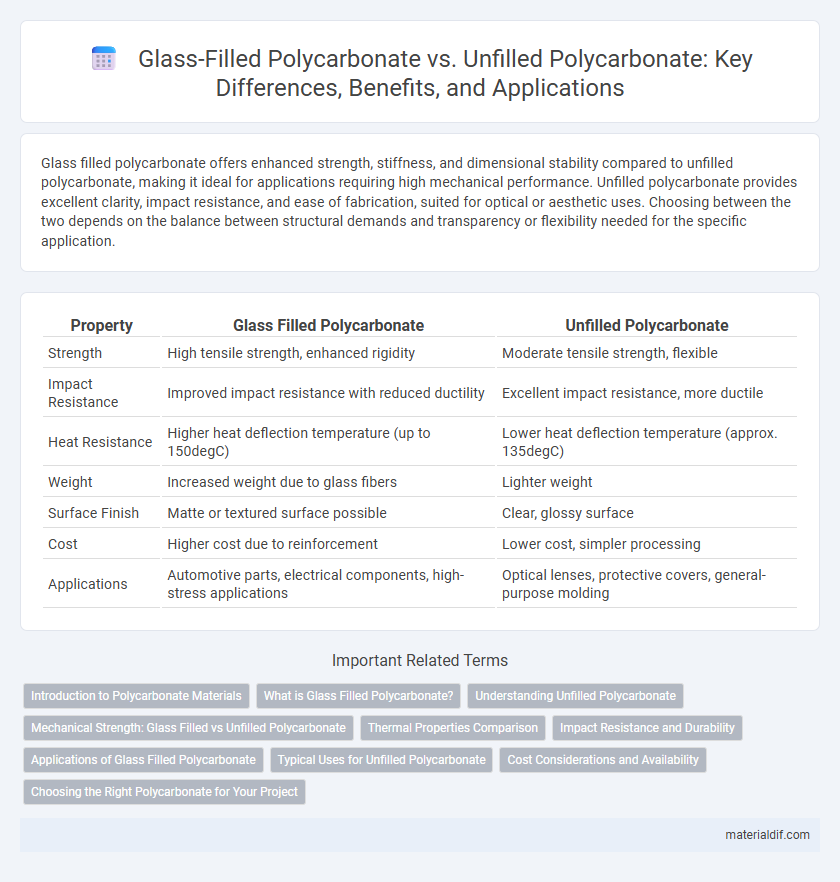
Glass filled polycarbonate offers enhanced strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability compared to unfilled polycarbonate, making it ideal for applications requiring high mechanical performance. Unfilled polycarbonate provides excellent clarity, impact resistance, and ease of fabrication, suited for optical or aesthetic uses. Choosing between the two depends on the balance between structural demands and transparency or flexibility needed for the specific application.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Filled Polycarbonate | Unfilled Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | High tensile strength, enhanced rigidity | Moderate tensile strength, flexible |
| Impact Resistance | Improved impact resistance with reduced ductility | Excellent impact resistance, more ductile |
| Heat Resistance | Higher heat deflection temperature (up to 150degC) | Lower heat deflection temperature (approx. 135degC) |
| Weight | Increased weight due to glass fibers | Lighter weight |
| Surface Finish | Matte or textured surface possible | Clear, glossy surface |
| Cost | Higher cost due to reinforcement | Lower cost, simpler processing |
| Applications | Automotive parts, electrical components, high-stress applications | Optical lenses, protective covers, general-purpose molding |
Introduction to Polycarbonate Materials
Glass filled polycarbonate features reinforced glass fibers that significantly enhance strength, rigidity, and thermal resistance compared to unfilled polycarbonate, which offers superior clarity and impact resistance but lower structural durability. Unfilled polycarbonate remains ideal for applications requiring transparency and lightweight properties, while glass filled variants are preferred in engineering components demanding higher mechanical performance. Understanding these material distinctions supports informed selection in industries such as automotive, electronics, and construction, where specific mechanical and thermal criteria guide polycarbonate use.
What is Glass Filled Polycarbonate?
Glass filled polycarbonate is a composite material that incorporates glass fibers into the polycarbonate matrix, significantly enhancing its mechanical strength, stiffness, and thermal stability compared to unfilled polycarbonate. This reinforcement improves impact resistance and dimensional stability, making glass filled polycarbonate ideal for demanding applications in automotive, electrical, and industrial components. The glass fibers also reduce the material's thermal expansion and improve its resistance to creep under load, contributing to longer-lasting performance in harsh environments.
Understanding Unfilled Polycarbonate
Unfilled polycarbonate offers excellent clarity, impact resistance, and good dimensional stability, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and toughness. Unlike glass-filled polycarbonate, unfilled polycarbonate maintains higher flexibility and better electrical insulation properties due to the absence of reinforcing fibers. This makes unfilled polycarbonate a preferred choice for optical components, electronics housings, and protective gear where lightweight and clear materials are essential.
Mechanical Strength: Glass Filled vs Unfilled Polycarbonate
Glass filled polycarbonate exhibits significantly enhanced mechanical strength compared to unfilled polycarbonate due to the incorporation of glass fibers that improve rigidity and impact resistance. This reinforcement results in higher tensile strength, better dimensional stability, and superior resistance to deformation under stress. Unfilled polycarbonate, while more flexible and easier to process, generally lacks the stiffness and strength required for high-load applications.
Thermal Properties Comparison
Glass filled polycarbonate exhibits significantly enhanced thermal properties compared to unfilled polycarbonate, with a higher heat deflection temperature typically around 140-160degC versus 120-130degC for unfilled grades. The incorporation of glass fibers increases thermal conductivity, reducing thermal expansion and improving dimensional stability under heat stress. This makes glass filled polycarbonate ideal for applications requiring superior heat resistance and mechanical strength in elevated temperature environments.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Glass filled polycarbonate exhibits significantly enhanced impact resistance and durability compared to unfilled polycarbonate due to the incorporation of glass fibers that reinforce the polymer matrix. This reinforcement increases tensile strength, reduces deformation under stress, and improves resistance to wear and environmental factors, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Unfilled polycarbonate, while offering good clarity and impact resistance, lacks the mechanical robustness and longevity of its glass filled counterpart in demanding conditions.
Applications of Glass Filled Polycarbonate
Glass filled polycarbonate offers enhanced mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and improved resistance to high temperatures compared to unfilled polycarbonate, making it ideal for demanding engineering applications. It is widely used in automotive components, electrical housings, and industrial machinery parts where durability and heat resistance are critical. The increased stiffness and reduced warpage also make glass filled polycarbonate suitable for structural applications in aerospace and consumer electronics.
Typical Uses for Unfilled Polycarbonate
Unfilled polycarbonate is commonly used in applications requiring high impact resistance and optical clarity, such as eyewear lenses, protective visors, and medical devices. Its lightweight and transparent properties make it ideal for consumer electronics, including smartphone screens and housings. The material's excellent dimensional stability also supports use in automotive components and electrical connectors where precision and durability are essential.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Glass filled polycarbonate typically costs 20-40% more than unfilled polycarbonate due to the added reinforcing glass fibers that improve strength and heat resistance. Availability of glass filled polycarbonate may be more limited, with fewer suppliers and longer lead times, whereas unfilled polycarbonate is widely stocked and readily accessible. Cost efficiency and supply reliability often drive the choice depending on required mechanical properties and project budget constraints.
Choosing the Right Polycarbonate for Your Project
Glass filled polycarbonate offers enhanced mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and improved resistance to wear and heat, making it ideal for high-performance applications requiring durability and rigidity. Unfilled polycarbonate provides greater transparency, impact resistance, and ease of fabrication, suited for projects prioritizing optical clarity and lightweight properties. Selecting the right polycarbonate depends on balancing the need for strength versus clarity, where glass filled variants excel in structural roles, and unfilled types are preferred for aesthetic or less demanding mechanical applications.
Glass Filled Polycarbonate vs Unfilled Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com