Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and clarity compared to glass-filled nylon, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and durability. Glass-filled nylon provides higher stiffness and heat resistance, suitable for structural components demanding mechanical strength. Both materials excel in different areas, with polycarbonate favored for optical clarity and toughness, while glass-filled nylon is chosen for enhanced rigidity and thermal stability.
Table of Comparison
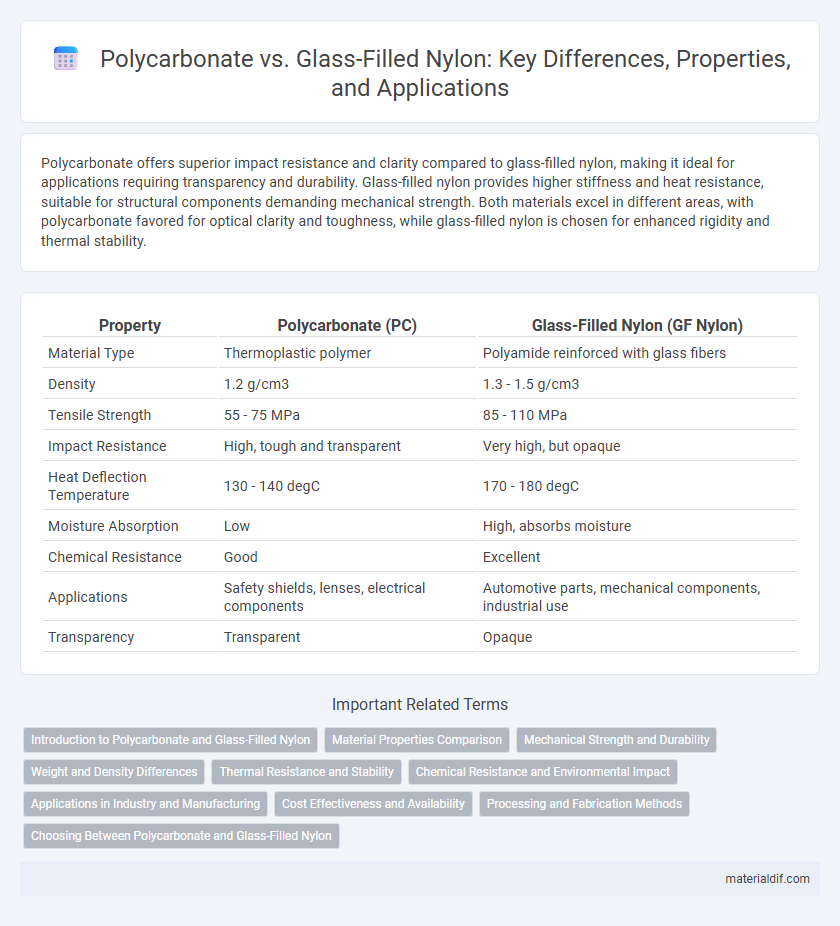
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Glass-Filled Nylon (GF Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Polyamide reinforced with glass fibers |
| Density | 1.2 g/cm3 | 1.3 - 1.5 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 55 - 75 MPa | 85 - 110 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | High, tough and transparent | Very high, but opaque |
| Heat Deflection Temperature | 130 - 140 degC | 170 - 180 degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | High, absorbs moisture |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Applications | Safety shields, lenses, electrical components | Automotive parts, mechanical components, industrial use |
| Transparency | Transparent | Opaque |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and Glass-Filled Nylon
Polycarbonate is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional impact resistance, optical clarity, and heat tolerance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and transparency. Glass-filled nylon, a composite material combining nylon with glass fibers, offers enhanced mechanical strength, stiffness, and thermal stability compared to standard nylon, suitable for structural and mechanical parts. Both materials serve distinct industrial needs, with polycarbonate favored for clear, impact-resistant components and glass-filled nylon chosen for robust, load-bearing applications.
Material Properties Comparison
Polycarbonate exhibits exceptional impact resistance and optical clarity compared to glass-filled nylon, which offers superior stiffness and dimensional stability due to its glass fiber reinforcement. Glass-filled nylon generally has higher thermal resistance and better wear properties, making it suitable for mechanical parts requiring high strength and rigidity. Polycarbonate is favored for applications demanding transparency and toughness, while glass-filled nylon excels in structural components requiring enhanced mechanical and thermal performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polycarbonate exhibits superior mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to glass-filled nylon, making it ideal for applications requiring high toughness and resilience. Glass-filled nylon offers increased stiffness and heat resistance but is more brittle under high-impact conditions. Polycarbonate's durability against cracking and deformation ensures longer-lasting performance in demanding environments.
Weight and Density Differences
Polycarbonate has a density of approximately 1.2 g/cm3, significantly lower than glass-filled nylon, which ranges from 1.3 to 1.5 g/cm3 depending on the glass content. This difference results in polycarbonate being lighter, making it ideal for applications requiring reduced weight without sacrificing strength. Weight-sensitive industries, such as automotive and aerospace, often prefer polycarbonate for its favorable strength-to-weight ratio compared to heavier glass-filled nylon composites.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Polycarbonate offers superior thermal resistance with a continuous use temperature around 115degC, compared to glass-filled nylon's typical range of 85-105degC, making it more suitable for high-heat applications. In terms of thermal stability, polycarbonate maintains dimensional integrity and mechanical properties better under prolonged heat exposure, whereas glass-filled nylon may experience increased brittleness and deformation. These characteristics make polycarbonate a preferred choice in environments requiring consistent performance at elevated temperatures.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Impact
Polycarbonate exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to glass-filled nylon, particularly against acids, alkalis, and hydrocarbons, making it more suitable for harsh chemical environments. Glass-filled nylon, while mechanically robust, tends to absorb moisture, which can degrade its chemical resistance over time and affect dimensional stability. Environmentally, polycarbonate offers better recyclability and typically has a lower environmental footprint due to its longer lifespan and efficient production processes.
Applications in Industry and Manufacturing
Polycarbonate offers exceptional impact resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for automotive headlamp lenses and protective screens in manufacturing environments. Glass-filled nylon provides superior mechanical strength and thermal stability, preferred for heavy-duty gears and structural components in industrial machinery. Industries often choose polycarbonate for transparent, lightweight applications while selecting glass-filled nylon for high-stress, load-bearing parts requiring enhanced durability.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Polycarbonate offers greater cost-effectiveness than glass-filled nylon due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making it ideal for budget-sensitive applications. Its widespread availability and ease of processing contribute to reduced lead times and improved supply chain efficiency compared to glass-filled nylon. Although glass-filled nylon provides superior mechanical strength, polycarbonate's balance of affordability and accessibility makes it a preferred choice for many industries.
Processing and Fabrication Methods
Polycarbonate is typically processed using injection molding, extrusion, and thermoforming techniques, which allow for high precision and complex geometries with excellent dimensional stability. Glass-filled nylon requires similar molding processes but often demands higher mold temperatures and slower cooling rates to prevent warping and ensure optimal fiber orientation for strength. Compared to glass-filled nylon, polycarbonate offers faster cycle times and easier post-processing options such as machining and drilling due to its superior toughness and ductility.
Choosing Between Polycarbonate and Glass-Filled Nylon
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and toughness. Glass-filled nylon provides enhanced mechanical strength, heat resistance, and dimensional stability suitable for structural components under high stress. Selection between polycarbonate and glass-filled nylon depends on balancing the need for visibility, toughness, and thermal endurance against rigidity and load-bearing capacity.
Polycarbonate vs Glass-filled Nylon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com