Sheet polycarbonate offers lightweight flexibility and ease of installation, making it ideal for glazing, roofing, and protective barriers. Solid polycarbonate, known for its superior impact resistance and clarity, is commonly used in applications requiring robust durability such as bulletproof windows and machine guards. Choosing between sheet and solid polycarbonate depends on the balance needed between weight, strength, and transparency for specific industrial or architectural projects.
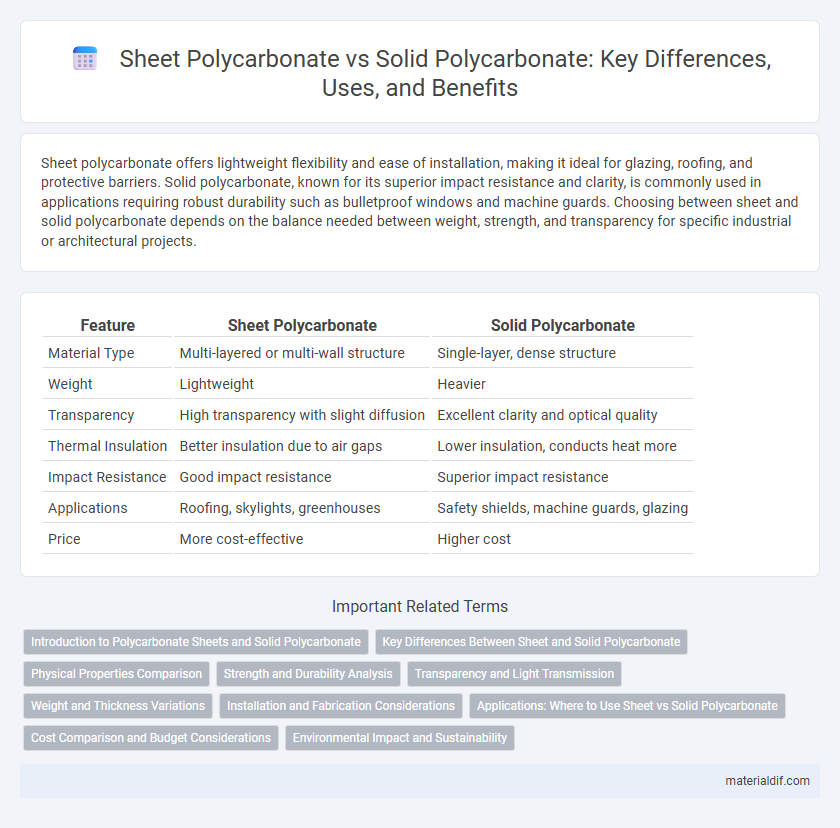
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sheet Polycarbonate | Solid Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Multi-layered or multi-wall structure | Single-layer, dense structure |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Transparency | High transparency with slight diffusion | Excellent clarity and optical quality |
| Thermal Insulation | Better insulation due to air gaps | Lower insulation, conducts heat more |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact resistance | Superior impact resistance |
| Applications | Roofing, skylights, greenhouses | Safety shields, machine guards, glazing |
| Price | More cost-effective | Higher cost |
Introduction to Polycarbonate Sheets and Solid Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate sheets feature a lightweight, multiwall structure that provides excellent thermal insulation and impact resistance, making them ideal for applications like roofing, skylights, and greenhouses. Solid polycarbonate offers a dense, transparent material with superior strength and optical clarity, commonly used in protective barriers, automotive components, and glazing panels. Both types exhibit high UV resistance and durability, but sheet polycarbonate excels in insulation and weight savings, whereas solid polycarbonate is preferred for rigidity and transparency.
Key Differences Between Sheet and Solid Polycarbonate
Sheet polycarbonate is typically manufactured as a lightweight, flexible material designed for applications needing impact resistance and transparency, commonly used in glazing, roofing, and protective barriers. Solid polycarbonate offers greater durability, higher strength, and enhanced optical clarity, making it suitable for demanding structural applications, machine guards, and optical lenses. Key differences lie in their thickness variations, impact resistance, and thermal insulation properties, with sheet polycarbonate providing better insulation and solid polycarbonate exhibiting superior mechanical strength.
Physical Properties Comparison
Sheet polycarbonate offers enhanced flexibility and impact resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring lightweight durability, while solid polycarbonate provides superior strength, higher optical clarity, and better thermal resistance for demanding structural uses. Sheet polycarbonate typically exhibits lower density and improved bending capabilities compared to solid polycarbonate, which is denser and maintains rigidity under stress. These physical property distinctions enable precise material selection for industries such as construction, automotive, and protective glazing.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Sheet polycarbonate offers flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight yet durable materials; its cellular structure provides excellent shock absorption. Solid polycarbonate exhibits superior strength and higher resistance to cracking under heavy loads, providing enhanced durability for structural applications. Both materials maintain high UV resistance and thermal stability, but solid polycarbonate's dense composition ensures increased longevity in extreme conditions.
Transparency and Light Transmission
Sheet polycarbonate offers high transparency with light transmission rates typically around 85-90%, making it ideal for applications requiring natural light diffusion and glare reduction. Solid polycarbonate provides even greater clarity and superior light transmission, often exceeding 90%, ensuring minimal distortion and excellent optical quality for demanding visual applications. Both types maintain UV resistance and impact strength, but solid polycarbonate is preferred when maximum transparency and light performance are critical.
Weight and Thickness Variations
Sheet polycarbonate typically offers a lighter weight option with thicknesses ranging from 0.75mm to 3mm, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility and easier handling. Solid polycarbonate, in contrast, presents greater density and thickness variations commonly between 3mm and 25mm, providing enhanced impact resistance and structural strength. Choosing between sheet and solid polycarbonate depends on the specific weight constraints and required thickness for durability in construction or industrial projects.
Installation and Fabrication Considerations
Sheet polycarbonate offers greater ease of installation due to its lightweight and flexibility, making it ideal for curved or irregular surfaces, whereas solid polycarbonate requires more precise cutting and handling because of its rigidity and thickness. Fabrication of sheet polycarbonate involves thermal forming and extrusion processes allowing various shapes and sizes, while solid polycarbonate demands CNC machining, drilling, or laser cutting to achieve custom dimensions. Proper allowance for expansion and contraction in sheet polycarbonate is essential during installation to prevent stress fractures, whereas solid polycarbonate's dimensional stability reduces this concern but increases fabrication complexity.
Applications: Where to Use Sheet vs Solid Polycarbonate
Sheet polycarbonate is ideal for applications requiring lightweight, impact-resistant, and transparent materials such as greenhouses, skylights, and protective barriers. Solid polycarbonate, known for its superior strength and clarity, is commonly used in bulletproof windows, machine guards, and eyewear lenses. Choosing between sheet and solid polycarbonate depends on balancing factors like thickness, optical clarity, and mechanical durability for specific industrial and architectural needs.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Sheet polycarbonate generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to solid polycarbonate, making it suitable for budget-conscious projects. Solid polycarbonate boasts higher impact resistance and clarity but comes at a premium price due to its density and manufacturing process. When balancing cost and performance, sheet polycarbonate provides a practical choice for applications requiring durability without exceeding budget constraints.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sheet polycarbonate typically has a lower environmental footprint due to its lightweight structure, reducing material usage and energy consumption during production and transportation. Solid polycarbonate offers superior durability and longevity, which can decrease the frequency of replacement and waste generation over time. Recycling capabilities of both forms vary, with sheet polycarbonate often being more easily repurposed in manufacturing, enhancing overall sustainability.
Sheet Polycarbonate vs Solid Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com