PC blend offers enhanced impact resistance and improved thermal stability compared to pure polycarbonate, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and heat resistance. Pure polycarbonate provides superior optical clarity and higher tensile strength, suitable for precision components and transparent products. Choosing between PC blend and pure polycarbonate depends on the specific performance requirements and environmental conditions of the end-use application.
Table of Comparison
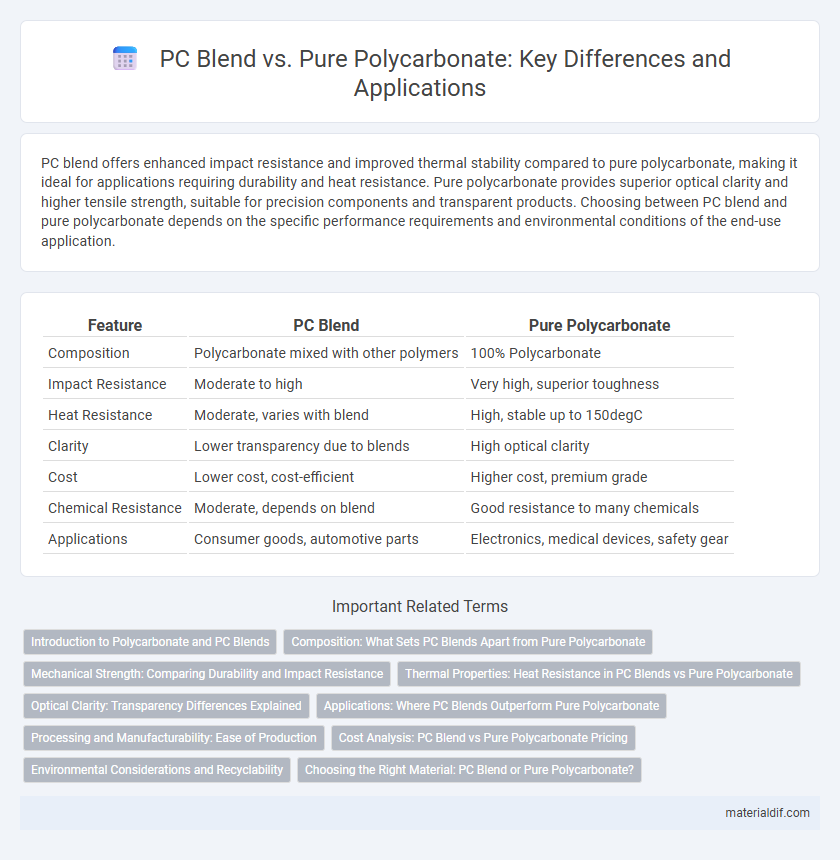
| Feature | PC Blend | Pure Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Polycarbonate mixed with other polymers | 100% Polycarbonate |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate to high | Very high, superior toughness |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, varies with blend | High, stable up to 150degC |
| Clarity | Lower transparency due to blends | High optical clarity |
| Cost | Lower cost, cost-efficient | Higher cost, premium grade |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, depends on blend | Good resistance to many chemicals |
| Applications | Consumer goods, automotive parts | Electronics, medical devices, safety gear |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and PC Blends
Polycarbonate (PC) is a durable, transparent thermoplastic widely used for its high impact resistance and thermal stability. PC blends combine polycarbonate with other polymers, enhancing specific properties such as chemical resistance, toughness, or flexibility, tailored for various industrial applications. Pure polycarbonate offers superior clarity and rigidity, while PC blends provide optimized performance for specialized manufacturing needs.
Composition: What Sets PC Blends Apart from Pure Polycarbonate
PC blends combine polycarbonate with other polymers such as acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) or polyester to enhance properties like impact resistance, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, differentiating them from pure polycarbonate which consists solely of polycarbonate resin. This composite structure alters the mechanical and thermal characteristics, offering improved processability and cost-effectiveness without compromising clarity or strength. The specific ratios and types of blended polymers determine the final material's performance, enabling customization for targeted applications in automotive, electronics, and construction industries.
Mechanical Strength: Comparing Durability and Impact Resistance
PC blends often exhibit enhanced mechanical strength due to the addition of materials like ABS or polyester, improving impact resistance and durability compared to pure polycarbonate. Pure polycarbonate demonstrates high inherent toughness and excellent impact resistance, but PC blends can offer more balanced mechanical properties tailored to specific applications. Testing shows that while pure PC provides superior clarity and stiffness, blends provide better overall durability in harsh environments.
Thermal Properties: Heat Resistance in PC Blends vs Pure Polycarbonate
PC blends typically exhibit enhanced heat resistance compared to pure polycarbonate due to the incorporation of materials like ABS or SAN, which improve thermal stability and reduce heat distortion. Pure polycarbonate offers consistent heat resistance with a glass transition temperature around 147degC, but PC blends can extend this range, making them suitable for applications requiring higher thermal endurance. These improvements in thermal properties make PC blends favorable for automotive parts, electrical components, and appliances exposed to elevated temperatures.
Optical Clarity: Transparency Differences Explained
Pure polycarbonate offers superior optical clarity with high transparency and minimal light distortion, making it ideal for applications requiring clear visibility. PC blends may introduce additives that slightly reduce transparency, resulting in a less crisp appearance and lower light transmission rates. Selecting pure polycarbonate ensures maximum optical performance for lenses, eyewear, and protective barriers.
Applications: Where PC Blends Outperform Pure Polycarbonate
PC blends outperform pure polycarbonate in applications requiring enhanced chemical resistance and improved impact strength, such as automotive components and electrical housings. These blends offer superior thermal stability and reduced brittleness, making them ideal for demanding environments like aerospace and industrial machinery. Their tailored mechanical properties also provide better durability in consumer electronics compared to pure polycarbonate.
Processing and Manufacturability: Ease of Production
PC blends offer improved flow properties that enhance ease of injection molding and extrusion compared to pure polycarbonate. Pure polycarbonate typically requires higher processing temperatures and precise control to avoid degradation during manufacturing. Manufacturers favor PC blends for faster cycle times and reduced energy consumption while maintaining sufficient mechanical strength.
Cost Analysis: PC Blend vs Pure Polycarbonate Pricing
Polycarbonate blends typically offer a cost advantage over pure polycarbonate due to the incorporation of less expensive polymers, which reduces raw material expenses and manufacturing costs. Pure polycarbonate, while more costly, provides superior clarity, impact resistance, and thermal stability, justifying its premium pricing in high-performance applications. Evaluating the price difference reveals that PC blends can reduce costs by 10-30% depending on the blend composition while maintaining adequate mechanical properties for many industrial uses.
Environmental Considerations and Recyclability
Polycarbonate (PC) blends often incorporate additives or other polymers to enhance performance, which can complicate recycling processes compared to pure polycarbonate. Pure polycarbonate exhibits higher recyclability and better environmental compatibility due to its consistent polymer structure and lower contamination risk during mechanical recycling. Choosing pure polycarbonate over PC blends supports improved closed-loop recycling efficiency and reduces the environmental impact associated with mixed-material waste streams.
Choosing the Right Material: PC Blend or Pure Polycarbonate?
PC blends offer enhanced impact resistance, improved chemical resistance, and better processability compared to pure polycarbonate, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and versatility. Pure polycarbonate provides superior optical clarity and high heat resistance, suitable for products where transparency and thermal stability are critical. Selecting between PC blend and pure polycarbonate depends on balancing performance requirements such as mechanical strength, aesthetic appeal, and environmental exposure in the intended application.
PC Blend vs Pure Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com