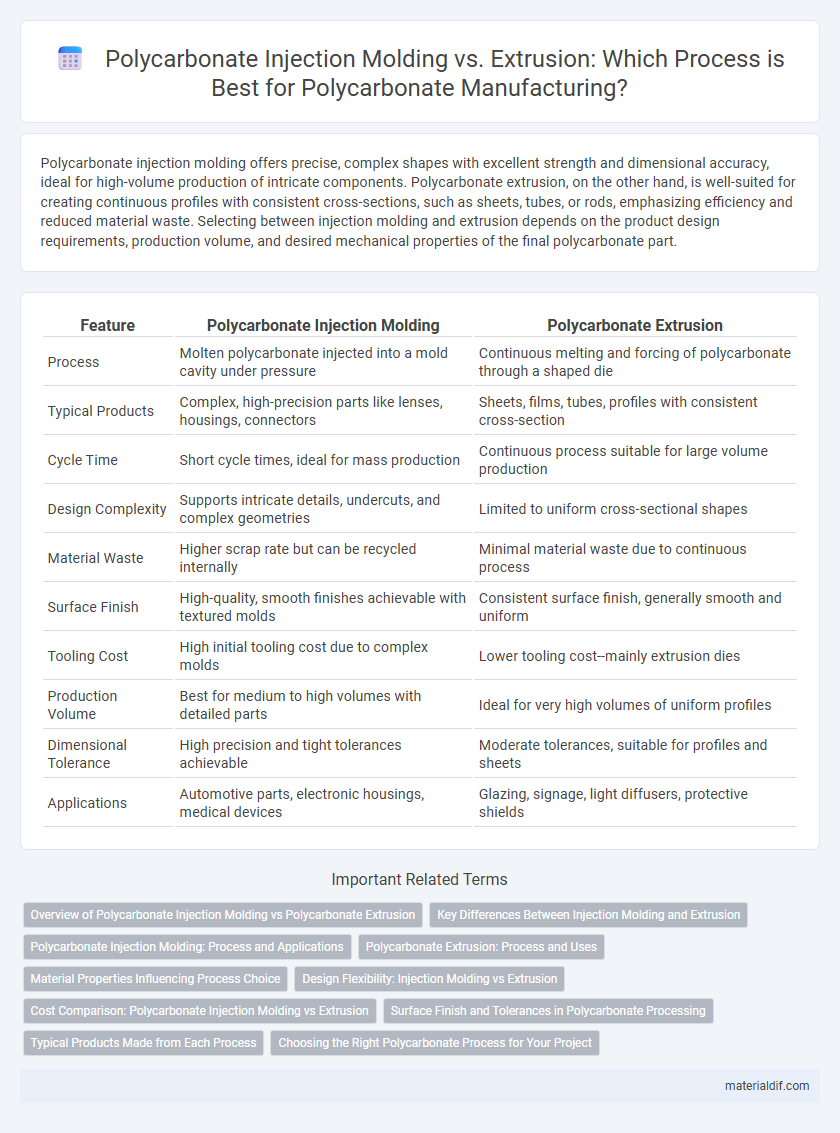
Polycarbonate injection molding offers precise, complex shapes with excellent strength and dimensional accuracy, ideal for high-volume production of intricate components. Polycarbonate extrusion, on the other hand, is well-suited for creating continuous profiles with consistent cross-sections, such as sheets, tubes, or rods, emphasizing efficiency and reduced material waste. Selecting between injection molding and extrusion depends on the product design requirements, production volume, and desired mechanical properties of the final polycarbonate part.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polycarbonate Injection Molding | Polycarbonate Extrusion |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Molten polycarbonate injected into a mold cavity under pressure | Continuous melting and forcing of polycarbonate through a shaped die |
| Typical Products | Complex, high-precision parts like lenses, housings, connectors | Sheets, films, tubes, profiles with consistent cross-section |
| Cycle Time | Short cycle times, ideal for mass production | Continuous process suitable for large volume production |
| Design Complexity | Supports intricate details, undercuts, and complex geometries | Limited to uniform cross-sectional shapes |
| Material Waste | Higher scrap rate but can be recycled internally | Minimal material waste due to continuous process |
| Surface Finish | High-quality, smooth finishes achievable with textured molds | Consistent surface finish, generally smooth and uniform |
| Tooling Cost | High initial tooling cost due to complex molds | Lower tooling cost--mainly extrusion dies |
| Production Volume | Best for medium to high volumes with detailed parts | Ideal for very high volumes of uniform profiles |
| Dimensional Tolerance | High precision and tight tolerances achievable | Moderate tolerances, suitable for profiles and sheets |
| Applications | Automotive parts, electronic housings, medical devices | Glazing, signage, light diffusers, protective shields |
Overview of Polycarbonate Injection Molding vs Polycarbonate Extrusion
Polycarbonate injection molding offers high precision and complex geometries by injecting molten polycarbonate into molds, enabling mass production of detailed parts. Polycarbonate extrusion, in contrast, involves forcing molten polycarbonate through a die to create continuous profiles like sheets or tubes, suitable for uniform cross-sectional shapes. Each method delivers distinct advantages in applications requiring either intricate design or consistent, large-scale shaping of polycarbonate materials.
Key Differences Between Injection Molding and Extrusion
Polycarbonate injection molding involves melting the polymer and injecting it into a mold to create detailed, complex shapes with high precision, ideal for manufacturing small to medium-sized parts such as lenses and housings. Polycarbonate extrusion, on the other hand, pushes melted polymer through a die to produce continuous profiles like sheets, tubes, or rods, making it suitable for large-scale, uniform cross-sectional products. The key differences lie in the process flow, product complexity, and applications: injection molding excels in detailed, high-strength components, while extrusion is preferred for long, consistent shapes with simpler geometries.
Polycarbonate Injection Molding: Process and Applications
Polycarbonate injection molding involves melting polycarbonate pellets and injecting the molten material into a precision-engineered mold cavity under high pressure, enabling the production of complex, high-strength, and dimensionally accurate parts. This process excels in manufacturing intricate components such as automotive parts, medical devices, and electronic housings where durability and thermal resistance are critical. Compared to extrusion, injection molding offers superior design flexibility, faster production cycles, and enhanced surface finish quality for polycarbonate parts.
Polycarbonate Extrusion: Process and Uses
Polycarbonate extrusion involves melting polycarbonate pellets and forcing the molten material through a shaped die to create continuous profiles such as sheets, tubes, or films with uniform cross-sections. This process is ideal for producing lightweight, impact-resistant components used in automotive parts, architectural glazing, and electronic housings due to its excellent optical clarity and thermal stability. Extruded polycarbonate products offer enhanced design flexibility and cost-efficiency for large-scale manufacturing compared to injection molding.
Material Properties Influencing Process Choice
Polycarbonate's high impact resistance and heat distortion temperature make it ideal for injection molding, enabling the production of complex, detailed parts with excellent mechanical strength. In contrast, extrusion is favored for creating continuous profiles due to polycarbonate's good flow properties and thermal stability, allowing for consistent uniformity in sheets or tubes. The choice between injection molding and extrusion largely depends on the required part geometry, with injection molding better suited for intricate designs and extrusion for simpler, continuous shapes.
Design Flexibility: Injection Molding vs Extrusion
Polycarbonate injection molding offers superior design flexibility with the ability to create complex geometries, intricate details, and undercuts that are difficult to achieve with extrusion. Injection molding enables precise control over wall thickness and allows for incorporation of features such as ribs, bosses, and threaded holes within a single part. In contrast, polycarbonate extrusion is limited to continuous, simpler cross-sectional shapes and is best suited for producing uniform profiles and lengths rather than intricate or highly detailed designs.
Cost Comparison: Polycarbonate Injection Molding vs Extrusion
Polycarbonate injection molding typically incurs higher initial tooling costs due to mold design and manufacturing, but offers lower per-unit costs for large production runs. Extrusion of polycarbonate is generally more cost-effective for continuous profiles and lower volume production, with minimal setup expenses and consistent material utilization. Evaluating total project scale and complexity is crucial for determining whether injection molding or extrusion provides the most economical solution.
Surface Finish and Tolerances in Polycarbonate Processing
Polycarbonate injection molding offers superior surface finish quality with smooth, glossy, and detailed textures ideal for aesthetic applications, while extrusion typically produces a more uniform but matte surface suitable for structural uses. Injection molding allows for tighter dimensional tolerances, often within +-0.005 inches, ensuring precision components, whereas extrusion generally has wider tolerance ranges, around +-0.010 inches, due to its continuous production nature. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the appropriate process to meet specific design and performance requirements in polycarbonate manufacturing.
Typical Products Made from Each Process
Polycarbonate injection molding is commonly used to produce complex, high-precision items such as electronic housings, automotive components, and optical lenses. In contrast, polycarbonate extrusion typically creates continuous profiles like sheets, films, and tubes for applications in glazing, signage, and protective barriers. Each process optimizes polycarbonate's impact resistance and transparency for different industrial needs.
Choosing the Right Polycarbonate Process for Your Project
Polycarbonate injection molding offers precise, complex shapes with high strength and optical clarity, ideal for detailed components and large production runs. In contrast, polycarbonate extrusion is suited for creating continuous profiles like sheets and tubes, providing flexibility for custom thickness and length. Selecting the right process depends on your project's design complexity, production volume, and functional requirements to ensure optimal material performance and cost-efficiency.
Polycarbonate Injection Molding vs Polycarbonate Extrusion Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com