Flame-retardant polycarbonate is engineered with additives that enhance fire resistance, preventing or slowing the spread of flames compared to non-flame-retardant polycarbonate, which lacks these protective properties. This makes flame-retardant polycarbonate ideal for applications requiring strict fire safety standards, such as in electrical or automotive components. Non-flame-retardant polycarbonate, while offering excellent impact resistance and clarity, is less suitable for environments where fire hazards must be mitigated.
Table of Comparison
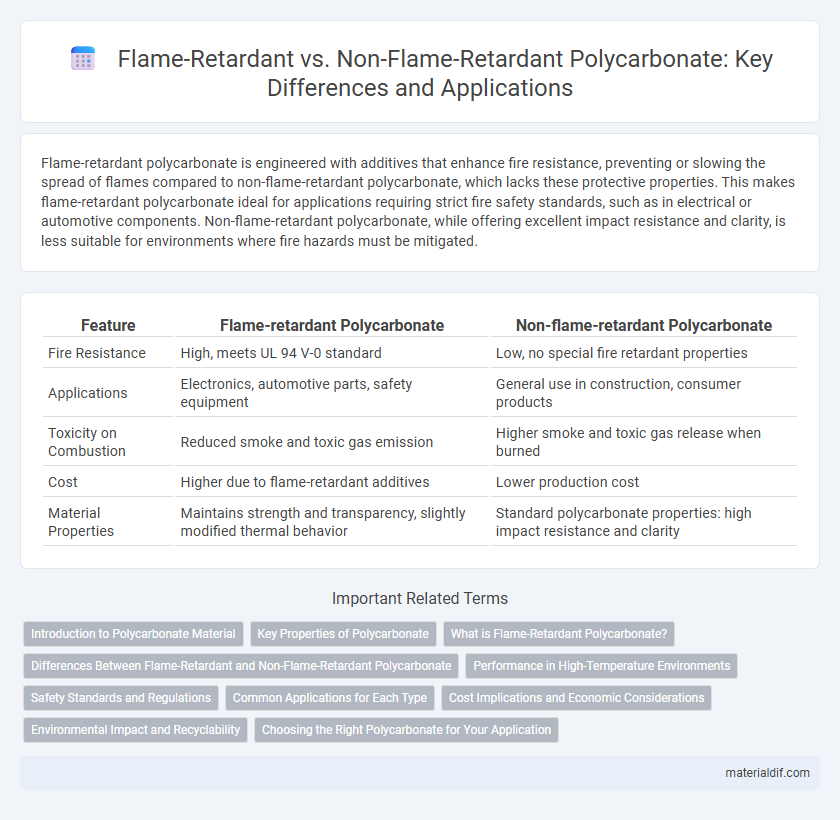
| Feature | Flame-retardant Polycarbonate | Non-flame-retardant Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | High, meets UL 94 V-0 standard | Low, no special fire retardant properties |
| Applications | Electronics, automotive parts, safety equipment | General use in construction, consumer products |
| Toxicity on Combustion | Reduced smoke and toxic gas emission | Higher smoke and toxic gas release when burned |
| Cost | Higher due to flame-retardant additives | Lower production cost |
| Material Properties | Maintains strength and transparency, slightly modified thermal behavior | Standard polycarbonate properties: high impact resistance and clarity |
Introduction to Polycarbonate Material
Polycarbonate is a durable thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and optical clarity, used extensively in electronics, automotive, and construction industries. Flame-retardant polycarbonate incorporates specialized additives that reduce flammability and enhance safety by preventing ignition and slowing fire spread. In contrast, non-flame-retardant polycarbonate lacks these additives, making it more susceptible to burning but generally more cost-effective and easier to process.
Key Properties of Polycarbonate
Flame-retardant polycarbonate exhibits enhanced resistance to ignition and self-extinguishing properties due to its chemical additives, making it suitable for applications demanding high safety standards. Non-flame-retardant polycarbonate offers superior clarity, impact resistance, and ease of fabrication, ideal for general-purpose uses where fire resistance is not critical. Both types maintain excellent dimensional stability, high heat resistance, and mechanical strength, key properties that define polycarbonate's versatility across various industries.
What is Flame-Retardant Polycarbonate?
Flame-retardant polycarbonate is a specially engineered type of polycarbonate resin infused with flame-retardant additives that significantly reduce its flammability and enhance fire resistance. This material complies with stringent safety standards such as UL 94 V-0, making it ideal for applications in electronics, automotive, and construction industries where fire safety is critical. Compared to non-flame-retardant polycarbonate, it offers superior protection by inhibiting ignition, delaying flame propagation, and minimizing smoke emission during combustion.
Differences Between Flame-Retardant and Non-Flame-Retardant Polycarbonate
Flame-retardant polycarbonate contains additives such as brominated compounds or phosphorus-based agents that enhance its resistance to ignition and slow down flame propagation, making it suitable for applications with stringent fire safety requirements. Non-flame-retardant polycarbonate lacks these additives, resulting in lower fire resistance and higher flammability, which limits its use to environments with minimal fire risk. The key differences lie in their thermal stability, smoke emission levels, and compliance with fire safety standards such as UL 94 V-0 rating for flame-retardant variants.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Flame-retardant polycarbonate exhibits superior thermal stability and maintains structural integrity at temperatures up to 130degC, significantly outperforming non-flame-retardant variants that tend to deform or degrade under high heat. The incorporation of flame retardants enhances resistance to ignition and reduces combustion hazards in critical applications such as electronics and automotive components. Non-flame-retardant polycarbonate, while more cost-effective, lacks these safety features and is less suitable for environments subject to frequent or prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures.
Safety Standards and Regulations
Flame-retardant polycarbonate complies with stringent safety standards such as UL 94 V-0, significantly reducing fire hazards in electrical and electronic applications compared to non-flame-retardant variants. Regulatory bodies like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) mandate specific flame retardance levels for materials used in public and industrial environments, where flame-retardant polycarbonate meets these requirements to ensure user safety. Non-flame-retardant polycarbonate, lacking these certifications, is unsuitable for high-risk applications due to its lower resistance to ignition and combustion.
Common Applications for Each Type
Flame-retardant polycarbonate is widely utilized in electronics housings, electrical components, and automotive parts requiring compliance with fire safety standards due to its enhanced resistance to ignition and flame propagation. Non-flame-retardant polycarbonate finds common application in optical lenses, eyewear, and various consumer goods where clarity, impact resistance, and lightweight properties are critical without the need for flame resistance. These distinct uses reflect the adaptation of polycarbonate materials tailored to safety protocols and performance demands across industries.
Cost Implications and Economic Considerations
Flame-retardant polycarbonate incurs higher production costs due to the incorporation of specialized additives and compliance with stringent safety standards, impacting overall material pricing. Non-flame-retardant polycarbonate offers a more economical option but lacks the enhanced fire resistance required for critical applications, potentially increasing liability and insurance costs. Manufacturers and buyers must weigh upfront material savings against long-term economic benefits associated with fire safety and regulatory adherence.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Flame-retardant polycarbonate contains additives such as brominated compounds or phosphorus-based agents that can hinder its recyclability and release toxic substances during degradation, posing environmental risks. Non-flame-retardant polycarbonate is generally easier to recycle and has a lower environmental footprint due to the absence of hazardous flame-retardant chemicals. Selection between these types depends on balancing fire safety requirements with sustainable waste management and ecological considerations.
Choosing the Right Polycarbonate for Your Application
Flame-retardant polycarbonate incorporates chemical additives that enhance its resistance to ignition and slow down flame spread, making it ideal for high-risk environments requiring stringent fire safety standards. Non-flame-retardant polycarbonate offers excellent impact resistance and optical clarity but lacks specialized fire protection, suitable for applications where flame exposure is minimal or controlled. Selecting the right polycarbonate depends on balancing fire safety requirements, mechanical performance, and cost-effectiveness tailored to specific industry standards and operational conditions.
Flame-retardant Polycarbonate vs Non-flame-retardant Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com