Solid polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and transparency. Multiwall polycarbonate features a layered structure that enhances thermal insulation and reduces weight, providing energy efficiency and structural strength. Choosing between solid and multiwall polycarbonate depends on whether the priority is toughness and visibility or insulation and lightweight performance.
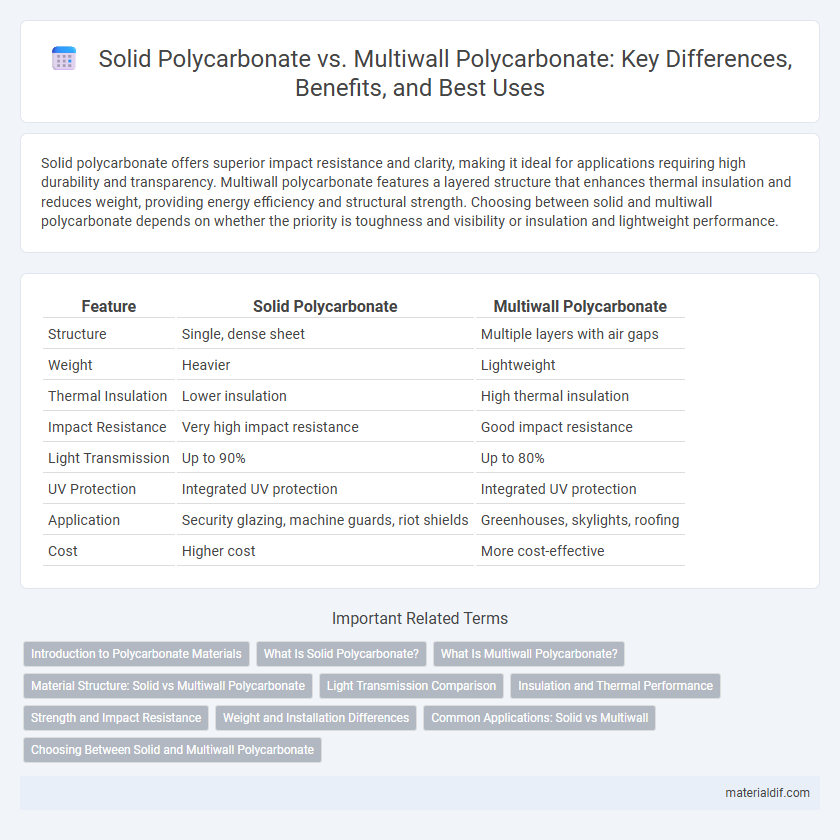
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solid Polycarbonate | Multiwall Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single, dense sheet | Multiple layers with air gaps |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Thermal Insulation | Lower insulation | High thermal insulation |
| Impact Resistance | Very high impact resistance | Good impact resistance |
| Light Transmission | Up to 90% | Up to 80% |
| UV Protection | Integrated UV protection | Integrated UV protection |
| Application | Security glazing, machine guards, riot shields | Greenhouses, skylights, roofing |
| Cost | Higher cost | More cost-effective |
Introduction to Polycarbonate Materials
Solid polycarbonate offers high impact resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and durability. Multiwall polycarbonate features a layered structure providing enhanced thermal insulation and lightweight strength, suited for roofing and greenhouses. Both materials exhibit excellent UV resistance and weatherability, tailored to distinct functional needs in construction and industrial uses.
What Is Solid Polycarbonate?
Solid polycarbonate is a transparent, durable thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and optical clarity, commonly used in applications like safety glazing, eyewear lenses, and protective barriers. Unlike multiwall polycarbonate, which features a layered structure to provide insulation and lightweight properties, solid polycarbonate offers superior strength and scratch resistance without internal air gaps. Its dense molecular composition ensures excellent weatherability and UV protection, making it ideal for environments requiring robust and clear materials.
What Is Multiwall Polycarbonate?
Multiwall polycarbonate is a lightweight, durable plastic sheet composed of multiple layers separated by internal ribs, offering enhanced thermal insulation compared to solid polycarbonate. Its cellular structure provides excellent impact resistance and improved energy efficiency, making it ideal for applications like greenhouses, skylights, and facade glazing. Unlike solid polycarbonate, multiwall variants significantly reduce heat transfer while maintaining high light transmission.
Material Structure: Solid vs Multiwall Polycarbonate
Solid polycarbonate features a dense, non-cavitated structure that delivers high impact resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring strength and transparency. Multiwall polycarbonate consists of multiple hollow layers separated by ribs, enhancing thermal insulation and reducing weight while providing moderate impact resistance. The multi-chamber design in multiwall polycarbonate improves energy efficiency in glazing systems compared to the solid variant.
Light Transmission Comparison
Solid polycarbonate sheets provide superior light transmission, typically allowing 88-92% of natural light to pass through, making them ideal for applications requiring maximum clarity and brightness. Multiwall polycarbonate panels feature multiple layers with air gaps, reducing light transmission to around 50-80%, which enhances insulation and diffuses light for softer illumination. Choosing between solid and multiwall polycarbonate depends on the desired balance between light clarity and thermal performance.
Insulation and Thermal Performance
Solid polycarbonate offers exceptional impact resistance with moderate thermal insulation, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and transparency. Multiwall polycarbonate features multiple layers separated by air channels, significantly enhancing thermal insulation and reducing heat transfer, ideal for energy-efficient building envelopes. The multiwall structure provides higher R-values and better condensation control compared to solid polycarbonate, optimizing thermal performance in cold and hot climates.
Strength and Impact Resistance
Solid polycarbonate features higher strength and superior impact resistance compared to multiwall polycarbonate, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum durability. Multiwall polycarbonate provides good impact resistance while offering enhanced thermal insulation due to its cellular structure. The dense, non-hollow composition of solid polycarbonate delivers exceptional toughness, whereas the layered design of multiwall panels balances strength with lightweight performance.
Weight and Installation Differences
Solid polycarbonate sheets are heavier than multiwall polycarbonate panels due to their dense, single-layer structure, which impacts handling and installation complexity. Multiwall polycarbonate is lighter, offering easier installation and reduced structural support requirements, making it ideal for large-span projects. The weight difference directly influences labor costs and mounting hardware choices, with multiwall polycarbonate favoring quicker, more cost-effective setups.
Common Applications: Solid vs Multiwall
Solid polycarbonate is commonly used in applications requiring high impact resistance and clarity, such as safety glazing, automotive parts, and optical lenses. Multiwall polycarbonate is favored for insulation and light diffusion in greenhouses, skylights, and roofing panels due to its layered structure. Both types provide UV protection but differ in thermal performance and weight, influencing their suitability for specific construction and industrial uses.
Choosing Between Solid and Multiwall Polycarbonate
Solid polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and strength, such as protective barriers and glazing. Multiwall polycarbonate features enhanced thermal insulation and reduced weight due to its layered structure, suited for energy-efficient roofing and greenhouse panels. Selecting between solid and multiwall polycarbonate depends on balancing factors like durability, thermal performance, and light transmission for specific project needs.
Solid Polycarbonate vs Multiwall Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com