Optical grade polycarbonate PET offers superior clarity, high light transmission, and minimal distortion, making it ideal for applications requiring precise visual performance such as eyewear lenses and optical discs. Industrial grade polycarbonate PET prioritizes durability and impact resistance over transparency, suited for manufacturing protective gear, automotive parts, and electronics casings. Choosing between optical and industrial grades depends on the balance between visual quality and mechanical strength needed for the specific use case.
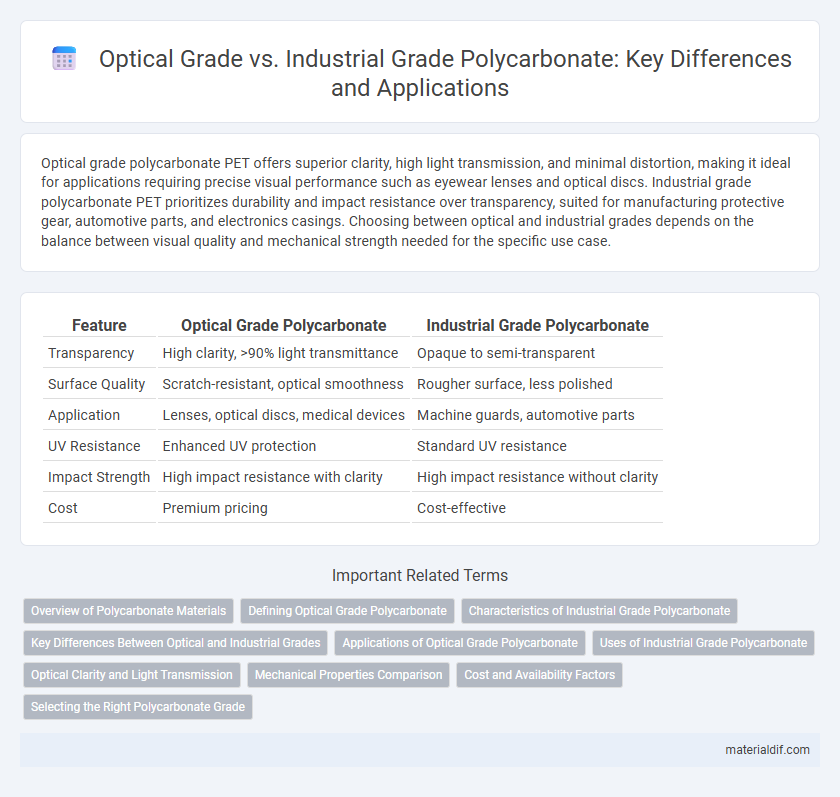
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Optical Grade Polycarbonate | Industrial Grade Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | High clarity, >90% light transmittance | Opaque to semi-transparent |
| Surface Quality | Scratch-resistant, optical smoothness | Rougher surface, less polished |
| Application | Lenses, optical discs, medical devices | Machine guards, automotive parts |
| UV Resistance | Enhanced UV protection | Standard UV resistance |
| Impact Strength | High impact resistance with clarity | High impact resistance without clarity |
| Cost | Premium pricing | Cost-effective |
Overview of Polycarbonate Materials
Optical grade polycarbonate offers superior light transmittance, clarity, and minimal distortion, making it ideal for lenses, eyewear, and optical lenses. Industrial grade polycarbonate provides enhanced toughness and impact resistance, suitable for construction, automotive parts, and electronic housings. Both grades deliver durability and heat resistance, but optical grade emphasizes visual performance while industrial grade prioritizes mechanical strength.
Defining Optical Grade Polycarbonate
Optical grade polycarbonate is engineered for superior clarity, light transmission, and minimal haze, making it ideal for lenses, eyewear, and optical components. Its molecular structure is precisely controlled to reduce impurities and internal stresses, ensuring consistent optical performance and durability. This contrasts with industrial grade polycarbonate, which prioritizes impact resistance and thermal stability over optical clarity for applications like automotive parts and protective gear.
Characteristics of Industrial Grade Polycarbonate
Industrial grade polycarbonate exhibits high impact resistance, thermal stability, and chemical durability, making it suitable for demanding applications like automotive parts and electrical components. Its optical clarity is lower than optical grade, with increased haze and reduced light transmission, prioritizing mechanical strength over transparency. This grade often undergoes additives and UV stabilizers to enhance performance in harsh environments.
Key Differences Between Optical and Industrial Grades
Optical grade polycarbonate offers superior light transmission, clarity, and minimal yellowing, making it ideal for lenses, eyewear, and optical films, whereas industrial grade polycarbonate prioritizes impact resistance and heat deflection for applications like automotive parts and electrical components. The molecular structure in optical grade is refined to reduce birefringence and internal stress, enhancing optical performance, while industrial grade is formulated to withstand harsh mechanical and environmental conditions. Cost differences also reflect material properties; optical grade tends to be more expensive due to its stringent quality and purity requirements compared to the more robust but less clear industrial grade.
Applications of Optical Grade Polycarbonate
Optical grade polycarbonate is engineered for high clarity and light transmission, making it ideal for applications such as lenses, eyewear, optical discs, and transparent covers in electronic devices. Its superior optical properties and impact resistance facilitate use in medical instruments, automotive lighting, and protective visors. Industrial grade polycarbonate, by contrast, is typically used where mechanical strength and durability are prioritized over optical clarity.
Uses of Industrial Grade Polycarbonate
Industrial grade polycarbonate is extensively used in applications requiring high impact resistance and durability, such as machine guards, safety helmets, and automotive components. Its enhanced toughness and thermal stability make it suitable for electrical housings and construction panels where mechanical strength is critical. Unlike optical grade polycarbonate, industrial grade prioritizes functionality over clarity, enabling cost-effective solutions in heavy-duty environments.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Optical grade polycarbonate exhibits superior optical clarity and light transmission, making it ideal for applications requiring precise visual performance such as lenses and protective eyewear. Industrial grade polycarbonate has reduced transparency with minor impurities or haze, which minimally affects light transmission but is suitable for structural and impact-resistant uses. The difference in optical clarity between the two grades is primarily due to the controlled manufacturing processes and additive formulations used in optical grade polycarbonate.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Optical grade polycarbonate exhibits higher impact resistance and greater tensile strength compared to industrial grade, making it ideal for applications requiring clarity without compromising durability. Industrial grade polycarbonate, while slightly lower in optical clarity, offers enhanced flexibility and better resistance to environmental stress cracking. These mechanical properties differences stem from variations in polymer purity and additives used during manufacturing, influencing performance in both structural and optical applications.
Cost and Availability Factors
Optical grade polycarbonate offers superior clarity and precision for applications like lenses and displays, but it commands a higher price due to stricter manufacturing standards and lower production volumes. Industrial grade polycarbonate is more cost-effective and widely available, suitable for general-purpose uses such as automotive parts and enclosures where optical clarity is less critical. The choice between these grades depends largely on budget constraints and the required optical properties of the end product.
Selecting the Right Polycarbonate Grade
Optical grade polycarbonate offers superior clarity, light transmission, and low birefringence, making it ideal for lenses, eyewear, and optical components. Industrial grade polycarbonate prioritizes impact resistance and durability for applications like machine guards, automotive parts, and electrical housings. Selecting the right polycarbonate grade depends on balancing optical performance requirements with mechanical strength and environmental resistance.
Optical Grade vs Industrial Grade Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com