Coated polycarbonate offers enhanced scratch resistance and UV protection compared to uncoated polycarbonate, extending the material's durability and clarity. The coating acts as a protective layer, preventing surface damage and discoloration from environmental factors. Uncoated polycarbonate, while more cost-effective, is more susceptible to scratches and yellowing over time, limiting its lifespan in outdoor or high-wear applications.
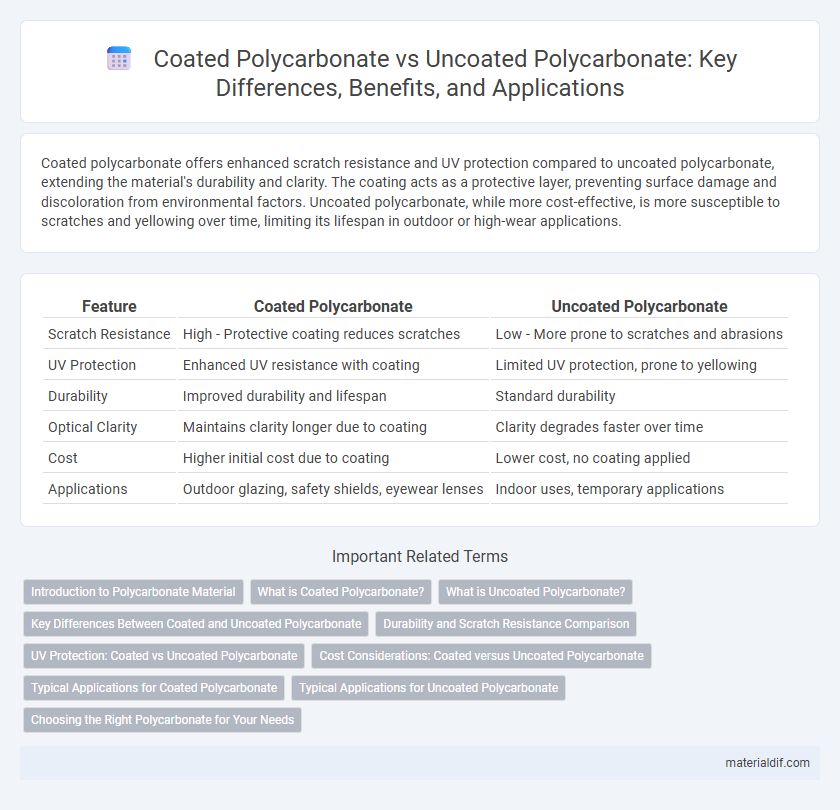
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Coated Polycarbonate | Uncoated Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Scratch Resistance | High - Protective coating reduces scratches | Low - More prone to scratches and abrasions |
| UV Protection | Enhanced UV resistance with coating | Limited UV protection, prone to yellowing |
| Durability | Improved durability and lifespan | Standard durability |
| Optical Clarity | Maintains clarity longer due to coating | Clarity degrades faster over time |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to coating | Lower cost, no coating applied |
| Applications | Outdoor glazing, safety shields, eyewear lenses | Indoor uses, temporary applications |
Introduction to Polycarbonate Material
Polycarbonate is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic widely used in manufacturing eyewear lenses, automotive parts, and electronic components. Coated polycarbonate features protective layers that enhance scratch resistance, UV protection, and overall longevity compared to uncoated polycarbonate, which is more susceptible to surface damage and degradation. These coatings significantly improve the material's performance in demanding applications requiring optical clarity and durability.
What is Coated Polycarbonate?
Coated polycarbonate features a protective layer that enhances its resistance to scratches, UV rays, and chemical exposure, significantly extending its durability compared to uncoated polycarbonate. This coating can include hard coatings, anti-reflective layers, or UV blockers, which improve the material's performance in applications such as eyewear lenses, automotive parts, and architectural panels. The added surface protection preserves clarity and structural integrity, making coated polycarbonate an ideal choice for outdoor and high-impact environments.
What is Uncoated Polycarbonate?
Uncoated polycarbonate is a transparent thermoplastic material known for its high impact resistance and optical clarity, lacking any surface treatments or protective layers. It offers excellent durability and flexibility but is more susceptible to scratches, UV damage, and chemical exposure compared to coated variants. This makes uncoated polycarbonate ideal for applications where cost efficiency and basic performance are prioritized over enhanced surface protection.
Key Differences Between Coated and Uncoated Polycarbonate
Coated polycarbonate features a protective layer that enhances scratch resistance, UV protection, and durability, making it ideal for outdoor applications and environments exposed to harsh conditions. Uncoated polycarbonate lacks this defense, leaving it more susceptible to scratches, discoloration, and degradation from UV exposure over time. The coating also improves the material's longevity and clarity, ensuring better performance in demanding uses compared to its uncoated counterpart.
Durability and Scratch Resistance Comparison
Coated polycarbonate offers enhanced durability and superior scratch resistance compared to uncoated polycarbonate due to its protective layers that shield against abrasion and UV damage. Uncoated polycarbonate is more prone to surface scratches and degradation when exposed to harsh environments or frequent handling. The coating significantly extends the lifespan and maintains optical clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term performance and surface integrity.
UV Protection: Coated vs Uncoated Polycarbonate
Coated polycarbonate offers superior UV protection by incorporating a specialized layer that blocks harmful ultraviolet rays, significantly reducing yellowing and material degradation over time. Uncoated polycarbonate lacks this protective layer, making it more susceptible to UV-induced damage, discoloration, and loss of mechanical properties when exposed to sunlight. The UV coating extends the lifespan and maintains the optical clarity of polycarbonate in outdoor applications, making it the preferred choice for environments with high sun exposure.
Cost Considerations: Coated versus Uncoated Polycarbonate
Coated polycarbonate typically incurs higher initial costs due to the application of protective layers that enhance scratch resistance and UV protection, extending the material's lifespan in outdoor and high-wear environments. Uncoated polycarbonate offers a lower upfront price but may require more frequent replacement or maintenance, increasing long-term expenses in comparison. Evaluating cost considerations between coated and uncoated polycarbonate involves balancing immediate budget constraints against durability and performance requirements over time.
Typical Applications for Coated Polycarbonate
Coated polycarbonate is commonly used in applications requiring enhanced scratch resistance and UV protection, such as eyewear lenses, automotive headlight covers, and outdoor signage. The coating extends the material's lifespan in harsh environments by preventing degradation from physical abrasion and solar exposure. These properties make coated polycarbonate ideal for use in safety gear, architectural glazing, and electronic displays.
Typical Applications for Uncoated Polycarbonate
Uncoated polycarbonate is typically used in applications where high impact resistance and optical clarity are essential, such as safety goggles, automotive headlamp lenses, and electronic display covers. Its inherent durability and UV resistance make it suitable for indoor and outdoor protective components without the need for additional surface treatments. Industrial machinery guards and architectural glazing also commonly utilize uncoated polycarbonate for its toughness and lightweight properties.
Choosing the Right Polycarbonate for Your Needs
Coated polycarbonate offers enhanced scratch resistance, UV protection, and improved durability, making it ideal for outdoor applications and environments exposed to harsh conditions. Uncoated polycarbonate provides greater affordability and flexibility for indoor uses where impact resistance is prioritized over surface protection. Selecting between coated and uncoated polycarbonate depends on factors such as exposure to sunlight, risk of abrasion, and budget constraints tailored to your specific project requirements.
Coated Polycarbonate vs Uncoated Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com