impact resistance and optical clarity make it ideal for protective barriers, lighting fixtures, and compact discs. Unlike UV-treated polycarbonate, it lacks enhanced weather resistance, limiting its use in outdoor environments.
Choosing the Right Polycarbonate for Your Project
UV-treated polycarbonate offers enhanced durability and resistance to yellowing, making it ideal for outdoor applications exposed to sunlight. Non-UV polycarbonate performs well indoors where UV exposure is minimal, providing cost-effective clarity and impact resistance. Selecting the right polycarbonate depends on environmental conditions and project longevity requirements, ensuring optimal performance and lifespan.
UV-treated Polycarbonate vs Non-UV Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com