Polycarbonate film offers flexibility, lightweight properties, and excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring thin, durable layers such as protective covers and displays. Polycarbonate plates provide greater rigidity and impact resistance, suited for structural uses like machine guards and transparent barriers. Choosing between polycarbonate film and plate depends on the need for flexibility versus strength and thickness requirements in the specific application.
Table of Comparison
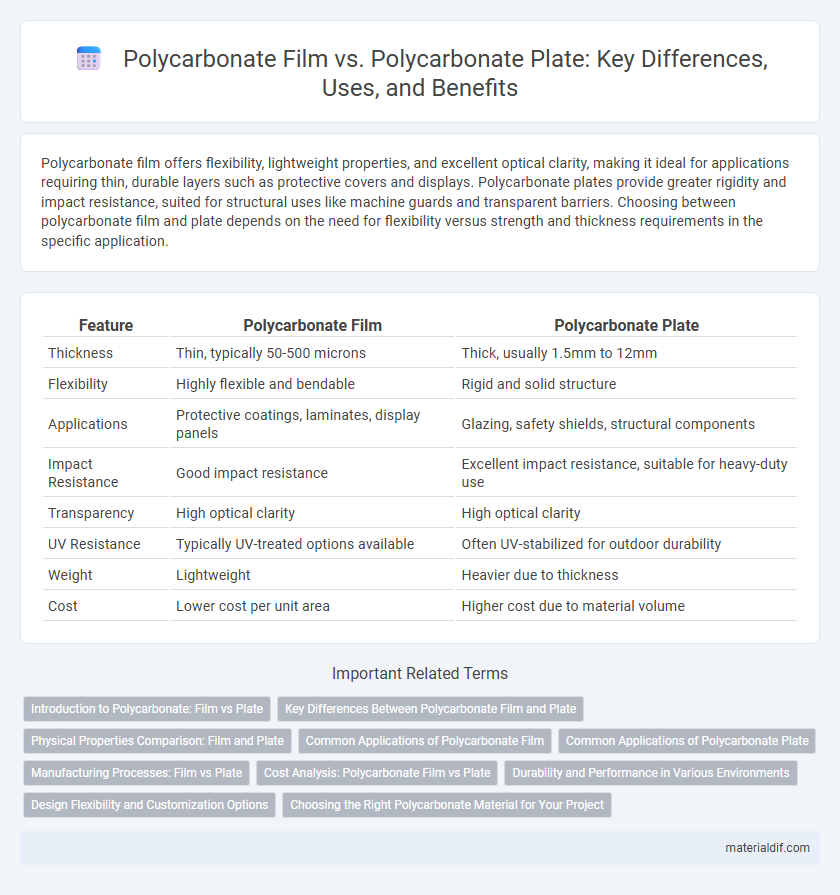
| Feature | Polycarbonate Film | Polycarbonate Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Thin, typically 50-500 microns | Thick, usually 1.5mm to 12mm |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and bendable | Rigid and solid structure |
| Applications | Protective coatings, laminates, display panels | Glazing, safety shields, structural components |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact resistance | Excellent impact resistance, suitable for heavy-duty use |
| Transparency | High optical clarity | High optical clarity |
| UV Resistance | Typically UV-treated options available | Often UV-stabilized for outdoor durability |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to thickness |
| Cost | Lower cost per unit area | Higher cost due to material volume |
Introduction to Polycarbonate: Film vs Plate
Polycarbonate film offers exceptional flexibility, lightweight properties, and high optical clarity, making it ideal for applications such as protective screens, laminates, and electronic displays. In contrast, polycarbonate plates provide superior rigidity, impact resistance, and structural strength, suitable for construction, glazing, and machinery guards. Understanding the distinct physical characteristics of polycarbonate film versus plate allows for optimal material selection based on specific performance requirements.
Key Differences Between Polycarbonate Film and Plate
Polycarbonate film is a thin, flexible material primarily used for protective coatings, screens, and laminates, offering high clarity and impact resistance. In contrast, polycarbonate plates are rigid, thicker sheets designed for structural applications, providing enhanced strength and durability for construction and industrial uses. The choice between film and plate depends on required flexibility, thickness, and mechanical performance.
Physical Properties Comparison: Film and Plate
Polycarbonate film offers superior flexibility and lightweight characteristics compared to polycarbonate plate, which provides enhanced rigidity and impact resistance. The film typically has a thickness range from 0.03 mm to 0.3 mm, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and durability without bulk. In contrast, polycarbonate plates range from 1 mm to 12 mm in thickness, delivering higher mechanical strength and thermal stability suitable for structural uses.
Common Applications of Polycarbonate Film
Polycarbonate film is extensively used in optical applications such as lenses, touchscreens, and protective screens due to its excellent transparency, high impact resistance, and UV protection. It is also widely applied in flexible electronics, solar panels, and security laminates where lightweight and flexible materials are essential. In contrast, polycarbonate plates are typically employed in rigid structural components, glazing, and industrial shields requiring robust mechanical strength and dimensional stability.
Common Applications of Polycarbonate Plate
Polycarbonate plates are widely used in applications requiring high impact resistance and optical clarity, such as protective barriers, machine guards, and transparent roofing. Their durability and flexibility make them ideal for safety visors, automotive components, and electronic device covers. These plates also serve in construction and signage industries due to their weather resistance and ease of fabrication.
Manufacturing Processes: Film vs Plate
Polycarbonate film is produced through a continuous extrusion or casting process that results in thin, flexible sheets ideal for applications requiring transparency and impact resistance. In contrast, polycarbonate plates are manufactured using injection molding or compression molding, creating thicker, rigid sheets designed for structural and protective uses. Differences in cooling rates and molecular orientation during these processes significantly influence the mechanical properties and optical clarity of the final products.
Cost Analysis: Polycarbonate Film vs Plate
Polycarbonate film typically offers a lower initial cost compared to polycarbonate plates due to its thinner gauge and flexible manufacturing process, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight and cost-effective solutions. Polycarbonate plates, while more expensive upfront, provide greater durability, impact resistance, and thickness, justifying the higher price for structural or protective uses. When considering total cost, the choice depends on application requirements, with polycarbonate film favored for budget-conscious projects and polycarbonate plates preferred for long-term performance and strength.
Durability and Performance in Various Environments
Polycarbonate film offers exceptional flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight and durable protective layers. In contrast, polycarbonate plates provide superior structural strength and rigidity, excelling in environments exposed to heavy mechanical stress and extreme temperatures. Both materials demonstrate excellent UV resistance and chemical stability, ensuring long-lasting performance across diverse industrial and outdoor settings.
Design Flexibility and Customization Options
Polycarbonate film offers superior design flexibility due to its thin, lightweight nature, allowing for easy cutting, shaping, and layering in various applications like electronics and packaging. Polycarbonate plates provide thicker, more rigid structures suitable for durable, load-bearing uses, but customization options are limited compared to films. The film's versatility in thickness and surface finishes supports diverse customization choices, while plates are typically customized through machining or molding processes.
Choosing the Right Polycarbonate Material for Your Project
Polycarbonate film offers flexibility, lightweight durability, and excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for applications such as protective screens, graphic overlays, and electronic displays. Polycarbonate plates provide superior impact resistance, structural strength, and thickness options, suitable for construction, glazing, and industrial components requiring robust protection. Selecting the right polycarbonate material depends on project requirements like flexibility, durability, transparency, and mechanical strength to balance performance and cost effectively.
Polycarbonate Film vs Polycarbonate Plate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com