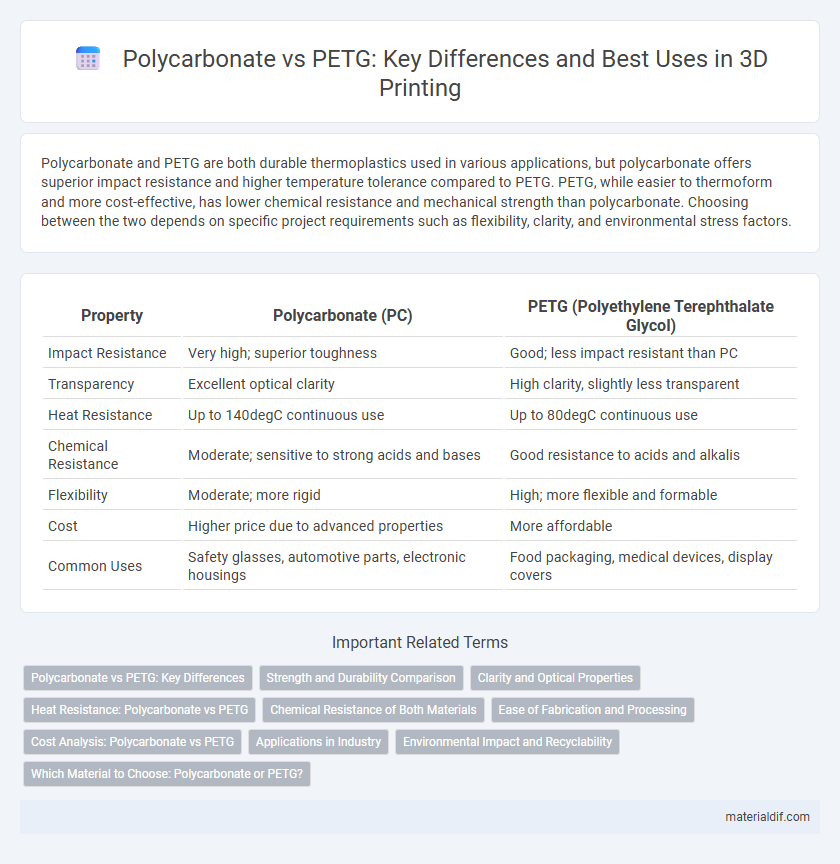
Polycarbonate and PETG are both durable thermoplastics used in various applications, but polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and higher temperature tolerance compared to PETG. PETG, while easier to thermoform and more cost-effective, has lower chemical resistance and mechanical strength than polycarbonate. Choosing between the two depends on specific project requirements such as flexibility, clarity, and environmental stress factors.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | Very high; superior toughness | Good; less impact resistant than PC |
| Transparency | Excellent optical clarity | High clarity, slightly less transparent |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 140degC continuous use | Up to 80degC continuous use |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate; sensitive to strong acids and bases | Good resistance to acids and alkalis |
| Flexibility | Moderate; more rigid | High; more flexible and formable |
| Cost | Higher price due to advanced properties | More affordable |
| Common Uses | Safety glasses, automotive parts, electronic housings | Food packaging, medical devices, display covers |
Polycarbonate vs PETG: Key Differences
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and higher temperature tolerance compared to PETG, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and heat resistance. While PETG excels in chemical resistance and ease of fabrication due to its lower melting point, polycarbonate provides greater structural strength and clarity. Differences in structural rigidity, UV stability, and cost also influence the choice between polycarbonate and PETG for engineering and manufacturing uses.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polycarbonate exhibits superior impact resistance and tensile strength compared to PETG, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and structural integrity. PETG offers good chemical resistance and flexibility but typically has lower hardness and scratch resistance than polycarbonate. The enhanced toughness of polycarbonate ensures longer lifespan and better performance under mechanical stress.
Clarity and Optical Properties
Polycarbonate offers superior clarity and impact resistance compared to PETG, making it ideal for applications requiring high optical performance. While PETG provides good transparency and is more flexible, polycarbonate maintains better visual clarity under prolonged exposure to light and harsh environments. Its inherent UV resistance and excellent light transmission properties distinguish polycarbonate in industries like eyewear, automotive glazing, and electronic displays.
Heat Resistance: Polycarbonate vs PETG
Polycarbonate exhibits superior heat resistance compared to PETG, with a glass transition temperature around 147degC, enabling it to withstand higher operational temperatures without deformation. PETG has a lower heat resistance, with a glass transition temperature near 80degC, making it less suitable for high-temperature applications. This thermal stability difference makes polycarbonate the preferred choice for environments requiring durability under heat stress.
Chemical Resistance of Both Materials
Polycarbonate exhibits excellent chemical resistance against oils, greases, and dilute acids but shows vulnerability to strong bases and solvents like acetone. PETG offers superior resistance to alcohols, acids, and many solvents, making it more versatile in chemical exposure scenarios. Comparing chemical resistance, PETG generally outperforms polycarbonate in withstanding a broader range of chemicals without degradation.
Ease of Fabrication and Processing
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and heat tolerance compared to PETG, making it easier to machine and thermoform without cracking or warping. PETG, however, excels in ease of cutting and thermoforming at lower temperatures, reducing energy consumption and processing time. Both materials provideGood chemical resistance, but polycarbonate requires more precise temperature control during fabrication to avoid discoloration and stress marks.
Cost Analysis: Polycarbonate vs PETG
Polycarbonate generally has a higher upfront cost compared to PETG due to its superior impact resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for demanding applications. PETG offers a more budget-friendly option with easier processing and good chemical resistance, suitable for cost-sensitive projects. The overall cost-effectiveness depends on the specific application requirements, including durability, environmental factors, and production volume.
Applications in Industry
Polycarbonate excels in industries requiring high impact resistance and optical clarity, such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing. PETG is favored for applications needing chemical resistance and ease of fabrication, including medical devices, food packaging, and display signage. Both materials serve distinct roles, with polycarbonate offering superior strength and heat resistance, while PETG provides flexibility and cost-effectiveness in industrial use.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polycarbonate offers high durability and impact resistance but presents challenges in recycling due to its complex chemical structure and limited recycling facilities. PETG, composed of polyethylene terephthalate glycol, is more widely accepted in recycling programs and boasts better environmental sustainability through easier processing and lower energy requirements. Both materials impact the environment differently, with PETG providing a more efficient recycling pathway and reduced ecological footprint compared to polycarbonate.
Which Material to Choose: Polycarbonate or PETG?
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and higher temperature tolerance compared to PETG, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and heat endurance. PETG provides greater chemical resistance and easier fabrication, which suits projects needing flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Selecting between polycarbonate and PETG depends on whether impact strength or chemical and processing advantages are prioritized for the specific use case.
Polycarbonate vs PETG Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com