Polycarbonate tubing offers lightweight durability and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring fluid transport or protective covers with structural resilience. In contrast, polycarbonate rods provide solid strength and rigidity, suited for mechanical components or load-bearing structures where impact resistance is essential. Choosing between tubing and rods depends on whether hollow or solid material properties best meet the specific project's functional demands.
Table of Comparison
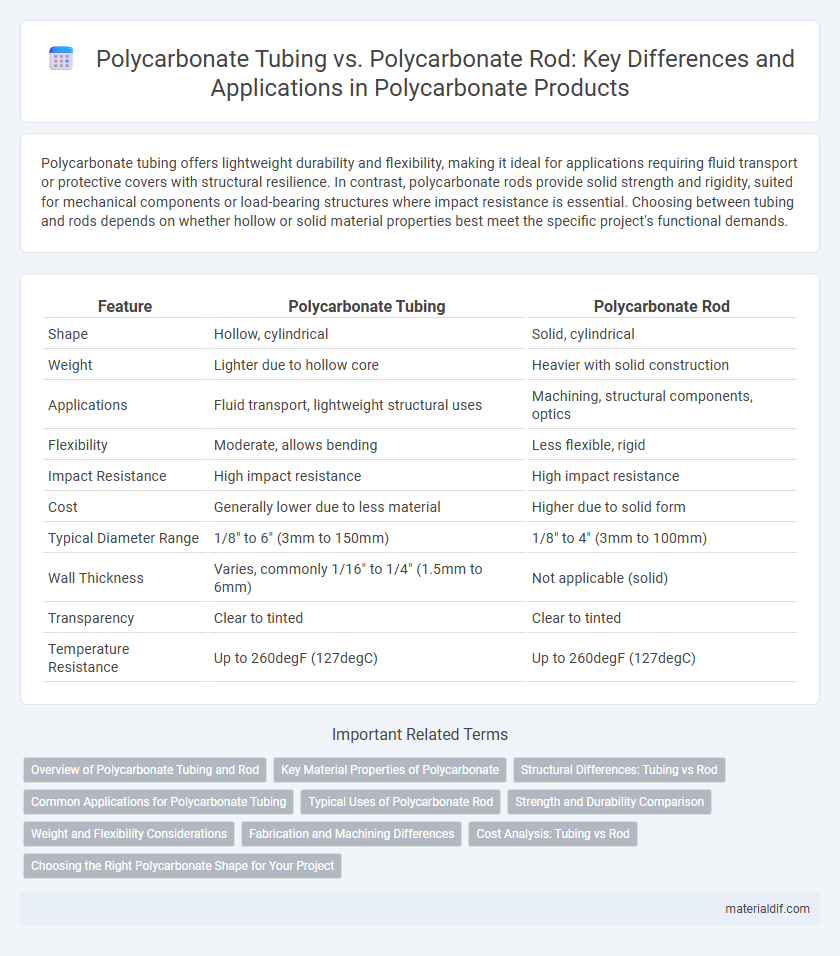
| Feature | Polycarbonate Tubing | Polycarbonate Rod |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Hollow, cylindrical | Solid, cylindrical |
| Weight | Lighter due to hollow core | Heavier with solid construction |
| Applications | Fluid transport, lightweight structural uses | Machining, structural components, optics |
| Flexibility | Moderate, allows bending | Less flexible, rigid |
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance | High impact resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower due to less material | Higher due to solid form |
| Typical Diameter Range | 1/8" to 6" (3mm to 150mm) | 1/8" to 4" (3mm to 100mm) |
| Wall Thickness | Varies, commonly 1/16" to 1/4" (1.5mm to 6mm) | Not applicable (solid) |
| Transparency | Clear to tinted | Clear to tinted |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 260degF (127degC) | Up to 260degF (127degC) |
Overview of Polycarbonate Tubing and Rod
Polycarbonate tubing offers a lightweight, flexible solution ideal for fluid handling, protective barriers, and structural applications requiring transparency and impact resistance. Polycarbonate rods provide greater rigidity and strength, making them suitable for machining, fabrication, and load-bearing components. Both forms exhibit excellent optical clarity, high impact resistance, and thermal stability, but tubing emphasizes hollow design for fluid transport while rods focus on solid construction for durability.
Key Material Properties of Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate tubing and polycarbonate rod both exhibit exceptional impact resistance, high optical clarity, and outstanding dimensional stability, making them ideal for engineering and industrial applications. Polycarbonate's inherent UV resistance and thermal stability allow it to maintain mechanical properties under varying environmental conditions, with tubing offering enhanced flexibility while rods provide superior rigidity. Both forms share excellent chemical resistance and lightweight attributes, but the choice depends on the structural requirements and specific use cases such as fluid handling for tubing or machining components for rods.
Structural Differences: Tubing vs Rod
Polycarbonate tubing features a hollow cylindrical structure that offers enhanced flexibility and reduced weight, making it ideal for applications requiring fluid passage or lightweight framing. In contrast, polycarbonate rods possess a solid cross-section, providing superior strength, rigidity, and impact resistance for structural components and load-bearing uses. The hollow design of tubing allows for easier bending and integration in complex assemblies, whereas rods deliver consistent material density and uniform mechanical properties throughout.
Common Applications for Polycarbonate Tubing
Polycarbonate tubing is widely used in medical, automotive, and industrial applications due to its excellent impact resistance, clarity, and flexibility. It is ideal for fluid transfer systems, protective covers, and structural components where transparency and durability are critical. Unlike polycarbonate rods, tubing allows for easy installation of liquids, gases, and wiring, making it essential in laboratory and manufacturing environments.
Typical Uses of Polycarbonate Rod
Polycarbonate rods are commonly used in applications requiring high strength, durability, and impact resistance, such as structural components, machine parts, and optical devices. They are ideal for machining into custom shapes for prototypes, optical lenses, and electrical insulation. Their versatility allows for use in automotive, aerospace, and industrial settings where precision and toughness are essential.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polycarbonate tubing exhibits enhanced strength due to its hollow structure, which allows for greater impact resistance while maintaining lightweight properties, making it ideal for protective applications. Polycarbonate rods offer superior durability through their solid, uniform composition, providing high rigidity and resistance to bending under heavy loads. Both materials deliver exceptional toughness, but tubing excels in weight-sensitive and impact-prone environments, whereas rods are preferred for structural components requiring maximum strength.
Weight and Flexibility Considerations
Polycarbonate tubing offers a lighter weight compared to polycarbonate rods due to its hollow structure, making it ideal for applications requiring reduced mass without compromising strength. The flexibility of polycarbonate tubing surpasses that of solid rods, allowing for easier bending and shaping in dynamic or curved installations. Choosing between tubing and rod depends on the specific balance needed between weight savings and mechanical flexibility.
Fabrication and Machining Differences
Polycarbonate tubing features a hollow, cylindrical shape ideal for applications requiring lightweight and structural strength, while polycarbonate rods are solid, providing enhanced rigidity and impact resistance. Machining polycarbonate tubing requires careful handling to prevent deformation of the thin walls, often necessitating specialized tools and slower feed rates, whereas rods allow for more straightforward cutting, drilling, and turning due to their uniform cross-section. Fabrication differences also include tubing's suitability for bending and forming into complex shapes versus rods, which are preferred for solid components and precise machining details.
Cost Analysis: Tubing vs Rod
Polycarbonate tubing generally offers cost savings compared to polycarbonate rod due to lower material usage and easier fabrication processes. Tubing's hollow structure reduces raw material expenses while maintaining strength and durability suitable for many industrial applications. Rods, often requiring more extensive machining and solid material, tend to incur higher production and material costs, making tubing a budget-friendly choice for weight-sensitive projects.
Choosing the Right Polycarbonate Shape for Your Project
Polycarbonate tubing offers hollow, cylindrical shapes ideal for applications requiring lightweight strength and fluid or cable protection, while polycarbonate rods provide solid, durable material suited for structural components and machining versatility. Selecting between tubing and rod depends on project needs such as weight considerations, load-bearing capacity, and ease of fabrication. Consider the specific mechanical properties, transparency, and thermal resistance of each polycarbonate form to optimize performance and cost-efficiency.
Polycarbonate Tubing vs Polycarbonate Rod Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com