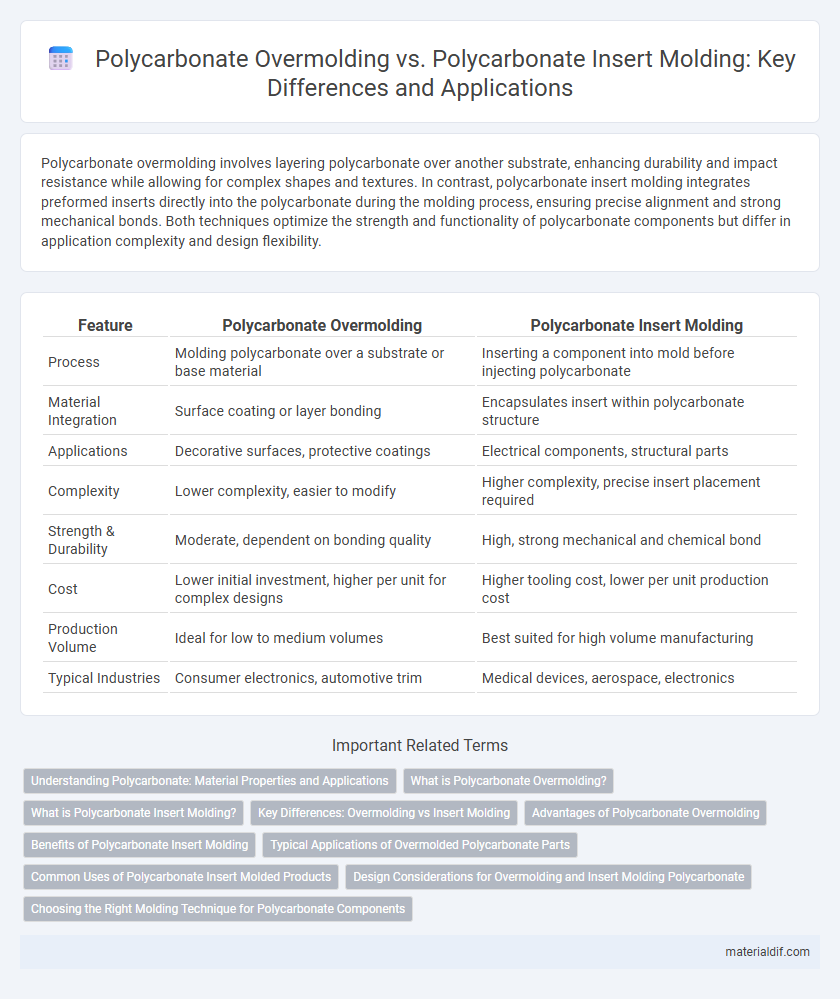
Polycarbonate overmolding involves layering polycarbonate over another substrate, enhancing durability and impact resistance while allowing for complex shapes and textures. In contrast, polycarbonate insert molding integrates preformed inserts directly into the polycarbonate during the molding process, ensuring precise alignment and strong mechanical bonds. Both techniques optimize the strength and functionality of polycarbonate components but differ in application complexity and design flexibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polycarbonate Overmolding | Polycarbonate Insert Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Molding polycarbonate over a substrate or base material | Inserting a component into mold before injecting polycarbonate |
| Material Integration | Surface coating or layer bonding | Encapsulates insert within polycarbonate structure |
| Applications | Decorative surfaces, protective coatings | Electrical components, structural parts |
| Complexity | Lower complexity, easier to modify | Higher complexity, precise insert placement required |
| Strength & Durability | Moderate, dependent on bonding quality | High, strong mechanical and chemical bond |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, higher per unit for complex designs | Higher tooling cost, lower per unit production cost |
| Production Volume | Ideal for low to medium volumes | Best suited for high volume manufacturing |
| Typical Industries | Consumer electronics, automotive trim | Medical devices, aerospace, electronics |
Understanding Polycarbonate: Material Properties and Applications
Polycarbonate's high impact resistance, thermal stability, and optical clarity make it ideal for overmolding and insert molding processes, enhancing product strength and design flexibility. Overmolding involves layering polycarbonate onto another substrate, providing superior durability in electronics and automotive parts, while insert molding integrates polycarbonate directly with metal or plastic inserts for robust, multi-material assemblies. These properties enable diverse applications in consumer electronics, medical devices, and industrial components, where precision and resilience are crucial.
What is Polycarbonate Overmolding?
Polycarbonate overmolding is a manufacturing process where a layer of polycarbonate material is molded over a pre-existing component or substrate to enhance durability, grip, or aesthetic appeal. This technique allows for precise control over material properties, enabling improved impact resistance and design flexibility in applications such as electronics and automotive parts. Unlike insert molding, polycarbonate overmolding uses a separate molding step, providing versatility in combining different materials and surface finishes.
What is Polycarbonate Insert Molding?
Polycarbonate insert molding is a manufacturing process where a polycarbonate material is molded directly over or around a preformed insert, such as a metal component, to create a single integrated part. This technique enhances the mechanical strength and dimensional stability of the final product by securely bonding dissimilar materials within one mold cycle. Insert molding with polycarbonate is commonly used in industries requiring durable, precise parts like automotive, electronics, and medical devices.
Key Differences: Overmolding vs Insert Molding
Polycarbonate overmolding involves molding a secondary material over a polycarbonate substrate to enhance functionality or aesthetics, whereas polycarbonate insert molding embeds pre-formed polycarbonate components directly into the mold during the injection process. Overmolding provides design flexibility and improved grip or sealing features, while insert molding ensures precise placement and strong mechanical bonds between dissimilar materials. Key differences lie in process timing, material interaction, and application suitability, with overmolding typically used for multi-material assemblies and insert molding favored for integrated, high-strength part assemblies.
Advantages of Polycarbonate Overmolding
Polycarbonate overmolding offers enhanced design flexibility by allowing multiple materials to be combined into a single component without compromising durability. This process improves impact resistance and mechanical strength while providing superior aesthetic finishes compared to polycarbonate insert molding. Overmolding also simplifies assembly, reducing manufacturing time and costs by eliminating the need for secondary operations.
Benefits of Polycarbonate Insert Molding
Polycarbonate insert molding offers enhanced structural integrity by permanently bonding inserts within the plastic, resulting in superior strength and durability compared to overmolding. This process reduces assembly time and cost by eliminating the need for secondary fastening or bonding operations. Additionally, insert molding improves precision and reliability in complex components, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
Typical Applications of Overmolded Polycarbonate Parts
Polycarbonate overmolding is commonly used in consumer electronics, automotive components, and medical devices due to its ability to combine durability with enhanced grip and aesthetic appeal. Typical applications include smartphone cases, dashboard panels, and surgical instrument handles where the soft overmolded layer improves user comfort and impact resistance. This process enables seamless integration of multiple materials, optimizing functionality and design flexibility in polycarbonate parts.
Common Uses of Polycarbonate Insert Molded Products
Polycarbonate insert molding is commonly used in the production of electronic housings, automotive components, and medical devices due to its ability to create strong, durable bonds between metal inserts and plastic parts. This process enhances mechanical strength and precision, making it ideal for applications requiring high load-bearing capacity and complex geometries. Overmolding, on the other hand, is typically employed for ergonomic grips and sealing features, whereas insert molding is preferred for structural and functional integrations in polycarbonate products.
Design Considerations for Overmolding and Insert Molding Polycarbonate
Design considerations for polycarbonate overmolding emphasize compatibility between the substrate and overmold materials to ensure strong adhesion and avoid delamination. Insert molding requires precise cavity design and proper placement of polycarbonate inserts to maintain dimensional accuracy and prevent warping during the molding process. Both methods demand careful thermal management to accommodate polycarbonate's high melting temperature and minimize residual stresses.
Choosing the Right Molding Technique for Polycarbonate Components
Polycarbonate overmolding offers enhanced design flexibility and improved grip by layering materials, making it ideal for components requiring varied textures or colors. In contrast, polycarbonate insert molding integrates pre-formed inserts within the polycarbonate matrix, providing superior structural strength and thermal resistance for load-bearing applications. Selecting the right molding technique depends on the specific performance requirements and aesthetic goals of the polycarbonate components.
Polycarbonate Overmolding vs Polycarbonate Insert Molding Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com