Monolithic polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring high strength and transparency. Multiwall polycarbonate features a layered structure that provides enhanced thermal insulation and reduced weight, suitable for energy-efficient building projects. Choosing between monolithic and multiwall polycarbonate depends on the balance needed between durability, light transmission, and insulation properties.
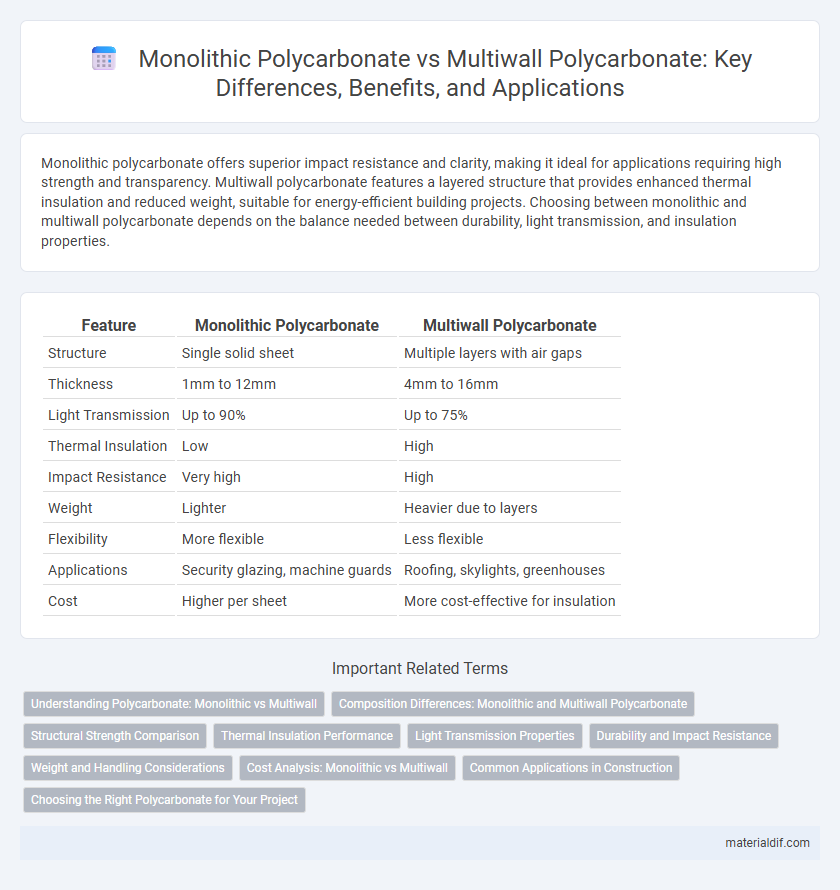
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Monolithic Polycarbonate | Multiwall Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single solid sheet | Multiple layers with air gaps |
| Thickness | 1mm to 12mm | 4mm to 16mm |
| Light Transmission | Up to 90% | Up to 75% |
| Thermal Insulation | Low | High |
| Impact Resistance | Very high | High |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier due to layers |
| Flexibility | More flexible | Less flexible |
| Applications | Security glazing, machine guards | Roofing, skylights, greenhouses |
| Cost | Higher per sheet | More cost-effective for insulation |
Understanding Polycarbonate: Monolithic vs Multiwall
Monolithic polycarbonate sheets offer high impact resistance and clear transparency, ideal for applications requiring maximum strength and optical clarity. Multiwall polycarbonate panels, featuring hollow channels, provide superior insulation and lightweight durability, making them suitable for energy-efficient roofing and glazing. Choosing between monolithic and multiwall polycarbonate depends on balancing factors such as thermal performance, structural strength, and cost-effectiveness.
Composition Differences: Monolithic and Multiwall Polycarbonate
Monolithic polycarbonate consists of a single solid sheet offering high impact resistance and optical clarity, while multiwall polycarbonate features a layered structure with hollow channels to enhance thermal insulation and reduce weight. The composition of monolithic polycarbonate is uniform, maximizing strength and transparency for applications like glazing and protective barriers. In contrast, multiwall polycarbonate's multi-layered design incorporates internal ribs that improve stiffness and energy efficiency, making it ideal for roofing and cladding systems.
Structural Strength Comparison
Monolithic polycarbonate offers superior structural strength due to its solid, uniform composition, making it highly resistant to impact and heavy loads. Multiwall polycarbonate, while lighter and providing better insulation, features a layered structure that reduces its overall strength compared to monolithic sheets. For applications demanding maximum durability and impact resistance, monolithic polycarbonate is the preferred choice.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Monolithic polycarbonate offers solid, transparent sheets with moderate thermal insulation, ideal for applications requiring high impact resistance and clarity. Multiwall polycarbonate features a hollow structure that traps air between layers, significantly enhancing thermal insulation performance by reducing heat transfer. This makes multiwall polycarbonate the preferred choice for energy-efficient glazing and structures where superior thermal regulation is critical.
Light Transmission Properties
Monolithic polycarbonate sheets offer superior light transmission, typically allowing around 80-90% of natural light to pass through, making them ideal for applications requiring maximum clarity. Multiwall polycarbonate panels, with their layered structure, reduce light transmission to approximately 40-70%, providing enhanced insulation and diffused lighting. The choice between monolithic and multiwall polycarbonate depends on the balance between light clarity and thermal performance needed in the project.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Monolithic polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and durability due to its solid, uniform structure, making it ideal for high-impact applications and environments requiring maximum strength. Multiwall polycarbonate, while offering good durability, features a layered design with air gaps that provide enhanced thermal insulation but slightly reduced impact resistance compared to monolithic sheets. Both types exhibit excellent UV resistance and weatherability, with monolithic sheets preferred for extreme impact scenarios and multiwall favored for lightweight, insulated construction projects.
Weight and Handling Considerations
Monolithic polycarbonate sheets are denser and heavier than multiwall polycarbonate panels, influencing transportation and installation efforts. Multiwall polycarbonate's lightweight structure enhances ease of handling and reduces labor costs in large-scale projects. Choosing the appropriate type depends on balancing strength requirements against weight limitations for efficient construction workflows.
Cost Analysis: Monolithic vs Multiwall
Monolithic polycarbonate typically incurs higher initial costs due to its solid structure and superior impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum strength and clarity. Multiwall polycarbonate offers more cost-effective solutions by providing excellent thermal insulation and weight reduction through its layered design, resulting in energy savings over time. When evaluating cost analysis, multiwall polycarbonate generally presents better long-term value in construction projects due to lower installation and energy expenses compared to monolithic sheets.
Common Applications in Construction
Monolithic polycarbonate is widely used in construction for transparent applications such as windows, skylights, and protective barriers due to its high impact resistance and clarity. Multiwall polycarbonate is favored for roofing, greenhouse panels, and insulation panels where thermal performance and lightweight durability are crucial. Both types offer UV protection and weather resistance but serve different roles based on structural and insulation needs.
Choosing the Right Polycarbonate for Your Project
Monolithic polycarbonate offers superior strength and clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum impact resistance and transparency such as glazing and protective barriers. Multiwall polycarbonate features a layered structure that provides enhanced insulation and lightweight properties, suitable for roofing, greenhouses, and energy-efficient building solutions. Selecting the right polycarbonate depends on project-specific needs like thermal performance, light diffusion, and structural demands to optimize cost-effectiveness and durability.
Monolithic Polycarbonate vs Multiwall Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com