Polycarbonate PET offers exceptional impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and high strength. Its UV resistance protects the material from degradation and discoloration when exposed to sunlight over extended periods. Balancing impact and UV resistance ensures long-lasting performance in both indoor and outdoor environments.
Table of Comparison
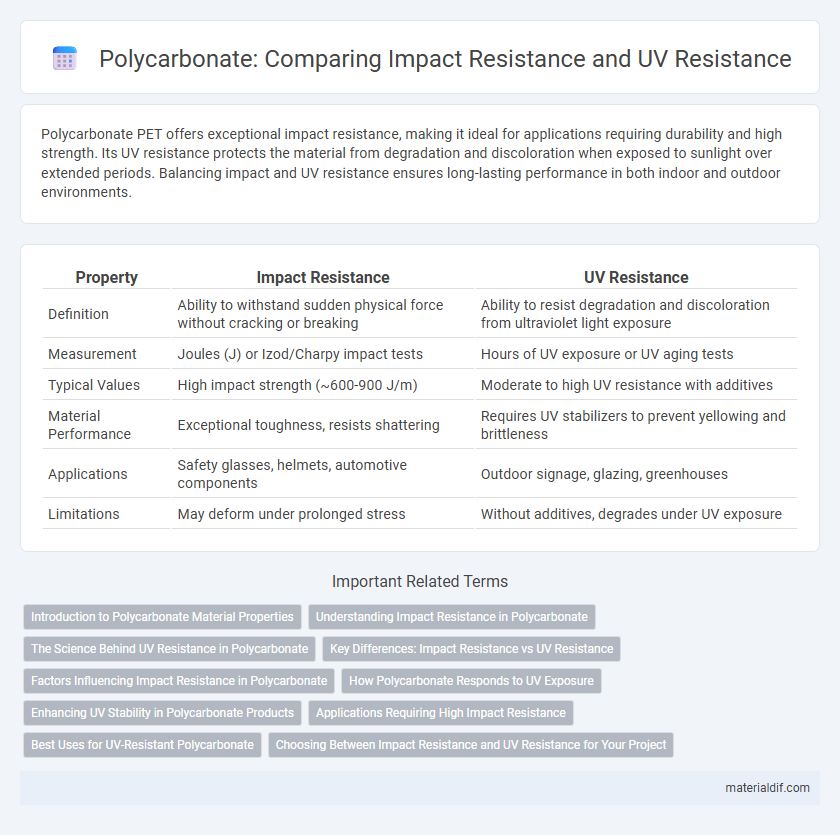
| Property | Impact Resistance | UV Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to withstand sudden physical force without cracking or breaking | Ability to resist degradation and discoloration from ultraviolet light exposure |
| Measurement | Joules (J) or Izod/Charpy impact tests | Hours of UV exposure or UV aging tests |
| Typical Values | High impact strength (~600-900 J/m) | Moderate to high UV resistance with additives |
| Material Performance | Exceptional toughness, resists shattering | Requires UV stabilizers to prevent yellowing and brittleness |
| Applications | Safety glasses, helmets, automotive components | Outdoor signage, glazing, greenhouses |
| Limitations | May deform under prolonged stress | Without additives, degrades under UV exposure |
Introduction to Polycarbonate Material Properties
Polycarbonate exhibits exceptional impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and high-performance protection, such as safety eyewear and automotive components. Its molecular structure provides strong resistance to sudden shocks while maintaining clarity and lightweight characteristics. Although polycarbonate offers moderate UV resistance, applying specialized coatings enhances its ability to withstand prolonged sunlight exposure without yellowing or degrading.
Understanding Impact Resistance in Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate offers exceptional impact resistance, making it highly durable and capable of withstanding significant force without cracking or breaking. This material absorbs and distributes energy effectively, which is critical in applications such as safety helmets, automotive components, and protective eyewear. While polycarbonate inherently provides strong impact resistance, its UV resistance requires enhancement through coatings or additives to prevent degradation and maintain performance over time.
The Science Behind UV Resistance in Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate exhibits exceptional impact resistance due to its molecular structure, which allows it to absorb and dissipate energy without fracturing. UV resistance in polycarbonate is achieved through the incorporation of UV stabilizers and absorbers that prevent the polymer chains from degrading when exposed to ultraviolet radiation. These additives form a protective barrier, reducing photo-oxidative damage and maintaining the material's clarity and mechanical strength over prolonged outdoor exposure.
Key Differences: Impact Resistance vs UV Resistance
Impact resistance in polycarbonate refers to its ability to withstand sudden physical forces or shocks without cracking or breaking, making it ideal for protective gear and safety glazing applications. UV resistance involves the material's capacity to endure prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation without degrading, which is essential for outdoor uses like roofing panels and greenhouses. Key differences lie in impact resistance focusing on mechanical durability, while UV resistance emphasizes chemical stability and longevity under sunlight.
Factors Influencing Impact Resistance in Polycarbonate
Impact resistance in polycarbonate is primarily influenced by its molecular structure, thickness, and the presence of additives such as impact modifiers. Environmental factors like temperature variations and UV exposure can degrade the polymer chains, reducing its toughness over time. Proper stabilization with UV absorbers and coatings enhances both impact resistance and UV resistance, extending the material's durability in outdoor applications.
How Polycarbonate Responds to UV Exposure
Polycarbonate exhibits exceptional impact resistance, maintaining structural integrity under significant stress, but prolonged UV exposure can degrade its surface and reduce durability. Its molecular structure is susceptible to photo-oxidation, causing yellowing and embrittlement over time without proper UV stabilizers. Integrating UV inhibitors enhances polycarbonate's resistance, preserving clarity and mechanical performance in outdoor applications.
Enhancing UV Stability in Polycarbonate Products
Polycarbonate exhibits exceptional impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and toughness. Enhancing UV stability in polycarbonate products involves incorporating UV absorbers and stabilizers, which prevent polymer degradation and discoloration caused by prolonged sun exposure. Advanced coatings and additives significantly improve the material's lifespan while maintaining its mechanical integrity under intense ultraviolet radiation.
Applications Requiring High Impact Resistance
Polycarbonate exhibits exceptional impact resistance, making it ideal for applications such as protective eyewear, automotive components, and riot shields where durability against sudden force is critical. While its UV resistance can degrade over time without additives, specialized coatings and UV stabilizers enhance longevity for outdoor use. High-impact applications prioritize untreated or coated polycarbonate to ensure maximum toughness and safety performance.
Best Uses for UV-Resistant Polycarbonate
UV-resistant polycarbonate excels in outdoor applications where prolonged exposure to sunlight occurs, such as skylights, greenhouses, and automotive headlamp lenses. This variant features a special UV-blocking coating that prevents yellowing and maintains clarity while preserving the material's inherent impact resistance. Its ability to withstand harsh UV radiation without degrading makes it ideal for durable, weather-resistant installations requiring long-term transparency and strength.
Choosing Between Impact Resistance and UV Resistance for Your Project
Selecting polycarbonate for your project depends on prioritizing impact resistance or UV resistance based on environmental needs and application stress factors. Impact resistance ensures durability against physical forces and is ideal for high-impact areas like safety shields, while UV resistance protects against sun damage, maintaining clarity and preventing material degradation in outdoor installations. Evaluating exposure conditions and performance requirements guides the optimal balance between toughness and weatherability for long-lasting results.
Impact Resistance vs UV Resistance Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com