Polycarbonate PET exhibits excellent chemical resistance, effectively withstanding exposure to oils, solvents, and various acids without degrading. Its weather resistance ensures durability against UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and moisture, making it suitable for outdoor applications. Balancing both properties, polycarbonate PET maintains structural integrity and clarity in harsh environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
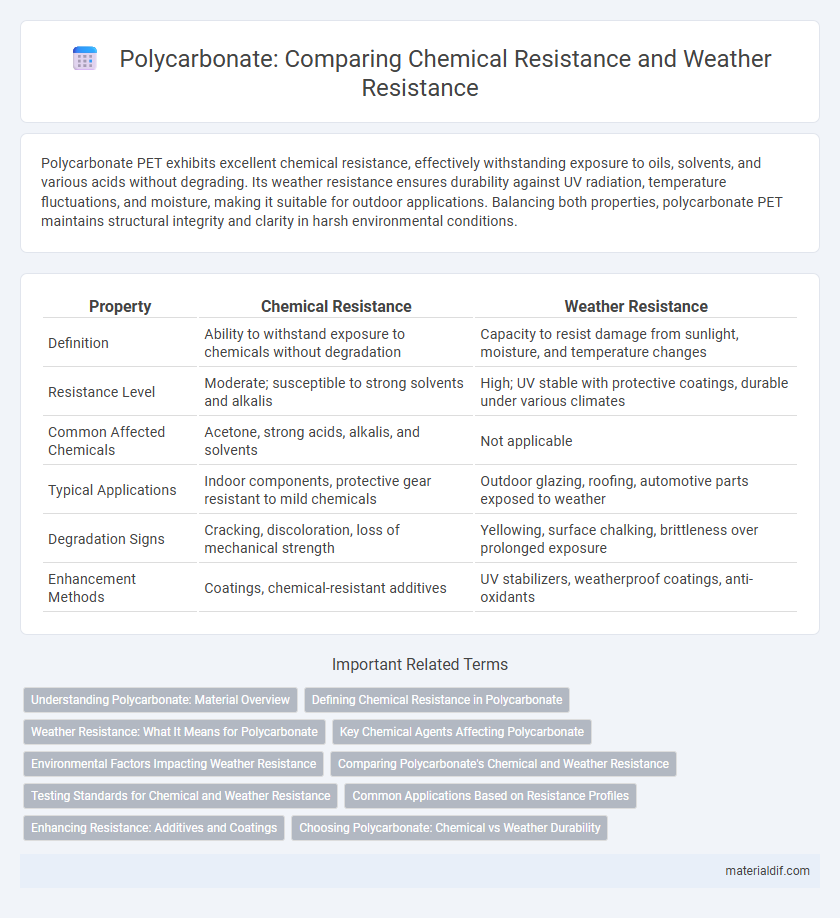
| Property | Chemical Resistance | Weather Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to withstand exposure to chemicals without degradation | Capacity to resist damage from sunlight, moisture, and temperature changes |
| Resistance Level | Moderate; susceptible to strong solvents and alkalis | High; UV stable with protective coatings, durable under various climates |
| Common Affected Chemicals | Acetone, strong acids, alkalis, and solvents | Not applicable |
| Typical Applications | Indoor components, protective gear resistant to mild chemicals | Outdoor glazing, roofing, automotive parts exposed to weather |
| Degradation Signs | Cracking, discoloration, loss of mechanical strength | Yellowing, surface chalking, brittleness over prolonged exposure |
| Enhancement Methods | Coatings, chemical-resistant additives | UV stabilizers, weatherproof coatings, anti-oxidants |
Understanding Polycarbonate: Material Overview
Polycarbonate exhibits excellent chemical resistance to many acids, alkalis, and oils, making it suitable for various industrial applications. Its superior weather resistance allows it to withstand prolonged exposure to UV radiation and temperature fluctuations without significant degradation. Understanding these properties highlights polycarbonate's versatility in both chemically demanding environments and outdoor settings.
Defining Chemical Resistance in Polycarbonate
Chemical resistance in polycarbonate refers to its ability to withstand degradation or damage when exposed to various chemicals such as acids, bases, oils, and solvents. This property is critical for applications where polycarbonate surfaces come into contact with harsh substances, preventing swelling, cracking, or discoloration. While chemical resistance ensures durability in chemical environments, it differs from weather resistance, which pertains to polycarbonate's ability to endure UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and moisture exposure.
Weather Resistance: What It Means for Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate exhibits exceptional weather resistance, maintaining its structural integrity and clarity under prolonged exposure to UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and moisture. This durability ensures its suitability for outdoor applications such as glazing, roofing, and automotive components, where performance must withstand harsh environmental conditions. Treatments like UV stabilizers further enhance polycarbonate's resistance to yellowing and degradation, extending its lifespan in outdoor environments.
Key Chemical Agents Affecting Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate exhibits strong resistance to water, mild acids, and alkalis but is vulnerable to aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons such as benzene, acetone, and trichloroethylene, which cause cracking and surface degradation. Weather resistance is generally effective due to UV stabilizers, but prolonged exposure to sunlight combined with chemical agents like acidic rain can accelerate polymer breakdown. Understanding these key chemical agents is critical for maintaining polycarbonate's structural integrity in outdoor and industrial applications.
Environmental Factors Impacting Weather Resistance
Polycarbonate exhibits excellent chemical resistance against many acids, bases, and oils but can degrade when exposed to certain organic solvents and alkaline substances. Weather resistance is primarily challenged by environmental factors such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation, temperature fluctuations, and moisture, which can cause surface chalking, yellowing, and reduced mechanical strength over time. Incorporating UV stabilizers and protective coatings significantly enhances polycarbonate's durability against these environmental stressors.
Comparing Polycarbonate's Chemical and Weather Resistance
Polycarbonate exhibits strong weather resistance, maintaining clarity and mechanical integrity under prolonged exposure to UV radiation and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Its chemical resistance is moderate, with vulnerability to alkaline substances, solvents, and certain acids that can cause surface degradation or embrittlement. Selecting polycarbonate requires balancing its excellent weather durability against its limited resistance to harsh chemicals depending on the intended environmental exposure.
Testing Standards for Chemical and Weather Resistance
Polycarbonate's chemical resistance is evaluated using standards such as ASTM D543, which tests the material's durability against various chemicals including acids, alkalis, and solvents. Weather resistance is assessed through accelerated aging tests like ASTM G154, simulating prolonged UV exposure and humidity effects to measure degradation. These testing standards provide critical data to ensure polycarbonate's performance in demanding chemical and environmental conditions.
Common Applications Based on Resistance Profiles
Polycarbonate's chemical resistance makes it ideal for applications in laboratories, medical devices, and protective equipment where exposure to solvents and cleaning agents is frequent. Weather resistance suits outdoor uses such as glazing, automotive components, and greenhouse panels, where UV stability and impact resistance are critical. Understanding these resistance profiles ensures proper material selection for durability and performance in specific environmental conditions.
Enhancing Resistance: Additives and Coatings
Polycarbonate's chemical resistance can be significantly enhanced through the incorporation of specific additives such as UV stabilizers and anti-oxidants, which protect the polymer chains from degradation by acids, alkalis, and solvents. Weather resistance is improved by applying surface coatings like silicone or fluoropolymer layers that shield the material from UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, preventing yellowing and brittleness. Combining these additives and coatings results in a durable polycarbonate product capable of maintaining mechanical strength and optical clarity in harsh environmental conditions.
Choosing Polycarbonate: Chemical vs Weather Durability
Polycarbonate excels in chemical resistance against mild acids, alkalis, and oils but may degrade with prolonged exposure to strong solvents or harsh chemicals. Its weather resistance is enhanced by UV stabilizers, making it suitable for outdoor applications where it can withstand sunlight, rain, and temperature fluctuations without yellowing or becoming brittle. Selecting polycarbonate for specific uses requires balancing chemical exposure risks against environmental weather conditions to ensure optimal durability and longevity.
Chemical Resistance vs Weather Resistance Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com