Twinwall polycarbonate offers superior insulation and lightweight durability due to its hollow structure, making it ideal for applications like roofing and greenhouses where thermal efficiency is crucial. Solid polycarbonate provides higher impact resistance and clarity, making it the preferred choice for bulletproof windows, safety shields, and other protective uses. Choosing between twinwall and solid polycarbonate depends on the need for thermal insulation versus strength and transparency.
Table of Comparison
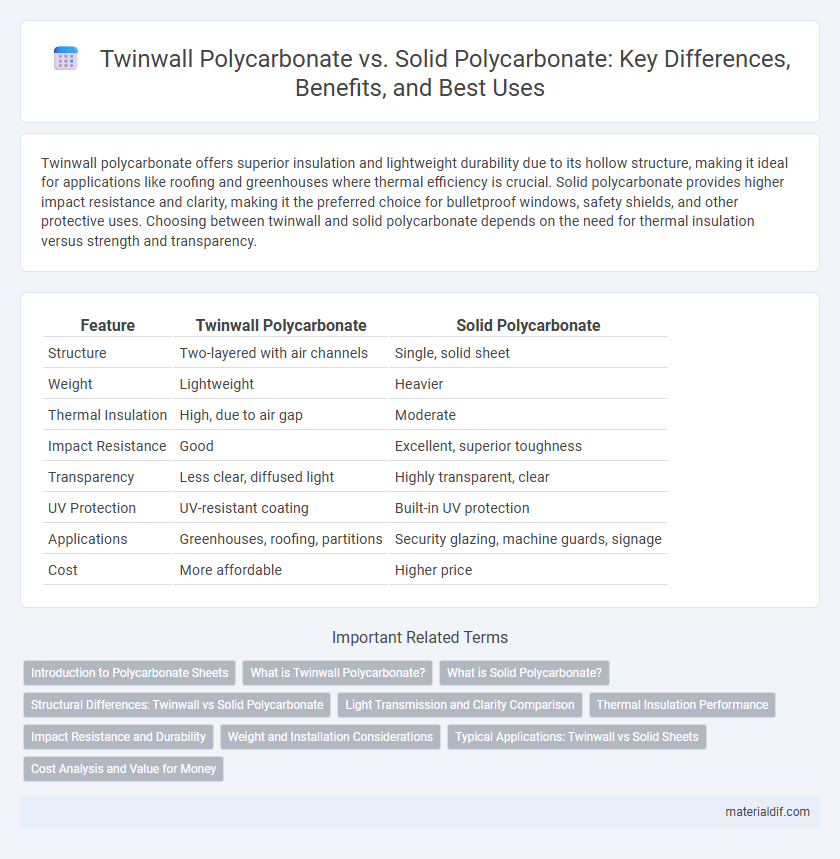
| Feature | Twinwall Polycarbonate | Solid Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Two-layered with air channels | Single, solid sheet |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Thermal Insulation | High, due to air gap | Moderate |
| Impact Resistance | Good | Excellent, superior toughness |
| Transparency | Less clear, diffused light | Highly transparent, clear |
| UV Protection | UV-resistant coating | Built-in UV protection |
| Applications | Greenhouses, roofing, partitions | Security glazing, machine guards, signage |
| Cost | More affordable | Higher price |
Introduction to Polycarbonate Sheets
Polycarbonate sheets are widely used for their durability, impact resistance, and lightweight properties in construction and manufacturing. Twinwall polycarbonate features a dual-layer structure with an air gap that enhances thermal insulation and reduces weight, making it ideal for applications requiring energy efficiency. Solid polycarbonate, known for its clarity and high strength, is preferred when maximum impact resistance and optical transparency are essential.
What is Twinwall Polycarbonate?
Twinwall polycarbonate is a lightweight, durable plastic material featuring two parallel layers separated by a ribbed structure, providing excellent insulation and impact resistance. Commonly used in greenhouses, skylights, and outdoor roofing, its design offers superior thermal performance compared to solid polycarbonate sheets. While solid polycarbonate is thicker and denser, twinwall polycarbonate balances strength with reduced weight and enhanced energy efficiency.
What is Solid Polycarbonate?
Solid polycarbonate is a highly durable, transparent thermoplastic known for its exceptional impact resistance and optical clarity. Unlike twinwall polycarbonate, which features a multi-wall structure for insulation and lightweight properties, solid polycarbonate is a dense, single-layer sheet commonly used in applications requiring maximum strength and transparency. Its resistance to UV radiation and high temperatures makes it ideal for protective glazing, automotive components, and bullet-resistant windows.
Structural Differences: Twinwall vs Solid Polycarbonate
Twinwall polycarbonate features a multi-wall structure with hollow channels between layers, enhancing thermal insulation and reducing weight without compromising strength. Solid polycarbonate consists of a single, dense sheet that offers superior impact resistance and clarity but is heavier and less insulating than twinwall panels. The structural difference makes twinwall ideal for roofing and glazing applications requiring light diffusion and insulation, whereas solid polycarbonate suits high-impact, transparent installations demanding maximum durability.
Light Transmission and Clarity Comparison
Twinwall polycarbonate offers diffuse light transmission, providing soft, evenly distributed natural light ideal for greenhouses and skylights, with clarity levels around 40-50%. Solid polycarbonate delivers superior clarity and light transmission, typically exceeding 80%, resembling glass while maintaining excellent impact resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring clear visibility. The choice between twinwall and solid polycarbonate depends on balancing light diffusion for glare reduction versus maximizing transparency for visual clarity.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Twinwall polycarbonate features a multi-wall structure that significantly enhances thermal insulation by trapping air between its layers, reducing heat transfer more effectively than solid polycarbonate. Solid polycarbonate, though impact-resistant and clear, offers less insulation due to its single-layer design, allowing more heat to pass through. For energy-efficient applications, twinwall polycarbonate is preferred as it provides superior thermal performance, reducing heating and cooling costs.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Twinwall polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance due to its multi-layered structure, which absorbs shocks and prevents cracking more effectively than solid polycarbonate. Solid polycarbonate, while highly durable and resistant to scratches, tends to be heavier and less flexible under impact stress. The honeycomb-like design of twinwall sheets provides enhanced durability in outdoor applications, making it ideal for long-lasting protective barriers and roofing.
Weight and Installation Considerations
Twinwall polycarbonate weighs significantly less than solid polycarbonate, making it easier to handle and install, especially on larger projects or vertical applications. The reduced weight leads to lower structural support requirements and faster installation times, enhancing overall efficiency. Solid polycarbonate, while heavier, offers more impact resistance but may demand sturdier framing and more labor during installation.
Typical Applications: Twinwall vs Solid Sheets
Twinwall polycarbonate sheets are commonly used in applications requiring lightweight insulation and diffuse light transmission, such as greenhouses, skylights, and roofing panels. Solid polycarbonate sheets provide superior impact resistance and clarity, making them ideal for security glazing, machine guards, and automotive components. Choosing between twinwall and solid sheets depends on balancing thermal insulation needs with strength and optical clarity in specific project requirements.
Cost Analysis and Value for Money
Twinwall polycarbonate offers significant cost savings compared to solid polycarbonate due to its lightweight structure and lower material consumption, making it ideal for large-scale applications requiring insulation and impact resistance. Although solid polycarbonate provides superior durability and clarity, its higher price per square meter often limits its use to areas demanding maximum strength and transparency. Evaluating value for money depends on project requirements, with twinwall polycarbonate delivering better insulation efficiency and cost-effectiveness for roofing and glazing, while solid polycarbonate is preferred for heavy-duty, high-impact applications.
Twinwall Polycarbonate vs Solid Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com