Polycarbonate sheets offer superior impact resistance and lightweight properties compared to glass sheets, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and safety. They provide excellent clarity and UV protection while being easier to cut and install than glass. Although glass sheets offer higher scratch resistance, polycarbonate sheets deliver greater flexibility and shatterproof performance in various environments.
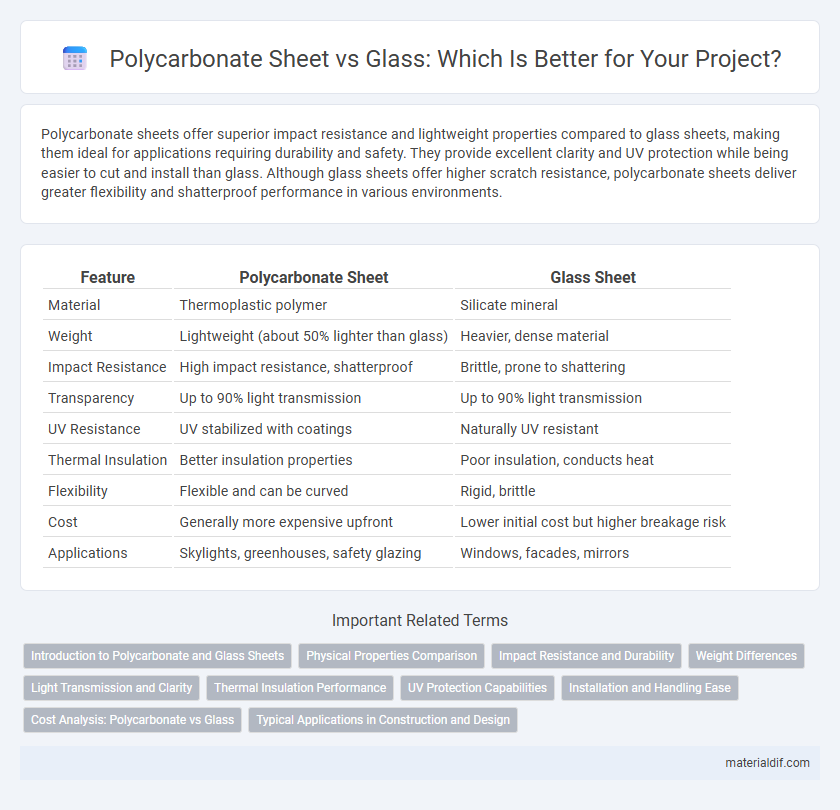
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polycarbonate Sheet | Glass Sheet |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Thermoplastic polymer | Silicate mineral |
| Weight | Lightweight (about 50% lighter than glass) | Heavier, dense material |
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance, shatterproof | Brittle, prone to shattering |
| Transparency | Up to 90% light transmission | Up to 90% light transmission |
| UV Resistance | UV stabilized with coatings | Naturally UV resistant |
| Thermal Insulation | Better insulation properties | Poor insulation, conducts heat |
| Flexibility | Flexible and can be curved | Rigid, brittle |
| Cost | Generally more expensive upfront | Lower initial cost but higher breakage risk |
| Applications | Skylights, greenhouses, safety glazing | Windows, facades, mirrors |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and Glass Sheets
Polycarbonate sheets are lightweight, impact-resistant thermoplastic materials known for their high durability and UV protection, commonly used in construction and glazing applications. Glass sheets offer superior clarity and scratch resistance but are heavier and more fragile, making them less suitable for dynamic environments. Both materials serve distinct purposes based on factors like strength, weight, transparency, and safety requirements.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polycarbonate sheets exhibit superior impact resistance, being up to 250 times stronger than glass sheets of the same thickness, making them highly durable against breakage. They offer excellent flexibility and are much lighter, with polycarbonate weighing approximately 1.2 g/cm3 compared to glass at around 2.5 g/cm3, facilitating easier handling and installation. Despite lower scratch resistance than glass, polycarbonate sheets provide better thermal insulation and UV protection, enhancing their suitability for outdoor applications.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Polycarbonate sheets exhibit significantly higher impact resistance compared to glass sheets, withstanding up to 250 times more force, making them ideal for applications requiring robust durability. Unlike glass, polycarbonate is virtually unbreakable and resistant to shattering, ensuring enhanced safety in environments prone to impact or extreme weather. The superior durability of polycarbonate sheets also provides long-term resistance to wear, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations, outperforming traditional glass in maintaining structural integrity over time.
Weight Differences
Polycarbonate sheets weigh approximately 60% less than glass sheets, making them a preferred choice for applications requiring lightweight materials. This significant weight difference enhances ease of installation and reduces structural load in construction projects. Polycarbonate offers similar transparency to glass but with improved impact resistance and better durability in lightweight applications.
Light Transmission and Clarity
Polycarbonate sheets offer superior impact resistance while maintaining excellent light transmission rates of up to 90%, closely rivaling the clarity of glass sheets, which typically allow 88-92% light transmission. Unlike glass, polycarbonate sheets provide better UV resistance and do not yellow over time, ensuring long-lasting clarity in various lighting conditions. Their lightweight nature combined with high transparency makes polycarbonate sheets an efficient alternative for applications requiring both strength and optical clarity.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Polycarbonate sheets provide superior thermal insulation compared to glass sheets, offering up to 200 times better impact resistance and lower heat transfer coefficients. This material reduces energy costs by minimizing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, making it ideal for energy-efficient building applications. Polycarbonate's thermal performance is measured by its low U-value, typically ranging from 2.4 to 3.0 W/m2K, significantly outperforming standard glass sheets with U-values around 5.7 W/m2K.
UV Protection Capabilities
Polycarbonate sheets offer superior UV protection compared to glass sheets, effectively blocking up to 99.9% of harmful ultraviolet rays while maintaining clarity and impact resistance. Unlike traditional glass, which often requires additional coatings to enhance UV defense, polycarbonate inherently filters UV radiation, reducing the risk of material degradation and long-term sun damage. This makes polycarbonate sheets ideal for applications requiring durable, lightweight, and UV-resistant materials such as skylights, greenhouses, and outdoor enclosures.
Installation and Handling Ease
Polycarbonate sheets offer superior installation and handling ease compared to glass sheets due to their lightweight structure and high impact resistance, reducing the risk of breakage during transport and setup. Their flexibility allows for cutting and shaping on-site without specialized tools, streamlining the installation process and minimizing labor costs. In contrast, glass sheets require careful handling, heavy equipment, and professional installation to prevent cracking, increasing overall project time and expenses.
Cost Analysis: Polycarbonate vs Glass
Polycarbonate sheets offer a cost-effective alternative to glass sheets, with prices typically ranging from $2 to $6 per square foot compared to glass, which can cost between $8 and $15 per square foot depending on thickness and quality. Installation expenses for polycarbonate are generally lower due to its lighter weight and ease of handling, reducing labor costs significantly. Long-term maintenance costs also favor polycarbonate, as it is more impact-resistant and less prone to breakage, lowering replacement and repair expenses over time.
Typical Applications in Construction and Design
Polycarbonate sheets offer superior impact resistance and lightweight properties, making them ideal for skylights, greenhouses, and protective barriers in construction. Glass sheets are preferred for applications requiring high clarity and scratch resistance, such as windows, facades, and interior partitions. Polycarbonate's flexibility and UV resistance also enhance its use in roofing and canopies where durability and weather resistance are critical.
Polycarbonate Sheet vs Glass Sheet Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com