Transparent polycarbonate offers exceptional clarity and high impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility and durability, such as protective eyewear and glazing. Opaque polycarbonate, on the other hand, provides enhanced UV resistance and a broader range of color options, suitable for aesthetic and functional uses like automotive parts and electronic housings. Choosing between transparent and opaque polycarbonate depends on the balance needed between light transmission, strength, and design specifications.
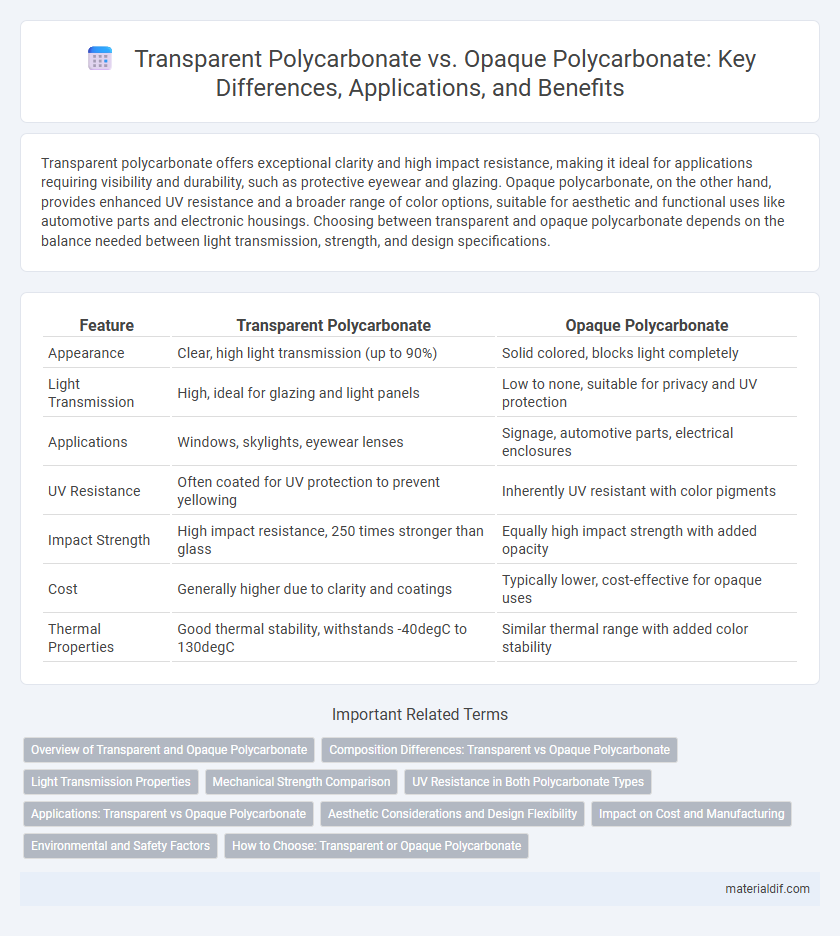
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transparent Polycarbonate | Opaque Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear, high light transmission (up to 90%) | Solid colored, blocks light completely |
| Light Transmission | High, ideal for glazing and light panels | Low to none, suitable for privacy and UV protection |
| Applications | Windows, skylights, eyewear lenses | Signage, automotive parts, electrical enclosures |
| UV Resistance | Often coated for UV protection to prevent yellowing | Inherently UV resistant with color pigments |
| Impact Strength | High impact resistance, 250 times stronger than glass | Equally high impact strength with added opacity |
| Cost | Generally higher due to clarity and coatings | Typically lower, cost-effective for opaque uses |
| Thermal Properties | Good thermal stability, withstands -40degC to 130degC | Similar thermal range with added color stability |
Overview of Transparent and Opaque Polycarbonate
Transparent polycarbonate offers high optical clarity with light transmittance up to 90%, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility and durability, such as safety glasses and protective shields. Opaque polycarbonate provides superior UV resistance and enhanced impact strength, commonly used for automotive parts and electronic housings where light blockage and robustness are essential. Both materials maintain excellent heat resistance and dimensional stability, with variations tailored to specific functional and aesthetic requirements.
Composition Differences: Transparent vs Opaque Polycarbonate
Transparent polycarbonate consists primarily of bisphenol A and carbonic acid derivatives, formulated to have minimal impurities and additives that could affect clarity, resulting in high light transmission up to 90%. Opaque polycarbonate incorporates pigments and fillers such as titanium dioxide or carbon black, which scatter and absorb light, reducing transparency while enhancing UV resistance and impact strength. These compositional variations influence not only optical properties but also thermal stability and chemical resistance tailored to specific industrial applications.
Light Transmission Properties
Transparent polycarbonate exhibits high light transmission, typically allowing up to 90% of visible light to pass through, making it ideal for applications requiring clear visibility and natural lighting. Opaque polycarbonate, in contrast, significantly reduces light transmission due to its pigment or additive content, providing enhanced privacy and UV protection. The choice between transparent and opaque polycarbonate depends on balancing the need for visibility with considerations of light diffusion and glare reduction.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Transparent polycarbonate exhibits high impact resistance and excellent tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring both durability and clarity. Opaque polycarbonate maintains comparable mechanical strength but offers enhanced UV resistance and surface hardness, which improves longevity in outdoor or abrasive environments. Both types provide robust mechanical performance, yet the choice depends on whether optical transparency or added protection is prioritized.
UV Resistance in Both Polycarbonate Types
Transparent polycarbonate exhibits high UV resistance due to its inherent clarity and protective coatings, making it ideal for applications requiring natural light transmission and weather durability. Opaque polycarbonate also offers excellent UV protection, often enhanced by added pigments that absorb UV rays and prevent material degradation. Both types maintain structural integrity under prolonged UV exposure, but transparent polycarbonate requires specialized UV stabilizers to preserve optical clarity over time.
Applications: Transparent vs Opaque Polycarbonate
Transparent polycarbonate is commonly used in applications requiring high optical clarity and impact resistance, such as eyewear lenses, automotive windows, and electronic displays. Opaque polycarbonate is preferred for structural components, electrical enclosures, and industrial housings where light diffusion or UV protection is essential. Both types offer durability and thermal stability, but transparency dictates their suitability for visible versus protective or aesthetic uses.
Aesthetic Considerations and Design Flexibility
Transparent polycarbonate offers superior clarity and light transmission, making it ideal for applications requiring visual appeal and natural illumination. Opaque polycarbonate provides a broader range of color options and surface finishes, enhancing customization and concealment of internal components. Designers benefit from transparent variants for sleek, modern aesthetics, while opaque types enable creative color matching and textured effects for diverse architectural and industrial uses.
Impact on Cost and Manufacturing
Transparent polycarbonate generally incurs higher manufacturing costs due to the need for precise raw material purity and advanced processing techniques to maintain optical clarity. Opaque polycarbonate allows for more flexible production methods and often uses cost-effective additives, resulting in lower material expenses and simpler molding processes. The choice between transparent and opaque polycarbonate significantly impacts overall cost efficiency and production complexity in industrial applications.
Environmental and Safety Factors
Transparent polycarbonate offers superior visibility and light transmission, making it ideal for applications requiring clear sightlines and natural lighting, while also maintaining high impact resistance and UV protection for environmental durability. Opaque polycarbonate provides enhanced privacy and better concealment of internal components, often used in environments demanding reduced light exposure or additional protection from UV degradation. Both types exhibit excellent fire resistance and recyclability, contributing to sustainable safety solutions in construction, automotive, and electronic industries.
How to Choose: Transparent or Opaque Polycarbonate
Transparent polycarbonate offers high optical clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility, such as windows, eyewear lenses, and protective shields. Opaque polycarbonate provides superior light blocking, enhanced thermal insulation, and increased durability, suitable for machine housings, electrical enclosures, and architectural panels. Choosing between transparent or opaque polycarbonate depends on whether the priority is visibility and light transmission or privacy, light obstruction, and structural strength.
Transparent Polycarbonate vs Opaque Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com