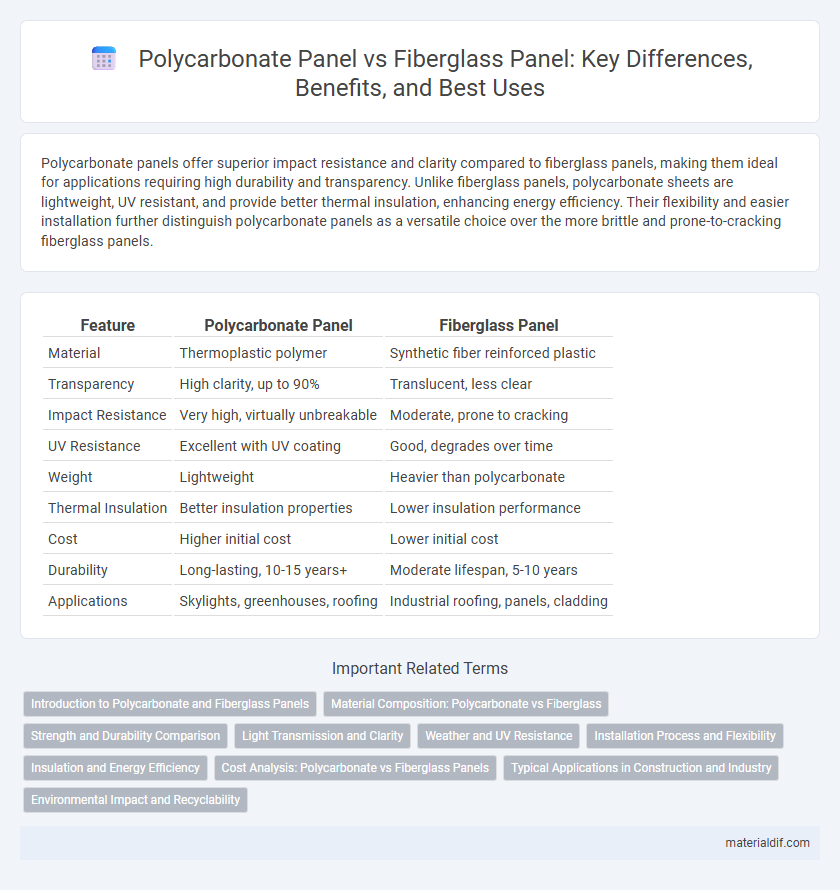
Polycarbonate panels offer superior impact resistance and clarity compared to fiberglass panels, making them ideal for applications requiring high durability and transparency. Unlike fiberglass panels, polycarbonate sheets are lightweight, UV resistant, and provide better thermal insulation, enhancing energy efficiency. Their flexibility and easier installation further distinguish polycarbonate panels as a versatile choice over the more brittle and prone-to-cracking fiberglass panels.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polycarbonate Panel | Fiberglass Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Thermoplastic polymer | Synthetic fiber reinforced plastic |
| Transparency | High clarity, up to 90% | Translucent, less clear |
| Impact Resistance | Very high, virtually unbreakable | Moderate, prone to cracking |
| UV Resistance | Excellent with UV coating | Good, degrades over time |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than polycarbonate |
| Thermal Insulation | Better insulation properties | Lower insulation performance |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Durability | Long-lasting, 10-15 years+ | Moderate lifespan, 5-10 years |
| Applications | Skylights, greenhouses, roofing | Industrial roofing, panels, cladding |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and Fiberglass Panels
Polycarbonate panels are lightweight, highly impact-resistant sheets made from durable thermoplastic polymers, commonly used in construction and industrial applications for their superior strength and transparency. Fiberglass panels consist of reinforced plastic containing woven glass fibers, offering excellent corrosion resistance and thermal insulation properties, often utilized in roofing and outdoor structures. Both materials provide distinct advantages, with polycarbonate panels excelling in impact resistance and clarity, while fiberglass panels deliver enhanced durability against environmental factors.
Material Composition: Polycarbonate vs Fiberglass
Polycarbonate panels are composed of thermoplastic polymers known for their high impact resistance and transparency, making them ideal for applications requiring clarity and durability. Fiberglass panels consist of woven glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, offering superior tensile strength and resistance to heat but less optical clarity compared to polycarbonate. The distinct material compositions influence their performance in environments demanding different balances of strength, weight, and light transmission.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polycarbonate panels exhibit superior impact resistance and high tensile strength, making them more durable under extreme weather conditions compared to fiberglass panels. The molecular structure of polycarbonate allows it to withstand heavy loads and resist cracking or shattering, while fiberglass panels tend to become brittle and degrade over time when exposed to UV radiation. Polycarbonate's enhanced durability and resilience make it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting, robust materials.
Light Transmission and Clarity
Polycarbonate panels offer superior light transmission of approximately 88-92%, providing exceptional clarity compared to fiberglass panels, which typically transmit about 75-85% of light but tend to have a more diffused appearance. The high optical clarity of polycarbonate results from its inherent transparency and smooth surface, making it ideal for applications requiring clear visibility and minimal distortion. Fiberglass panels, while durable, often contain translucent fibers that scatter light, reducing overall clarity and luminous efficiency.
Weather and UV Resistance
Polycarbonate panels exhibit superior weather and UV resistance compared to fiberglass panels, maintaining clarity and structural integrity under prolonged sun exposure. Their UV-resistant coatings prevent yellowing and degradation, ensuring long-term durability in harsh climates. Fiberglass panels tend to suffer from surface chalking and reduced strength when exposed to UV rays over time.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Polycarbonate panels offer a straightforward installation process due to their lightweight nature and ability to be cut easily with standard tools, unlike fiberglass panels which require special handling to avoid cracking. Polycarbonate demonstrates superior flexibility, allowing it to bend without breaking and adapt to various architectural shapes, while fiberglass panels tend to be more rigid and prone to snapping under stress. These characteristics make polycarbonate an ideal choice for projects demanding quick installation and curved applications.
Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Polycarbonate panels offer superior insulation properties compared to fiberglass panels, with higher R-values that reduce heat transfer and enhance energy efficiency in buildings. Their ability to block UV rays while allowing natural light transmission minimizes the need for artificial lighting and temperature control. This combination of thermal insulation and light diffusion makes polycarbonate panels a more effective choice for energy-saving construction.
Cost Analysis: Polycarbonate vs Fiberglass Panels
Polycarbonate panels typically cost more upfront than fiberglass panels but offer greater long-term value due to their superior impact resistance and durability. Fiberglass panels have lower initial expenses but often require more frequent replacement and maintenance, increasing total lifecycle costs. Evaluating cost-effectiveness, polycarbonate panels provide enhanced strength and UV protection, reducing overall operational expenses despite higher initial investments.
Typical Applications in Construction and Industry
Polycarbonate panels are widely utilized in construction for skylights, roofing, and greenhouse glazing due to their high impact resistance and excellent light transmission. Fiberglass panels are commonly chosen for industrial roofing, cladding, and wall panels because of their corrosion resistance and affordability. Both materials serve essential roles in industrial environments, with polycarbonate favored for durability and clarity, while fiberglass excels in chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polycarbonate panels offer superior environmental benefits due to their high durability and longer lifespan compared to fiberglass panels, reducing the frequency of replacements and waste generation. Both materials are recyclable, but polycarbonate recycling processes are more established and efficient, enabling closed-loop reuse and minimizing landfill impact. Fiberglass panels, while lightweight, pose greater challenges in recycling due to composite material composition, often resulting in increased environmental burden.
Polycarbonate Panel vs Fiberglass Panel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com