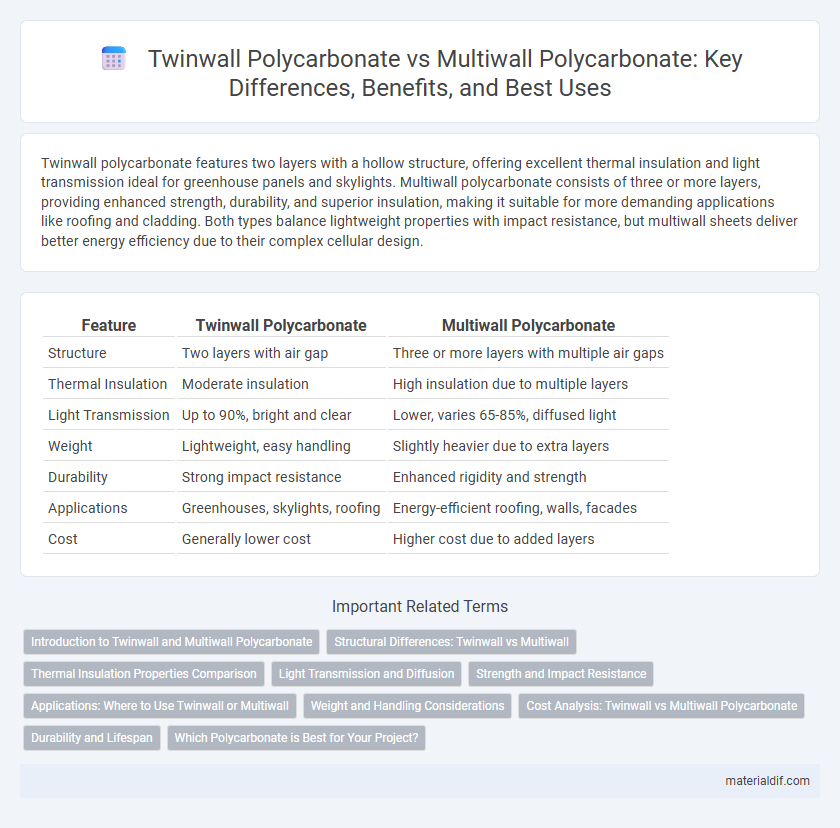
Twinwall polycarbonate features two layers with a hollow structure, offering excellent thermal insulation and light transmission ideal for greenhouse panels and skylights. Multiwall polycarbonate consists of three or more layers, providing enhanced strength, durability, and superior insulation, making it suitable for more demanding applications like roofing and cladding. Both types balance lightweight properties with impact resistance, but multiwall sheets deliver better energy efficiency due to their complex cellular design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Twinwall Polycarbonate | Multiwall Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Two layers with air gap | Three or more layers with multiple air gaps |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation | High insulation due to multiple layers |
| Light Transmission | Up to 90%, bright and clear | Lower, varies 65-85%, diffused light |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy handling | Slightly heavier due to extra layers |
| Durability | Strong impact resistance | Enhanced rigidity and strength |
| Applications | Greenhouses, skylights, roofing | Energy-efficient roofing, walls, facades |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to added layers |
Introduction to Twinwall and Multiwall Polycarbonate
Twinwall polycarbonate features two parallel sheets connected by vertical ribs, creating a lightweight yet durable panel with excellent thermal insulation and impact resistance. Multiwall polycarbonate consists of three or more layers interconnected by webbed ribs, offering enhanced strength, superior thermal insulation, and increased rigidity ideal for roofing and glazing applications. Both types provide UV protection and high light transmission, but multiwall panels deliver improved energy efficiency for construction and greenhouse projects.
Structural Differences: Twinwall vs Multiwall
Twinwall polycarbonate features two layers separated by vertical ribs, offering moderate insulation and impact resistance suitable for lightweight structures. Multiwall polycarbonate consists of three or more layers with interconnected walls, enhancing thermal insulation, rigidity, and structural strength for demanding architectural applications. The increased layers in multiwall sheets create more insulating air pockets, resulting in superior energy efficiency compared to twinwall panels.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Twinwall polycarbonate features two layers separated by a single air gap, providing moderate thermal insulation with a typical U-value around 2.8 W/m2K, making it suitable for applications requiring basic energy efficiency. Multiwall polycarbonate consists of multiple layers with several air chambers, significantly enhancing thermal insulation, often achieving U-values as low as 1.4 W/m2K, which reduces heat transfer and improves energy savings. The increased number of layers in multiwall panels traps more air, a poor heat conductor, thereby offering superior thermal performance compared to twinwall structures.
Light Transmission and Diffusion
Twinwall polycarbonate panels typically offer higher light transmission rates of around 70-80%, allowing more natural light to pass through while providing moderate diffusion to reduce glare. Multiwall polycarbonate sheets usually have lower light transmission, around 50-60%, but excel in diffusing light evenly across surfaces due to their multiple layers and air gaps. Choosing between twinwall and multiwall polycarbonate depends on balancing the need for maximum light intake with enhanced light diffusion for privacy or glare reduction.
Strength and Impact Resistance
Twinwall polycarbonate features a dual-layer structure that offers moderate strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for lightweight applications with some durability requirements. Multiwall polycarbonate, with its multiple layers and internal ribs, provides enhanced structural strength and superior impact resistance, ideal for demanding environments and heavy-duty usage. Both types deliver excellent UV protection and thermal insulation, but multiwall polycarbonate better withstands high-impact forces and heavy loads due to its thicker, reinforced design.
Applications: Where to Use Twinwall or Multiwall
Twinwall polycarbonate is ideal for applications requiring lightweight, impact-resistant panels such as greenhouse glazing, roofing, and skylights due to its excellent thermal insulation and translucency. Multiwall polycarbonate is preferable for projects needing higher insulation performance and structural strength, making it suitable for industrial partitions, cold storage, and solar panel covers. Both types offer UV protection and weather resistance, but choosing between twinwall and multiwall depends on specific insulation and load-bearing requirements.
Weight and Handling Considerations
Twinwall polycarbonate sheets are lighter than multiwall polycarbonate, making them easier to handle and install for applications requiring frequent adjustments or portability. The reduced weight of twinwall panels also lowers transportation costs and minimizes structural support requirements compared to the heavier, thicker multiwall options. Multiwall polycarbonate offers enhanced insulation but demands more effort and sturdiness during handling due to its increased mass and rigidity.
Cost Analysis: Twinwall vs Multiwall Polycarbonate
Twinwall polycarbonate typically offers a lower initial cost compared to multiwall polycarbonate, making it an economical choice for budget-sensitive projects. Multiwall polycarbonate, with its additional layers, provides enhanced thermal insulation and structural strength, justifying the higher price in applications requiring energy efficiency and durability. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, consider lifecycle expenses such as maintenance, energy savings, and longevity alongside the upfront material costs to determine the optimal polycarbonate option.
Durability and Lifespan
Twinwall polycarbonate offers excellent impact resistance with a typical lifespan of 10 to 12 years, making it durable for various applications, especially in roofing and greenhouses. Multiwall polycarbonate, with its additional layers, provides enhanced insulation and strength, extending its lifespan up to 15 years while maintaining high durability against UV radiation and weather conditions. Both types deliver robust performance, but multiwall polycarbonate is preferred for projects requiring longer durability and superior thermal efficiency.
Which Polycarbonate is Best for Your Project?
Twinwall polycarbonate offers lightweight durability with excellent insulation and is ideal for projects requiring strength and flexibility, such as roofing and greenhouses. Multiwall polycarbonate provides superior thermal insulation due to its multiple layers and is best suited for applications demanding energy efficiency and noise reduction, like conservatories or industrial buildings. Choosing the best polycarbonate depends on factors like structural requirements, insulation needs, and budget constraints of your specific project.
Twinwall Polycarbonate vs Multiwall Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com