Polycarbonate PET with UV resistance offers superior protection against sun damage, preventing yellowing and degradation over time, thereby extending the material's lifespan. In contrast, non-UV resistant polycarbonate PET is more susceptible to discoloration and structural weakening when exposed to prolonged sunlight. Choosing UV resistant polycarbonate PET ensures enhanced durability and maintains optical clarity in outdoor applications.
Table of Comparison
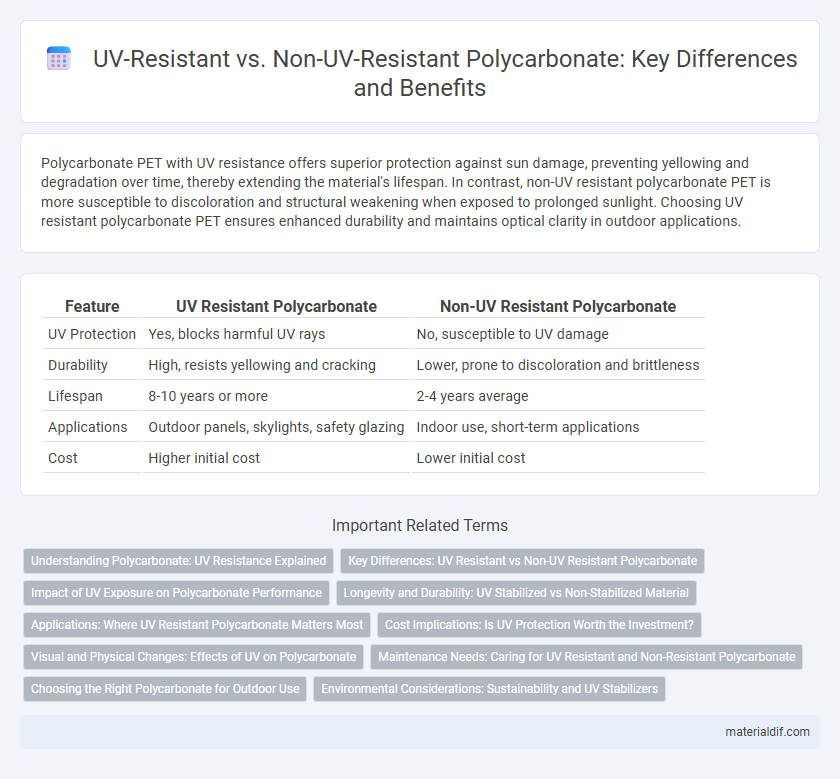
| Feature | UV Resistant Polycarbonate | Non-UV Resistant Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| UV Protection | Yes, blocks harmful UV rays | No, susceptible to UV damage |
| Durability | High, resists yellowing and cracking | Lower, prone to discoloration and brittleness |
| Lifespan | 8-10 years or more | 2-4 years average |
| Applications | Outdoor panels, skylights, safety glazing | Indoor use, short-term applications |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
Understanding Polycarbonate: UV Resistance Explained
Polycarbonate with UV resistance incorporates specialized coatings or additives that block ultraviolet rays, significantly enhancing durability by preventing yellowing, brittleness, and degradation over time. Non-UV resistant polycarbonate lacks these protective measures, making it susceptible to damage and reduced lifespan when exposed to prolonged sunlight. Understanding the differences in UV resistance is crucial for applications requiring long-term outdoor use, ensuring material performance and longevity.
Key Differences: UV Resistant vs Non-UV Resistant Polycarbonate
UV resistant polycarbonate features a protective coating that blocks harmful ultraviolet rays, preventing yellowing, brittleness, and degradation over time, which significantly extends the material's lifespan in outdoor applications. Non-UV resistant polycarbonate lacks this coating, making it susceptible to UV radiation damage, leading to reduced clarity, increased brittleness, and shorter durability when exposed to sunlight. Choosing UV resistant polycarbonate is crucial for maintaining structural integrity and visual appearance in environments with prolonged sun exposure.
Impact of UV Exposure on Polycarbonate Performance
Polycarbonate with UV resistance maintains its structural integrity and clarity when exposed to prolonged sunlight, preventing yellowing and surface degradation. Non-UV resistant polycarbonate rapidly deteriorates under UV exposure, resulting in reduced impact strength and increased brittleness. This degradation significantly compromises the material's durability and lifespan in outdoor applications.
Longevity and Durability: UV Stabilized vs Non-Stabilized Material
UV stabilized polycarbonate offers enhanced longevity and durability by resisting degradation from prolonged sun exposure, preventing discoloration, and maintaining structural integrity. Non-UV resistant polycarbonate deteriorates faster under sunlight, leading to yellowing, brittleness, and reduced mechanical strength over time. Choosing UV stabilized material ensures extended service life and reliable performance in outdoor applications.
Applications: Where UV Resistant Polycarbonate Matters Most
UV resistant polycarbonate is essential in outdoor applications such as skylights, greenhouses, and automotive parts where prolonged sun exposure can degrade material performance. Non-UV resistant polycarbonate suits indoor uses like electronic housings and machine guards, where UV exposure is minimal or absent. Selecting UV resistant variants ensures longevity, clarity retention, and mechanical strength under harsh sunlight conditions.
Cost Implications: Is UV Protection Worth the Investment?
UV-resistant polycarbonate sheets typically cost 15-30% more than non-UV variants due to the inclusion of specialized coatings or additives that block harmful ultraviolet rays. Investing in UV protection extends the material's lifespan by preventing yellowing, brittleness, and structural degradation, which can reduce long-term replacement and maintenance expenses. While upfront costs are higher, the enhanced durability and reduced need for frequent replacements make UV-resistant polycarbonate a cost-effective choice for outdoor applications.
Visual and Physical Changes: Effects of UV on Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate with UV resistance exhibits minimal yellowing and retains optical clarity over prolonged sun exposure, whereas non-UV resistant polycarbonate tends to develop significant discoloration and surface chalking. Physical degradation in non-UV resistant polycarbonate includes increased brittleness and micro-cracking that compromise structural integrity. UV stabilizers incorporated in UV-resistant polycarbonate act as a protective barrier, preventing polymer chain breakdown and preserving both visual and mechanical properties.
Maintenance Needs: Caring for UV Resistant and Non-Resistant Polycarbonate
UV-resistant polycarbonate requires minimal maintenance due to its protective coating that prevents yellowing and degradation from sun exposure, significantly extending its lifespan. Non-UV resistant polycarbonate demands regular cleaning and inspection to address surface brittleness and discoloration caused by prolonged ultraviolet radiation. Proper maintenance of UV-resistant materials reduces replacement frequency, whereas non-UV resistant variants often incur higher costs and labor for upkeep and eventual replacement.
Choosing the Right Polycarbonate for Outdoor Use
Polycarbonate with UV resistance features a specialized coating that prevents yellowing and degradation from prolonged sun exposure, ensuring durability and clarity in outdoor applications. Non-UV resistant polycarbonate lacks this protective layer, leading to brittleness and discoloration when exposed to ultraviolet rays over time. Selecting UV-resistant polycarbonate is crucial for outdoor use to maintain material integrity, appearance, and performance in harsh environmental conditions.
Environmental Considerations: Sustainability and UV Stabilizers
Polycarbonate with UV resistance incorporates UV stabilizers that extend material lifespan by preventing degradation from solar radiation, reducing plastic waste and environmental impact. Non-UV resistant polycarbonate degrades faster under UV exposure, leading to increased replacement frequency and higher ecological footprint. Utilizing UV-stabilized polycarbonate supports sustainability by minimizing resource consumption and enhancing durability in outdoor applications.
UV Resistance vs Non-UV Resistance Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com