Polycarbonate glazing offers superior clarity and impact resistance, making it ideal for windows and transparent roofing applications where light transmission is crucial. Polycarbonate paneling provides enhanced durability and thermal insulation, suited for structural installations needing strength and weather resistance. Choosing between glazing and paneling depends on whether transparency or robust shielding is the priority for your polycarbonate pet project.
Table of Comparison
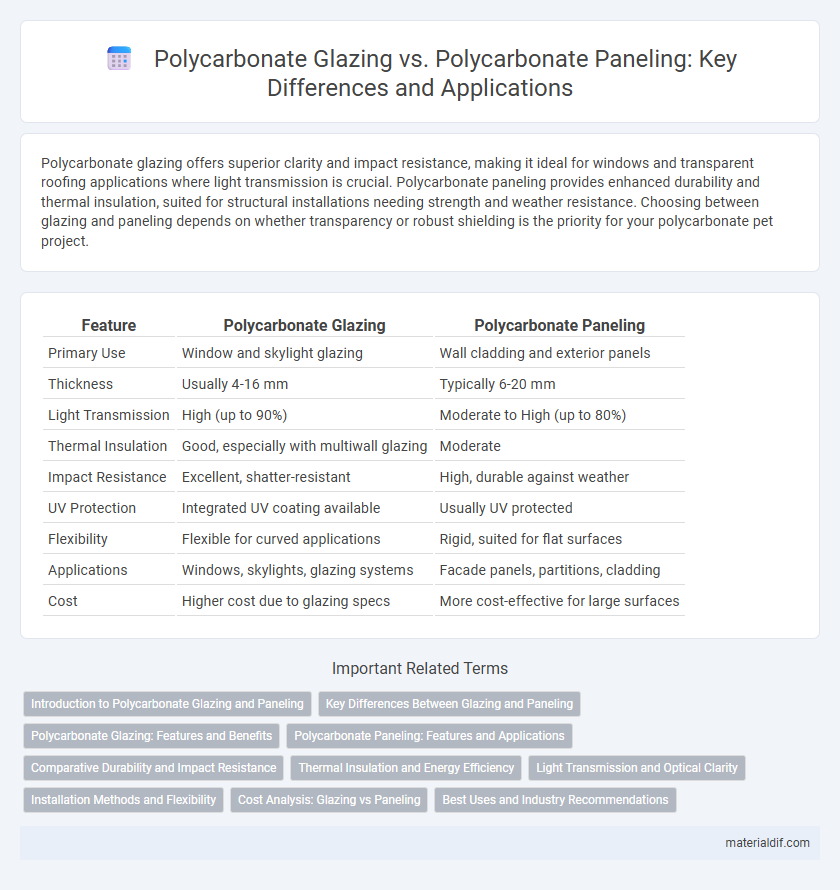
| Feature | Polycarbonate Glazing | Polycarbonate Paneling |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Window and skylight glazing | Wall cladding and exterior panels |
| Thickness | Usually 4-16 mm | Typically 6-20 mm |
| Light Transmission | High (up to 90%) | Moderate to High (up to 80%) |
| Thermal Insulation | Good, especially with multiwall glazing | Moderate |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent, shatter-resistant | High, durable against weather |
| UV Protection | Integrated UV coating available | Usually UV protected |
| Flexibility | Flexible for curved applications | Rigid, suited for flat surfaces |
| Applications | Windows, skylights, glazing systems | Facade panels, partitions, cladding |
| Cost | Higher cost due to glazing specs | More cost-effective for large surfaces |
Introduction to Polycarbonate Glazing and Paneling
Polycarbonate glazing offers superior transparency and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications such as windows, skylights, and protective barriers where light transmission and durability are crucial. Polycarbonate paneling, often used in roofing, walls, and facades, emphasizes structural strength, weather resistance, and insulation properties, providing versatile solutions for industrial and commercial construction. Both glazing and paneling leverage polycarbonate's lightweight and UV-resistant characteristics, but glazing prioritizes optical clarity while paneling focuses on mechanical robustness and thermal efficiency.
Key Differences Between Glazing and Paneling
Polycarbonate glazing offers superior transparency and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications like windows and skylights where light transmission is crucial. Polycarbonate paneling provides enhanced structural support and weather resistance, suited for roofing and wall cladding in industrial and commercial buildings. The key differences lie in their thickness, finish, and intended use, with glazing emphasizing clarity and paneling prioritizing durability and insulation.
Polycarbonate Glazing: Features and Benefits
Polycarbonate glazing offers exceptional impact resistance and high light transmission, making it ideal for windows, skylights, and safety shields in both residential and commercial applications. Its UV protection and thermal insulation properties enhance energy efficiency while maintaining durability in harsh weather conditions. Compared to polycarbonate paneling, glazing provides superior clarity and a smoother finish, ensuring better aesthetics and visibility.
Polycarbonate Paneling: Features and Applications
Polycarbonate paneling offers exceptional impact resistance, lightweight durability, and excellent thermal insulation, making it ideal for both industrial and architectural applications. Its versatility allows for use in greenhouse walls, soundproofing barriers, and protective cladding, providing enhanced UV protection and weather resistance. The modular design and ease of installation contribute to cost-effective solutions in construction and renovation projects.
Comparative Durability and Impact Resistance
Polycarbonate glazing offers superior impact resistance with high transparency, making it ideal for applications requiring clear visibility and robust protection, such as windows and skylights. Polycarbonate paneling provides enhanced durability against environmental stresses like UV radiation and weather exposure, suitable for roofing and wall cladding. Both materials excel in toughness, but glazing prioritizes optical clarity while paneling emphasizes long-term structural endurance.
Thermal Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Polycarbonate glazing offers superior thermal insulation due to its multi-wall structure, which effectively reduces heat transfer and enhances energy efficiency in buildings. In contrast, polycarbonate paneling, typically solid and thinner, provides less insulation and may result in higher energy consumption for heating and cooling. Choosing polycarbonate glazing can significantly improve a building's thermal performance and lower energy costs compared to standard polycarbonate paneling.
Light Transmission and Optical Clarity
Polycarbonate glazing offers superior light transmission and optical clarity compared to polycarbonate paneling, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum transparency and visual precision. Glazing-grade polycarbonate typically transmits up to 90% of visible light with minimal distortion, whereas standard polycarbonate panels may transmit slightly less light due to their thicker, textured surfaces designed for durability. The enhanced optical clarity in glazing materials ensures sharper, more accurate visibility, crucial for windows, skylights, and protective shields.
Installation Methods and Flexibility
Polycarbonate glazing typically involves installing thinner, transparent sheets in window or facade systems using glazing beads or structural frames, offering high flexibility for curved or angled surfaces. In contrast, polycarbonate paneling usually comprises thicker, rigid panels fixed with screws or fasteners onto walls or roofs, providing less flexibility but greater structural strength. Installation methods for glazing prioritize seamless integration and light transmission, while paneling focuses on durability and weather resistance.
Cost Analysis: Glazing vs Paneling
Polycarbonate glazing typically incurs higher upfront costs compared to polycarbonate paneling due to its enhanced clarity, thickness, and specialized manufacturing processes. Paneling offers a more cost-effective solution for large-scale applications where light transmission is less critical but durability and impact resistance remain essential. Evaluating lifecycle expenses, polycarbonate glazing may prove more economical in environments requiring superior thermal insulation and UV protection, whereas paneling minimizes material and installation costs in industrial or agricultural settings.
Best Uses and Industry Recommendations
Polycarbonate glazing offers superior clarity and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications such as skylights, windows, and protective barriers in the automotive and construction industries. Polycarbonate paneling provides enhanced thermal insulation and structural strength, recommended for industrial roofing, wall cladding, and greenhouse panels. Industry experts suggest choosing glazing for aesthetic transparency and light transmission, while paneling is preferred for durability and weather resistance in large-scale or exterior installations.
Polycarbonate Glazing vs Polycarbonate Paneling Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com