Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and transparency compared to SAN, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and clarity. SAN provides better chemical resistance and stiffness, suitable for products exposed to solvents and higher temperatures. Choosing between polycarbonate and SAN depends on the specific requirements for strength, clarity, and chemical exposure in your project.
Table of Comparison
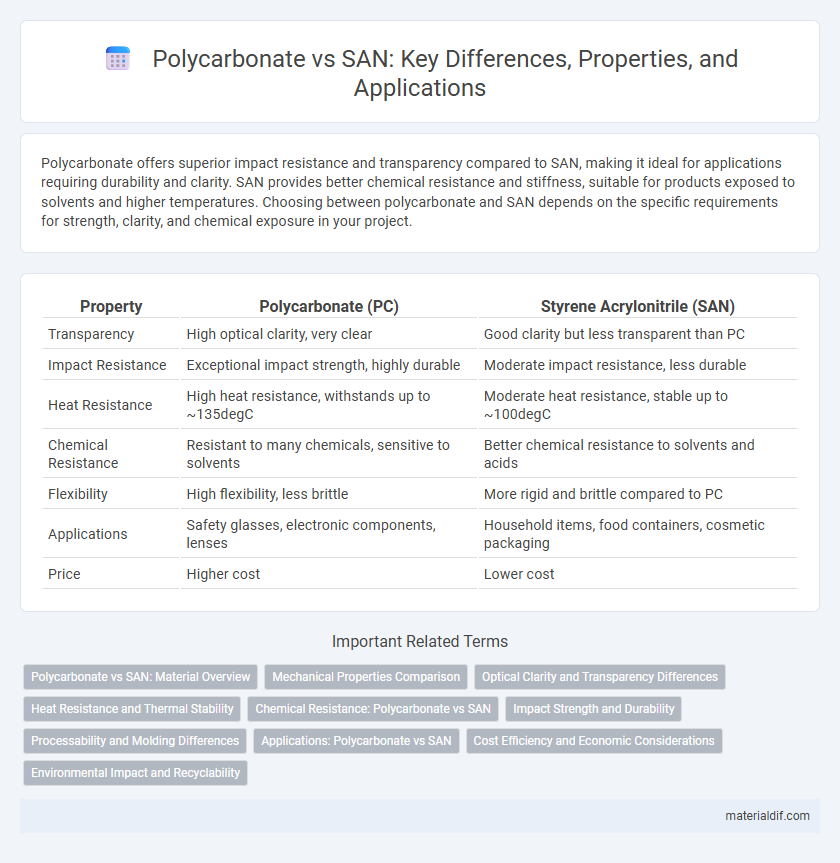
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Styrene Acrylonitrile (SAN) |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | High optical clarity, very clear | Good clarity but less transparent than PC |
| Impact Resistance | Exceptional impact strength, highly durable | Moderate impact resistance, less durable |
| Heat Resistance | High heat resistance, withstands up to ~135degC | Moderate heat resistance, stable up to ~100degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to many chemicals, sensitive to solvents | Better chemical resistance to solvents and acids |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, less brittle | More rigid and brittle compared to PC |
| Applications | Safety glasses, electronic components, lenses | Household items, food containers, cosmetic packaging |
| Price | Higher cost | Lower cost |
Polycarbonate vs SAN: Material Overview
Polycarbonate is a durable, high-impact thermoplastic known for its transparency, heat resistance, and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for applications requiring toughness and optical clarity. SAN (Styrene Acrylonitrile) is a rigid, transparent polymer with good chemical resistance and surface hardness but lower impact strength and heat resistance compared to polycarbonate. Polycarbonate outperforms SAN in impact resistance and temperature tolerance, while SAN offers better chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness for less demanding environments.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polycarbonate exhibits superior impact resistance and higher tensile strength compared to SAN (Styrene Acrylonitrile), making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced durability. While SAN offers better rigidity and dimensional stability, polycarbonate's exceptional toughness allows it to withstand greater mechanical stress and strain without fracturing. The difference in flexural modulus also highlights polycarbonate's flexibility versus SAN's stiffness, influencing material selection based on mechanical performance requirements.
Optical Clarity and Transparency Differences
Polycarbonate exhibits superior optical clarity and transparency compared to Styrene Acrylonitrile (SAN), making it the preferred choice for applications requiring high light transmission and minimal distortion. Polycarbonate typically provides light transmission rates of around 88-90%, whereas SAN usually transmits about 80-85%, resulting in less visually clear materials. The inherent molecular structure of polycarbonate also offers better impact resistance while maintaining clear visibility, which is crucial for lenses, eyewear, and protective covers.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Polycarbonate demonstrates superior heat resistance compared to SAN (Styrene Acrylonitrile), with a higher glass transition temperature around 147degC, enabling it to maintain structural integrity under elevated temperatures. SAN exhibits lower thermal stability, typically softening near 100degC, making it less suitable for high-temperature applications. The enhanced thermal properties of polycarbonate allow for greater durability in heat-intensive environments, such as automotive parts and electronic housings.
Chemical Resistance: Polycarbonate vs SAN
Polycarbonate exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to SAN (Styrene Acrylonitrile), particularly against alkalis, oils, and alcohols, ensuring durability in harsh environments. SAN tends to be more vulnerable to stress cracking and degradation when exposed to solvents and certain chemicals. This chemical resilience makes polycarbonate a preferred choice for applications requiring long-term resistance to chemical exposure.
Impact Strength and Durability
Polycarbonate offers superior impact strength compared to SAN (Styrene Acrylonitrile), making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and resistance to sudden impacts. While SAN provides good stiffness and chemical resistance, it lacks the toughness and shatter-resistant properties inherent to polycarbonate. This enhanced impact strength and durability position polycarbonate as a preferred choice for protective gear, safety equipment, and automotive components.
Processability and Molding Differences
Polycarbonate offers superior processability compared to SAN (Styrene-Acrylonitrile) due to its higher thermal stability and impact resistance, enabling molders to use a wider temperature range and achieve better flow during injection molding. Polycarbonate's inherent toughness requires specialized mold design to avoid stress cracking, while SAN typically molds faster with lower shrinkage but has reduced impact resistance. The choice between polycarbonate and SAN hinges on the balance between mold cycle time, mechanical properties, and dimensional stability tailored to specific application requirements.
Applications: Polycarbonate vs SAN
Polycarbonate excels in applications requiring high impact resistance and optical clarity, such as in automotive parts, eyewear lenses, and electronic housings. SAN (Styrene-Acrylonitrile) offers better chemical resistance and dimensional stability, making it suitable for appliance components, food containers, and medical device parts. Choosing between polycarbonate and SAN depends on the specific performance requirements like toughness, transparency, and resistance to heat or chemicals for the target application.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Polycarbonate offers higher impact resistance and greater durability compared to SAN (Styrene Acrylonitrile), often justifying its higher initial cost in applications requiring longevity and strength. SAN is generally more affordable, making it a budget-friendly choice for less demanding uses where economic constraints are a priority. Evaluating total lifecycle cost, including maintenance and replacement, reveals polycarbonate's cost efficiency in high-performance or safety-critical environments.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polycarbonate (PC) exhibits a lower environmental impact compared to Styrene-Acrylonitrile (SAN) due to its superior durability and longer lifecycle, which reduces the frequency of replacement and waste generation. PC is more widely accepted in recycling streams, particularly in the production of durable goods, while SAN recycling is limited by its chemical composition and lower demand in recycling markets. Enhanced recyclability of PC contributes to reduced landfill accumulation and promotes circular economy practices within the plastics industry.
Polycarbonate vs SAN Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com