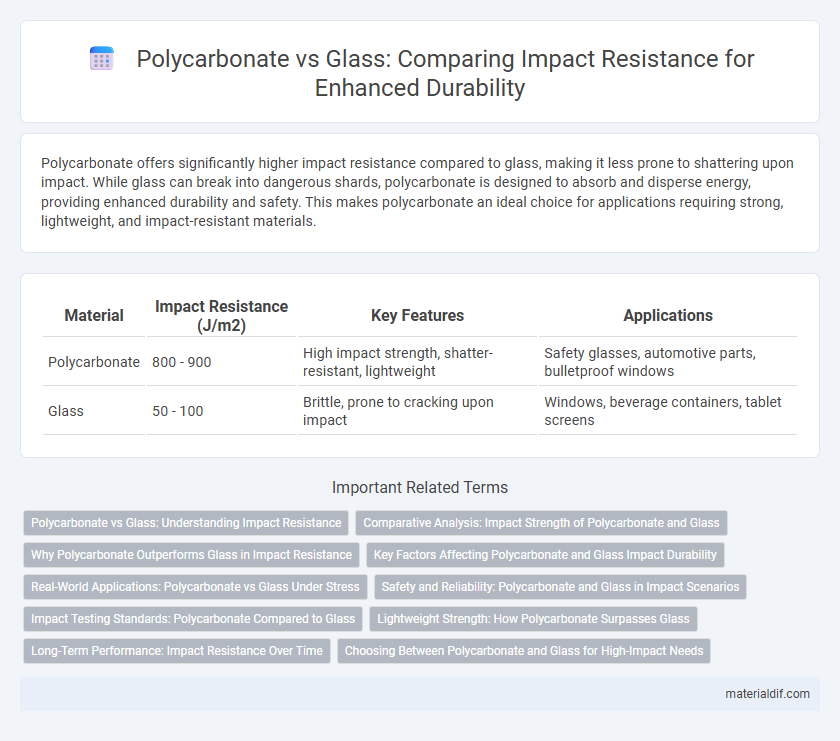
Polycarbonate offers significantly higher impact resistance compared to glass, making it less prone to shattering upon impact. While glass can break into dangerous shards, polycarbonate is designed to absorb and disperse energy, providing enhanced durability and safety. This makes polycarbonate an ideal choice for applications requiring strong, lightweight, and impact-resistant materials.
Table of Comparison
| Material | Impact Resistance (J/m2) | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate | 800 - 900 | High impact strength, shatter-resistant, lightweight | Safety glasses, automotive parts, bulletproof windows |
| Glass | 50 - 100 | Brittle, prone to cracking upon impact | Windows, beverage containers, tablet screens |
Polycarbonate vs Glass: Understanding Impact Resistance
Polycarbonate offers significantly higher impact resistance compared to glass, with the ability to withstand impacts up to 250 times greater without shattering. While glass is brittle and prone to cracking or breaking under stress, polycarbonate's molecular structure allows it to absorb and dissipate energy, making it ideal for safety applications such as eyewear lenses, protective barriers, and automotive components. This exceptional toughness combined with its lightweight nature positions polycarbonate as a superior alternative in impact-resistant design solutions.
Comparative Analysis: Impact Strength of Polycarbonate and Glass
Polycarbonate exhibits impact resistance approximately 250 times greater than that of glass, making it a superior choice for applications requiring high durability and safety. While glass is rigid and prone to shattering upon impact, polycarbonate's molecular structure allows it to absorb and disperse energy, preventing fractures and enhancing longevity. This comparative analysis underscores polycarbonate's advantage in environments where impact strength is critical, such as in automotive, construction, and protective equipment industries.
Why Polycarbonate Outperforms Glass in Impact Resistance
Polycarbonate exhibits superior impact resistance compared to glass due to its molecular structure, which allows for high energy absorption and flexibility without cracking. Unlike glass, which is brittle and prone to shattering upon impact, polycarbonate can withstand significant force and deformation before breaking. This makes polycarbonate the preferred material for applications requiring durability and safety, such as protective eyewear, automotive components, and clear barriers.
Key Factors Affecting Polycarbonate and Glass Impact Durability
Polycarbonate exhibits superior impact resistance compared to glass due to its higher tensile strength and molecular structure, which allows it to absorb and dissipate energy more effectively. Key factors affecting polycarbonate's impact durability include its thickness, temperature resistance, and potential for stress cracking under UV exposure. Glass impact resistance is primarily influenced by its type (tempered or laminated), surface treatments, and brittleness, making it more susceptible to shattering upon high impact.
Real-World Applications: Polycarbonate vs Glass Under Stress
Polycarbonate exhibits significantly higher impact resistance than glass, making it ideal for applications requiring durability, such as safety visors, automotive windows, and protective barriers. Unlike glass, which often shatters upon impact, polycarbonate absorbs and disperses energy without fracturing, enhancing user safety in environments prone to collisions or debris. This superior toughness ensures polycarbonate is preferred in real-world scenarios demanding high performance and reliable impact resistance.
Safety and Reliability: Polycarbonate and Glass in Impact Scenarios
Polycarbonate exhibits significantly higher impact resistance than glass, absorbing energy without shattering, which enhances safety by reducing the risk of injury from sharp fragments. In impact scenarios, polycarbonate maintains structural integrity, providing reliable protection in applications such as automotive windshields, protective eyewear, and safety barriers. Glass, while harder and scratch-resistant, tends to break on impact, compromising reliability and increasing potential hazards in safety-critical environments.
Impact Testing Standards: Polycarbonate Compared to Glass
Polycarbonate demonstrates significantly higher impact resistance compared to glass, as evidenced by standardized impact testing such as ASTM D256 and EN 12600. In tests like the Charpy and Izod impact methods, polycarbonate exhibits superior energy absorption and crack resistance, resulting in less breakage under sudden force. Glass typically fails at lower impact levels due to its brittle nature, whereas polycarbonate resists shattering, making it ideal for safety applications requiring durability under impact.
Lightweight Strength: How Polycarbonate Surpasses Glass
Polycarbonate offers exceptional impact resistance, absorbing shocks with significantly less risk of shattering compared to glass. Weighing nearly half as much as glass, polycarbonate provides superior lightweight strength ideal for protective applications. Its ability to withstand high-impact forces while maintaining structural integrity makes it a preferred choice over traditional glass in safety and durability.
Long-Term Performance: Impact Resistance Over Time
Polycarbonate exhibits superior long-term impact resistance compared to glass, maintaining its structural integrity under repeated stress and harsh environmental conditions. Unlike glass, which is prone to cracking and shattering over time due to brittleness, polycarbonate offers enhanced durability and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring longevity. Over extended periods, polycarbonate's ability to absorb and dissipate impact energy ensures sustained performance and reduced risk of failure.
Choosing Between Polycarbonate and Glass for High-Impact Needs
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance compared to glass, with a resistance to shattering up to 250 times greater, making it ideal for environments requiring high durability and safety. Glass, although scratch-resistant, is more prone to cracking and breaking under impact, limiting its use in high-impact applications such as safety glazing, riot shields, and protective eyewear. Selecting polycarbonate over glass ensures enhanced protection without sacrificing clarity, crucial for applications demanding both transparency and toughness.
Polycarbonate impact resistance vs Glass impact resistance Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com