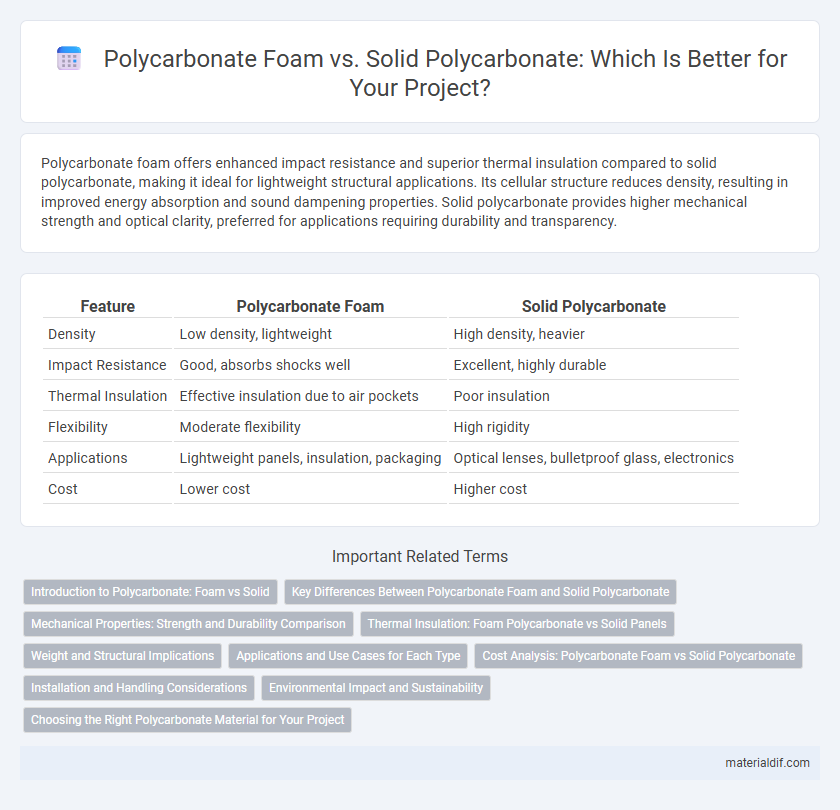
Polycarbonate foam offers enhanced impact resistance and superior thermal insulation compared to solid polycarbonate, making it ideal for lightweight structural applications. Its cellular structure reduces density, resulting in improved energy absorption and sound dampening properties. Solid polycarbonate provides higher mechanical strength and optical clarity, preferred for applications requiring durability and transparency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polycarbonate Foam | Solid Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low density, lightweight | High density, heavier |
| Impact Resistance | Good, absorbs shocks well | Excellent, highly durable |
| Thermal Insulation | Effective insulation due to air pockets | Poor insulation |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High rigidity |
| Applications | Lightweight panels, insulation, packaging | Optical lenses, bulletproof glass, electronics |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Polycarbonate: Foam vs Solid
Polycarbonate foam offers lightweight properties with excellent thermal insulation and impact absorption, making it suitable for applications requiring reduced weight and enhanced energy efficiency. Solid polycarbonate provides superior rigidity, clarity, and mechanical strength, ideal for structural components and transparent protective barriers. Understanding the differences in density, thermal conductivity, and mechanical performance is essential when selecting between foam and solid polycarbonate for specific industrial or engineering uses.
Key Differences Between Polycarbonate Foam and Solid Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate foam has a cellular structure with trapped gas bubbles, making it lightweight and impact-absorbing, whereas solid polycarbonate is dense and offers superior strength and clarity. The foam version excels in thermal insulation and sound absorption, while solid polycarbonate provides better mechanical durability and optical transparency. Applications of polycarbonate foam include lightweight panels and cushioning materials, while solid polycarbonate is commonly used in lenses, bulletproof windows, and durable housings.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability Comparison
Polycarbonate foam exhibits lower density and reduced mechanical strength compared to solid polycarbonate, making it less suitable for high-impact applications. Solid polycarbonate offers superior tensile strength, high impact resistance, and excellent durability under stress, which ensures better performance in structural and protective uses. The choice between foam and solid forms depends on balancing weight reduction with the need for robust mechanical properties.
Thermal Insulation: Foam Polycarbonate vs Solid Panels
Polycarbonate foam offers superior thermal insulation compared to solid polycarbonate panels due to its cellular structure that traps air, reducing heat transfer. Solid polycarbonate panels, while durable and impact-resistant, conduct heat more efficiently, resulting in lower insulation performance. Foam polycarbonate is ideal for applications requiring enhanced energy efficiency and temperature regulation.
Weight and Structural Implications
Polycarbonate foam offers significant weight reduction compared to solid polycarbonate, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight materials without sacrificing durability. The cellular structure of polycarbonate foam provides enhanced energy absorption and impact resistance, while solid polycarbonate delivers superior rigidity and tensile strength for load-bearing uses. Choosing between foam and solid forms depends on balancing weight constraints with structural performance requirements in specific engineering or design projects.
Applications and Use Cases for Each Type
Polycarbonate foam is preferred in automotive and aerospace industries due to its lightweight, excellent shock absorption, and thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for protective padding and energy-absorbing components. Solid polycarbonate is commonly used in construction, optical lenses, and electronic devices because of its high impact resistance, transparency, and dimensional stability. The specific application determines the choice: foam for lightweight cushioning and insulation, solid for structural strength and clear visibility.
Cost Analysis: Polycarbonate Foam vs Solid Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate foam offers significant cost savings compared to solid polycarbonate due to its lower material density and reduced raw material consumption. Manufacturing processes for foam typically require less energy, resulting in decreased production costs, making it a budget-friendly alternative in applications prioritizing lightness and insulation. Solid polycarbonate, while more expensive, delivers superior mechanical strength and impact resistance, justifying its higher price in demanding structural applications.
Installation and Handling Considerations
Polycarbonate foam offers lightweight properties that simplify installation by reducing structural load, making it ideal for applications requiring easy handling and rapid assembly. Solid polycarbonate, while more durable and impact-resistant, demands careful handling to avoid scratches and typically requires specialized tools for cutting and fitting. Choosing between foam and solid polycarbonate hinges on balancing ease of installation with the required strength and durability for specific project needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polycarbonate foam offers a significantly lower environmental impact compared to solid polycarbonate due to its reduced material density and lighter weight, which decrease transportation emissions and raw material consumption. The foamed structure enables energy savings during production and enhances recyclability by facilitating mechanical processing and reducing landfill waste. Sustainable applications of polycarbonate foam are expanding in automotive and construction sectors where durability and eco-efficient material use are critical.
Choosing the Right Polycarbonate Material for Your Project
Polycarbonate foam offers excellent insulation, lightweight properties, and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring thermal control and weight reduction, such as automotive interiors and protective padding. Solid polycarbonate provides superior clarity, high mechanical strength, and UV resistance, suited for structural components, glazing, and transparent barriers. Selecting between foam and solid polycarbonate depends on project requirements like weight constraints, thermal performance, and transparency needs to ensure optimal material performance and cost-efficiency.
Polycarbonate Foam vs Solid Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com