Polycarbonate offers exceptional impact resistance, making it highly durable against physical shocks and ideal for protective gear and automotive components. However, its UV resistance is comparatively lower, requiring coatings or additives to prevent degradation and yellowing when exposed to prolonged sunlight. Balancing impact resistance with enhanced UV protection through specialized treatments ensures polycarbonate maintains both strength and clarity in outdoor applications.
Table of Comparison
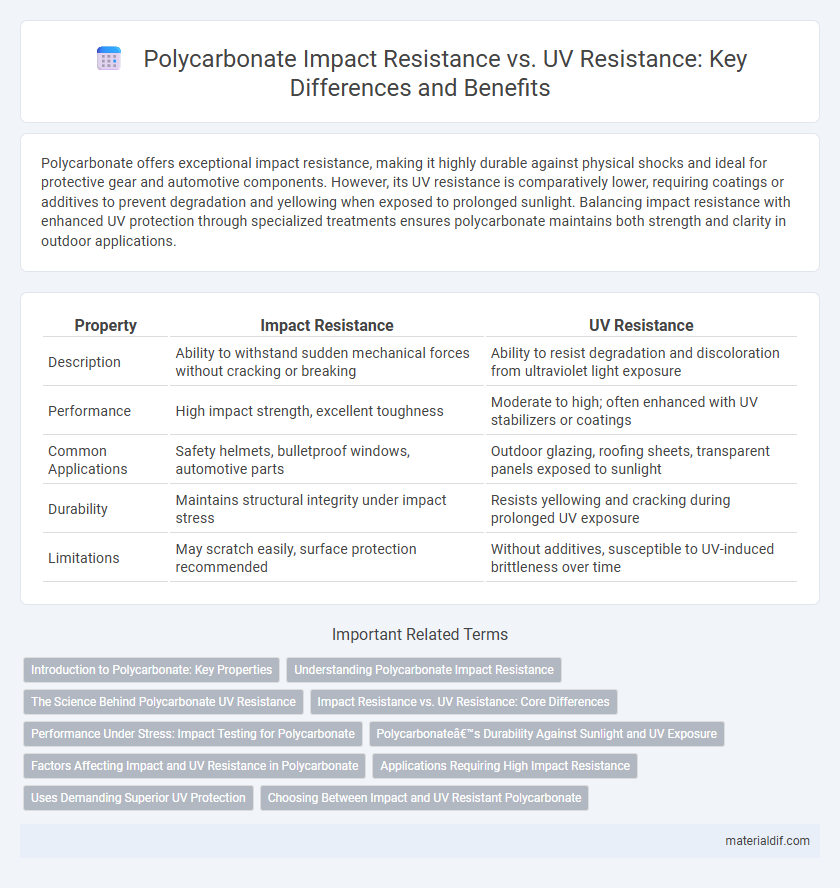
| Property | Impact Resistance | UV Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Ability to withstand sudden mechanical forces without cracking or breaking | Ability to resist degradation and discoloration from ultraviolet light exposure |
| Performance | High impact strength, excellent toughness | Moderate to high; often enhanced with UV stabilizers or coatings |
| Common Applications | Safety helmets, bulletproof windows, automotive parts | Outdoor glazing, roofing sheets, transparent panels exposed to sunlight |
| Durability | Maintains structural integrity under impact stress | Resists yellowing and cracking during prolonged UV exposure |
| Limitations | May scratch easily, surface protection recommended | Without additives, susceptible to UV-induced brittleness over time |
Introduction to Polycarbonate: Key Properties
Polycarbonate is renowned for its exceptional impact resistance, making it a preferred material in applications requiring durability and toughness, such as safety helmets and automotive components. Its UV resistance is enhanced through specialized coatings or additives, preventing yellowing and degradation from prolonged sun exposure, which is critical for outdoor uses like glazing and eyewear lenses. These key properties position polycarbonate as a versatile polymer balancing physical strength and environmental resilience.
Understanding Polycarbonate Impact Resistance
Polycarbonate impact resistance is a key property that allows the material to absorb and disperse energy from sudden forces, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and protection. This thermoplastic polymer exhibits a high degree of toughness due to its molecular structure, which prevents cracking or shattering under impact. Understanding polycarbonate impact resistance involves analyzing its ability to maintain structural integrity under stress, in contrast to its UV resistance, which primarily protects it from degradation caused by ultraviolet light exposure.
The Science Behind Polycarbonate UV Resistance
Polycarbonate's UV resistance originates from its molecular structure, which contains aromatic rings that absorb and dissipate ultraviolet light, preventing polymer degradation. UV stabilizers such as hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) and UV absorbers are often integrated into polycarbonate formulations to enhance this protective effect. Despite its inherent impact resistance, untreated polycarbonate can yellow and become brittle under prolonged UV exposure without these specialized additives.
Impact Resistance vs. UV Resistance: Core Differences
Polycarbonate impact resistance refers to its ability to withstand heavy physical forces without cracking or breaking, making it ideal for protective gear and safety applications. In contrast, polycarbonate UV resistance measures its capacity to endure prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light without degrading or yellowing, which is crucial for outdoor use. These core differences highlight that impact resistance ensures structural durability under mechanical stress, while UV resistance preserves optical clarity and material longevity under sun exposure.
Performance Under Stress: Impact Testing for Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate exhibits exceptional impact resistance, with a high tensile strength of approximately 70 MPa and the ability to withstand impacts without cracking or breaking, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under mechanical stress. Its UV resistance can be enhanced through coatings or additives, which help maintain material integrity and prevent degradation under prolonged sun exposure, but this does not significantly affect its impact performance. Impact testing for polycarbonate typically involves high-velocity impact simulations that confirm its superior toughness compared to other plastics like acrylic or glass, ensuring reliable performance in safety and protective gear.
Polycarbonate’s Durability Against Sunlight and UV Exposure
Polycarbonate exhibits exceptional impact resistance, making it highly durable against physical stress and environmental wear. Its UV resistance is enhanced through specialized coatings that prevent yellowing and degradation when exposed to prolonged sunlight. These combined properties ensure polycarbonate maintains structural integrity and clarity in outdoor applications where sunlight and UV exposure are significant factors.
Factors Affecting Impact and UV Resistance in Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate impact resistance is primarily influenced by molecular structure, thickness, and the presence of additives like impact modifiers. UV resistance in polycarbonate depends on stabilizers such as UV absorbers and hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS), as well as surface treatments or coatings to prevent degradation. Environmental factors including temperature, exposure duration, and intensity of UV radiation significantly affect both impact and UV resistance performance.
Applications Requiring High Impact Resistance
Polycarbonate demonstrates exceptional impact resistance, making it ideal for applications like safety goggles, automotive components, and protective shields where durability under stress is crucial. While UV resistance is important for outdoor use, impact resistance remains the primary criterion in high-strength requirements, often achieved through specific additives or coatings to maintain clarity and toughness. Industries prioritize impact-resistant polycarbonate for environments subject to physical impact, ensuring long-lasting performance without compromising safety or structural integrity.
Uses Demanding Superior UV Protection
Polycarbonate impact resistance makes it ideal for applications requiring toughness, such as protective gear and safety glazing, due to its high durability under force. However, uses demanding superior UV protection, like outdoor signage and skylights, rely on UV-stabilized polycarbonate variants engineered with UV-absorbers to prevent degradation and yellowing. This specialized UV resistance ensures long-term clarity and material integrity in harsh sunlight, surpassing standard polycarbonate's performance.
Choosing Between Impact and UV Resistant Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate impact resistance ensures high durability against physical shocks, making it ideal for safety and protective applications such as helmets and machine guards. UV-resistant polycarbonate offers extended lifespan and clarity by preventing yellowing and degradation when exposed to sunlight, which is crucial for outdoor uses like skylights and greenhouse panels. Choosing between impact and UV resistant polycarbonate depends on the environment and specific application needs, where impact resistance prioritizes toughness and UV resistance enhances long-term optical performance.
Polycarbonate Impact Resistance vs Polycarbonate UV Resistance Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com