Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and clarity compared to PVC, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and transparency. Unlike PVC, polycarbonate is more resistant to high temperatures and maintains structural integrity under stress. Its lightweight nature and environmental resistance provide enhanced performance in both industrial and consumer products.
Table of Comparison
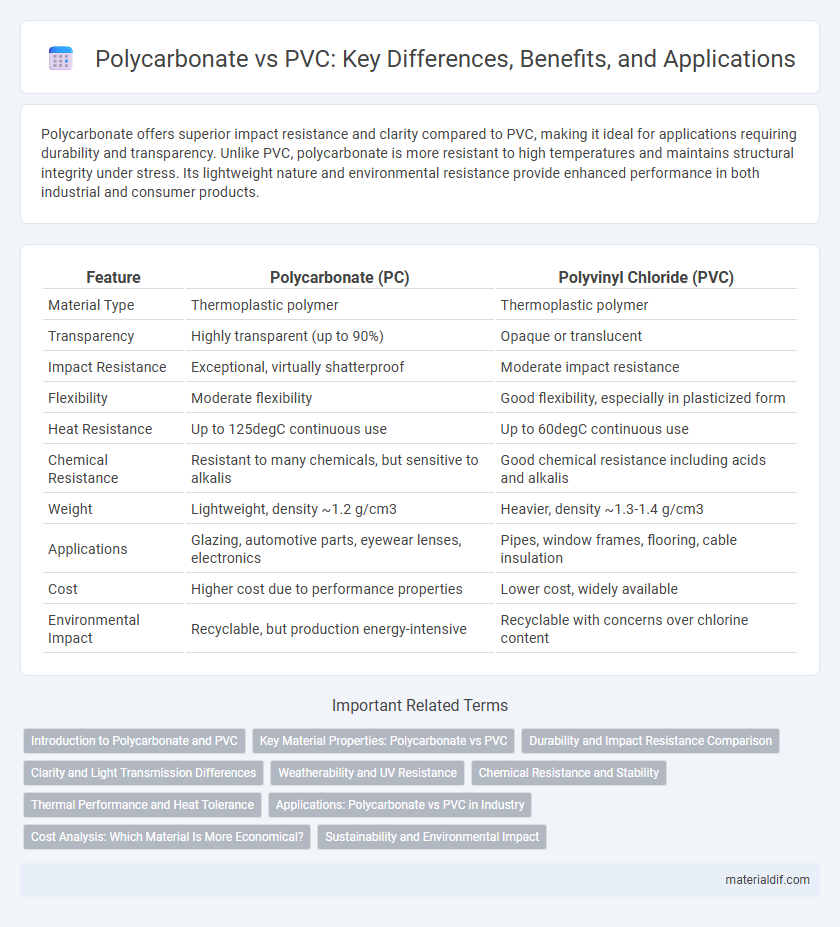
| Feature | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Transparency | Highly transparent (up to 90%) | Opaque or translucent |
| Impact Resistance | Exceptional, virtually shatterproof | Moderate impact resistance |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Good flexibility, especially in plasticized form |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 125degC continuous use | Up to 60degC continuous use |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to many chemicals, but sensitive to alkalis | Good chemical resistance including acids and alkalis |
| Weight | Lightweight, density ~1.2 g/cm3 | Heavier, density ~1.3-1.4 g/cm3 |
| Applications | Glazing, automotive parts, eyewear lenses, electronics | Pipes, window frames, flooring, cable insulation |
| Cost | Higher cost due to performance properties | Lower cost, widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, but production energy-intensive | Recyclable with concerns over chlorine content |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and PVC
Polycarbonate is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic known for its clarity and strength, commonly used in automotive, construction, and electronics industries. PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a versatile, cost-effective plastic notable for its chemical resistance and insulation properties, frequently applied in piping, window frames, and electrical cable coatings. Both materials offer unique benefits: polycarbonate excels in toughness and transparency, while PVC is favored for affordability and chemical stability.
Key Material Properties: Polycarbonate vs PVC
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and higher transparency compared to PVC, making it ideal for applications requiring clear, durable materials. PVC exhibits excellent chemical resistance and corrosion resistance, providing enhanced weatherability in outdoor environments. Thermal performance also differs significantly; polycarbonate has a higher heat deflection temperature, enabling it to withstand elevated temperatures better than PVC.
Durability and Impact Resistance Comparison
Polycarbonate exhibits superior durability and impact resistance compared to PVC, making it ideal for applications requiring high strength and toughness. Polycarbonate's impact resistance is approximately 250 times greater than that of glass and significantly outperforms PVC, which tends to be more brittle under stress. The material's inherent toughness allows polycarbonate to withstand heavy impacts and harsh environmental conditions without cracking or breaking, unlike PVC that may degrade over time when exposed to UV light and mechanical strain.
Clarity and Light Transmission Differences
Polycarbonate offers superior clarity with light transmission rates of around 88-90%, significantly higher than PVC, which typically transmits only 80-85%. The inherent optical transparency of polycarbonate makes it ideal for applications requiring clear, distortion-free visibility, such as glazing and optical lenses. PVC often exhibits a slight haze that reduces overall light penetration, limiting its use in situations where maximum clarity is essential.
Weatherability and UV Resistance
Polycarbonate demonstrates superior weatherability and UV resistance compared to PVC, maintaining clarity and structural integrity under prolonged exposure to sunlight and harsh environmental conditions. Its inherent UV-stabilizing properties prevent yellowing and brittleness, making it ideal for outdoor applications such as glazing and roofing. PVC, while cost-effective, tends to degrade faster when exposed to UV radiation, resulting in discoloration and reduced durability over time.
Chemical Resistance and Stability
Polycarbonate exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to PVC, maintaining stability when exposed to various solvents, oils, and acids, which can degrade PVC over time. Its high thermal stability allows polycarbonate to withstand elevated temperatures without significant deformation or chemical breakdown. PVC tends to experience chemical softening and dimensional changes when exposed to strong chemicals, limiting its use in harsh environments.
Thermal Performance and Heat Tolerance
Polycarbonate offers superior thermal performance compared to PVC, with a higher melting point around 267degC, enabling it to withstand elevated temperatures without deformation. PVC typically has a lower heat tolerance, melting at approximately 100-260degC depending on its formulation, which can limit its use in high-heat applications. The enhanced heat resistance of polycarbonate makes it ideal for environments requiring durability and dimensional stability under thermal stress.
Applications: Polycarbonate vs PVC in Industry
Polycarbonate exhibits superior impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for applications like eyewear lenses, automotive headlamps, and protective barriers, where durability and transparency are critical. PVC is widely used in construction for pipes, window frames, and electrical cable insulation due to its excellent chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness. Industries prefer polycarbonate for high-performance, lightweight components, while PVC dominates in scenarios requiring robust, weather-resistant materials at a lower price point.
Cost Analysis: Which Material Is More Economical?
Polycarbonate generally has a higher upfront cost compared to PVC, but its superior durability and impact resistance often result in lower long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. PVC offers a more budget-friendly initial investment, making it ideal for projects with tight cost constraints, though it may incur higher costs over time due to less resilience. For applications requiring longevity and strength, polycarbonate's cost-effectiveness improves when factoring in lifespan and performance efficiency.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Polycarbonate exhibits higher sustainability compared to PVC due to its superior durability and recyclability, reducing the frequency of replacement and waste generation. Unlike PVC, polycarbonate does not release harmful dioxins or chlorine-based compounds during production or disposal, minimizing environmental toxicity. Additionally, polycarbonate's ability to be recycled multiple times supports circular economy practices and lowers carbon footprint.
Polycarbonate vs PVC Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com