Polycarbonate glazing offers superior impact resistance and lighter weight compared to traditional glass glazing, making it ideal for safety and durability in architectural applications. It provides excellent UV protection while maintaining high optical clarity, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing glare. Unlike glass, polycarbonate is easier to fabricate and install, reducing overall construction time and costs.
Table of Comparison
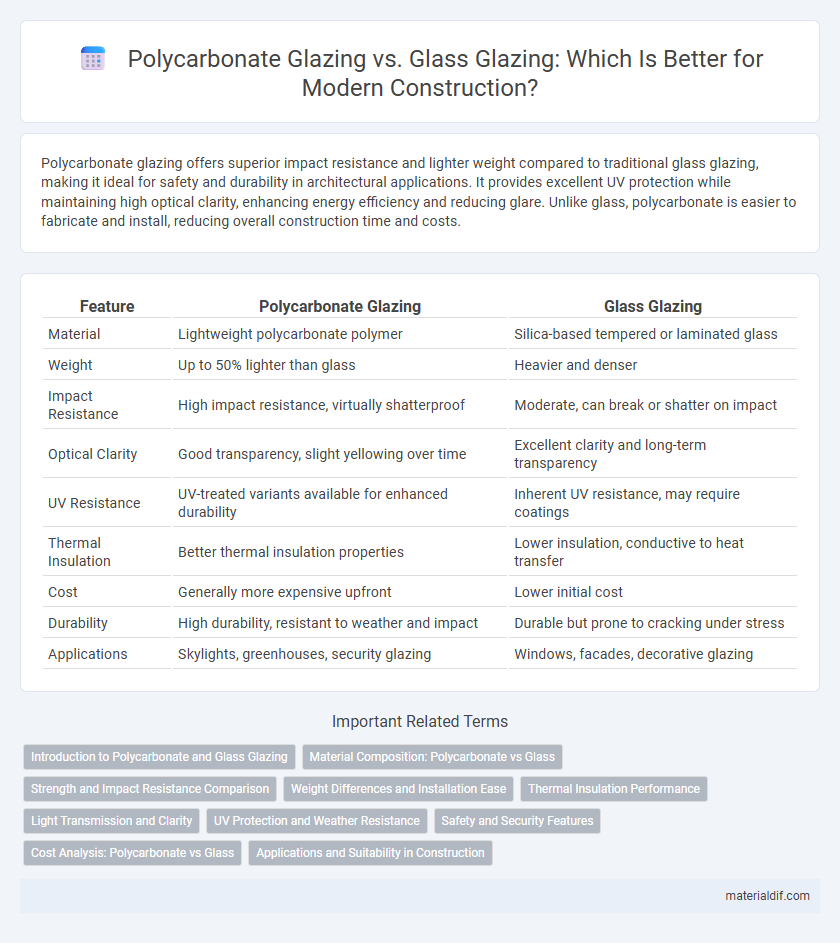
| Feature | Polycarbonate Glazing | Glass Glazing |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Lightweight polycarbonate polymer | Silica-based tempered or laminated glass |
| Weight | Up to 50% lighter than glass | Heavier and denser |
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance, virtually shatterproof | Moderate, can break or shatter on impact |
| Optical Clarity | Good transparency, slight yellowing over time | Excellent clarity and long-term transparency |
| UV Resistance | UV-treated variants available for enhanced durability | Inherent UV resistance, may require coatings |
| Thermal Insulation | Better thermal insulation properties | Lower insulation, conductive to heat transfer |
| Cost | Generally more expensive upfront | Lower initial cost |
| Durability | High durability, resistant to weather and impact | Durable but prone to cracking under stress |
| Applications | Skylights, greenhouses, security glazing | Windows, facades, decorative glazing |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and Glass Glazing
Polycarbonate glazing offers superior impact resistance and lightweight durability compared to conventional glass. While glass glazing provides excellent clarity and scratch resistance, polycarbonate excels in high-strength applications and UV protection. Both materials serve distinct purposes in construction, with polycarbonate being favored for safety and flexibility, and glass prized for aesthetic transparency and hardness.
Material Composition: Polycarbonate vs Glass
Polycarbonate glazing is composed of a durable thermoplastic polymer known for its high impact resistance and lightweight properties, while glass glazing consists primarily of silica-based materials offering superior hardness and scratch resistance. Polycarbonate's molecular structure allows it to absorb and disperse energy more effectively, making it ideal for safety applications, whereas glass's rigid, crystalline composition provides exceptional clarity and thermal stability. The distinct material compositions influence their performance characteristics, with polycarbonate excelling in flexibility and shatter resistance, and glass providing enhanced optical clarity and longevity under environmental exposure.
Strength and Impact Resistance Comparison
Polycarbonate glazing exhibits significantly higher impact resistance than glass glazing, with polycarbonate being up to 250 times stronger than traditional glass. This superior strength makes polycarbonate an ideal choice for environments requiring enhanced durability and safety, such as in security windows or protective barriers. Unlike glass, polycarbonate resists shattering under impact, reducing the risk of injury and property damage.
Weight Differences and Installation Ease
Polycarbonate glazing weighs up to 70% less than traditional glass, significantly reducing structural load and making it ideal for large roofing and facade applications. Its lightweight nature simplifies handling and installation, requiring fewer support fixtures and enabling faster project completion compared to heavier glass panels. Polycarbonate's impact resistance also minimizes breakage risks during installation, enhancing overall safety and efficiency on site.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Polycarbonate glazing offers superior thermal insulation compared to traditional glass glazing due to its multi-wall structure and low thermal conductivity, effectively reducing heat transfer. Polycarbonate panels can achieve U-values as low as 1.5 W/m2K, whereas standard single-pane glass typically ranges around 5.8 W/m2K, making polycarbonate an energy-efficient choice for climate control. This enhanced insulation performance contributes to significant energy savings in both heating and cooling applications.
Light Transmission and Clarity
Polycarbonate glazing offers higher impact resistance than glass glazing while maintaining comparable light transmission rates, typically around 88-92%, ensuring excellent clarity for various applications. Glass glazing generally provides slightly better optical clarity with light transmission near 90-95%, but it is more fragile and prone to shattering. Polycarbonate's superior durability and UV resistance make it favorable for environments requiring both safety and strong light transmission without significant loss of visual quality.
UV Protection and Weather Resistance
Polycarbonate glazing offers superior UV protection compared to traditional glass glazing, effectively blocking up to 99.9% of harmful ultraviolet rays, which helps prevent material degradation and skin damage. Its impact resistance and weather resistance are significantly higher, making polycarbonate panels less prone to cracking, yellowing, or warping under extreme weather conditions. Glass glazing, while durable, lacks the same level of UV filtration and is more susceptible to breakage and weather-induced wear over time.
Safety and Security Features
Polycarbonate glazing offers superior impact resistance compared to traditional glass glazing, making it highly effective in environments requiring enhanced safety and security. Its ability to withstand significant force without shattering reduces the risk of injury and unauthorized entry, which is critical in security-sensitive applications. Polycarbonate sheets also provide excellent penetration resistance, making them ideal for protective barriers and secure enclosures.
Cost Analysis: Polycarbonate vs Glass
Polycarbonate glazing offers significant cost advantages over glass glazing due to its lower material and installation expenses, often costing up to 50% less. Polycarbonate panels are lightweight, reducing structural support and labor costs compared to heavier, more fragile glass sheets. Although glass glazing generally provides better scratch resistance and longevity, the initial investment and repair costs make polycarbonate a more budget-friendly option for applications demanding impact resistance and flexibility.
Applications and Suitability in Construction
Polycarbonate glazing offers superior impact resistance and lightweight properties compared to traditional glass glazing, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and safety, such as skylights, greenhouses, and security enclosures. Its excellent thermal insulation and UV resistance enhance energy efficiency and longevity, suitable for both commercial and residential construction projects. Glass glazing remains preferred for aesthetic clarity and scratch resistance, often used in facades and interior partitions where visual appeal and hardness are prioritized.
Polycarbonate Glazing vs Glass Glazing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com