Polycarbonate sheets offer flexibility and are ideal for applications requiring easy cutting and shaping, while polycarbonate panels are thicker and designed for enhanced strength and durability. Sheets are commonly used for DIY projects, greenhouse covers, and skylights, whereas panels are preferred in construction and industrial settings for their resistance to impact and weather. Both provide lightweight, UV-resistant protection but vary in thickness and rigidity depending on the intended use.
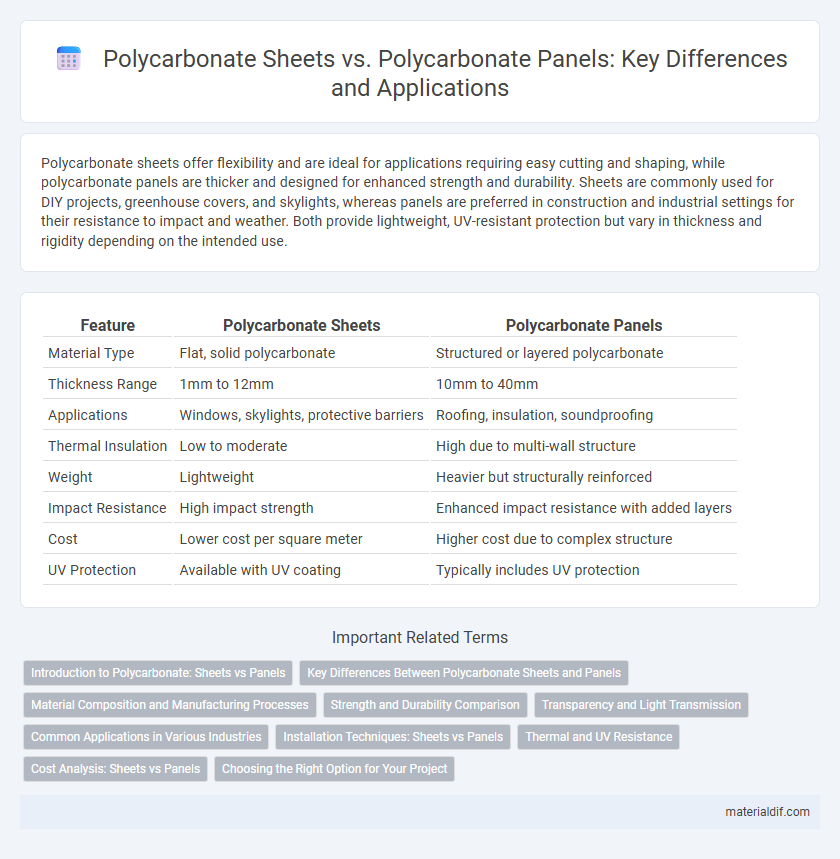
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polycarbonate Sheets | Polycarbonate Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Flat, solid polycarbonate | Structured or layered polycarbonate |
| Thickness Range | 1mm to 12mm | 10mm to 40mm |
| Applications | Windows, skylights, protective barriers | Roofing, insulation, soundproofing |
| Thermal Insulation | Low to moderate | High due to multi-wall structure |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier but structurally reinforced |
| Impact Resistance | High impact strength | Enhanced impact resistance with added layers |
| Cost | Lower cost per square meter | Higher cost due to complex structure |
| UV Protection | Available with UV coating | Typically includes UV protection |
Introduction to Polycarbonate: Sheets vs Panels
Polycarbonate sheets and panels are versatile materials commonly used in construction, offering exceptional impact resistance and clarity. Sheets typically refer to flat, thin layers suitable for glazing, roofing, and protective barriers, while panels are often thicker and sometimes include multi-wall structures for enhanced insulation. Both types provide UV resistance and lightweight strength, making them ideal choices for architectural and industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Polycarbonate Sheets and Panels
Polycarbonate sheets are thin, flexible, and primarily used for glazing applications, offering high impact resistance and excellent light transmission. Polycarbonate panels tend to be thicker, rigid, and designed for structural purposes such as roofing and wall cladding, providing enhanced durability and thermal insulation. Key differences include thickness, rigidity, and typical use cases, with sheets favoring transparency and panels focusing on strength and insulation.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Polycarbonate sheets are typically produced through extrusion, resulting in continuous, flat products with uniform thickness, whereas polycarbonate panels are often manufactured by compression molding or lamination, offering enhanced structural rigidity and customized shapes. Both sheets and panels share a base material composed of thermoplastic polymers known for high impact resistance and optical clarity, but panels may include additional layers or reinforcements to improve thermal insulation and load-bearing capacity. The choice between sheets and panels depends on the specific application requirements, balancing factors like flexibility, durability, and manufacturing precision.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polycarbonate sheets and polycarbonate panels both offer exceptional strength, with sheets typically providing higher impact resistance due to their uniform thickness and solid structure. Panels often incorporate multiwall designs that enhance durability by offering improved insulation and resistance to cracking under stress. When evaluating strength and durability, solid polycarbonate sheets generally outperform panels in terms of impact resistance, while panels excel in thermal performance and structural integrity over larger spans.
Transparency and Light Transmission
Polycarbonate sheets offer superior transparency and higher light transmission rates, typically around 88-92%, making them ideal for applications requiring clear visibility and natural lighting. In contrast, polycarbonate panels often have a multiwall or corrugated structure that reduces transparency but enhances thermal insulation and impact resistance. Choosing between sheets and panels depends on the balance between maximum light diffusion and durability needs in architectural or industrial projects.
Common Applications in Various Industries
Polycarbonate sheets are extensively used in the construction industry for roofing, skylights, and greenhouses due to their lightweight, impact resistance, and UV protection, making them ideal for outdoor and structural applications. Polycarbonate panels are preferred in automotive manufacturing, electronics, and signage for their durability, thermal insulation, and ability to be molded into precise shapes to enhance product design and performance. Both materials serve essential roles across industries such as architecture, transportation, and advertising, where transparent yet robust solutions are required.
Installation Techniques: Sheets vs Panels
Polycarbonate sheets offer straightforward installation with flexibility for cutting and shaping, making them ideal for DIY projects and custom applications, while polycarbonate panels usually come pre-assembled or framed, streamlining the installation process for larger-scale or commercial projects. Sheets require precise measurement and additional sealing materials to prevent water ingress, whereas panels often integrate gasket systems and mounting brackets to ensure secure, weatherproof fits. Choosing between sheets and panels depends on the installation environment, with sheets favored for versatility and panels preferred for quicker, more standardized setups.
Thermal and UV Resistance
Polycarbonate sheets exhibit superior thermal resistance with heat deflection temperatures typically around 135degC, making them ideal for applications requiring stability under high temperatures. Polycarbonate panels, often thicker and reinforced, offer enhanced UV resistance due to specialized coatings that prevent yellowing and degradation from prolonged sun exposure. Both materials maintain excellent impact strength, but the choice depends on the specific thermal and UV resistance requirements for outdoor or industrial use.
Cost Analysis: Sheets vs Panels
Polycarbonate sheets generally offer a lower initial cost compared to polycarbonate panels, making them a budget-friendly option for lightweight and straightforward applications. However, polycarbonate panels, often pre-fabricated with added structural support and insulation, may have higher upfront expenses but provide better long-term value through enhanced durability and energy efficiency. Budget considerations should balance immediate material costs against performance benefits and installation requirements.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Project
Polycarbonate sheets offer a lightweight, durable option ideal for applications requiring easy cutting and installation, such as windows or skylights. Polycarbonate panels provide enhanced structural strength and are better suited for larger construction projects like roofing or facades where load-bearing capacity is essential. Evaluating the specific needs of your project, including impact resistance, size, and thermal performance, ensures selecting the right polycarbonate form for optimal results.
Polycarbonate Sheets vs Polycarbonate Panels Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com