BPA-free polycarbonate offers a safer alternative by eliminating the risk of bisphenol-A leaching, which is linked to potential health concerns such as hormonal disruptions. Polycarbonate containing BPA is durable and clear but may pose health risks, especially when exposed to heat or acidic substances. Choosing BPA-free polycarbonate ensures safety without compromising the material's strength and transparency.
Table of Comparison
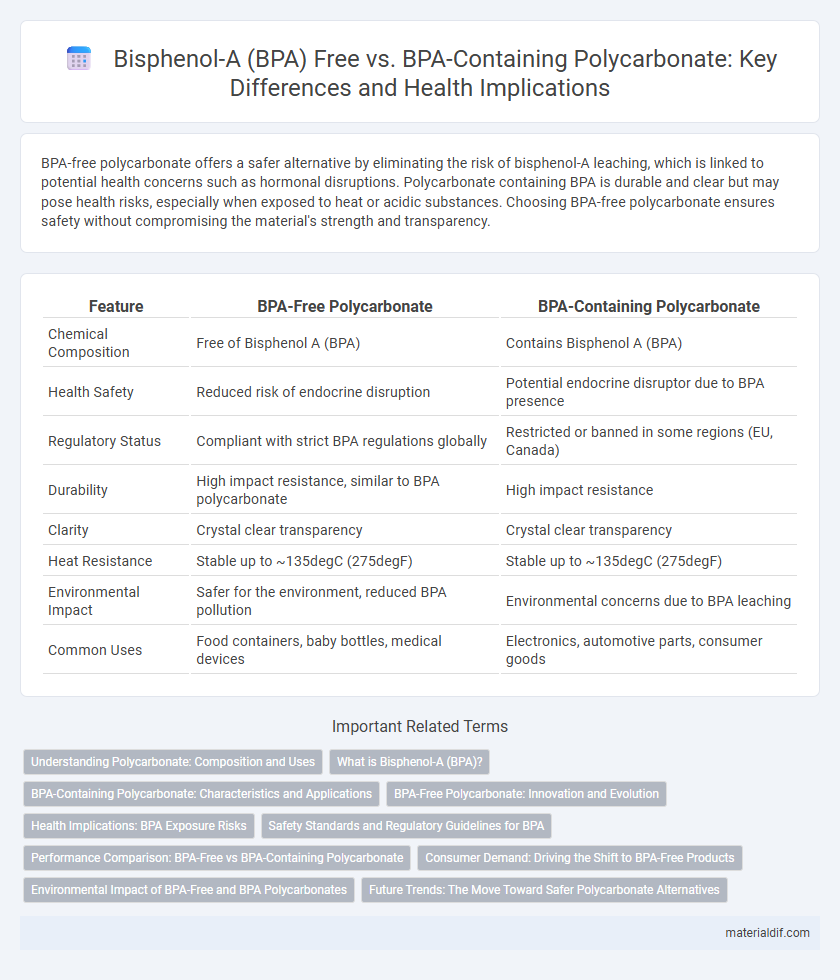
| Feature | BPA-Free Polycarbonate | BPA-Containing Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Free of Bisphenol A (BPA) | Contains Bisphenol A (BPA) |
| Health Safety | Reduced risk of endocrine disruption | Potential endocrine disruptor due to BPA presence |
| Regulatory Status | Compliant with strict BPA regulations globally | Restricted or banned in some regions (EU, Canada) |
| Durability | High impact resistance, similar to BPA polycarbonate | High impact resistance |
| Clarity | Crystal clear transparency | Crystal clear transparency |
| Heat Resistance | Stable up to ~135degC (275degF) | Stable up to ~135degC (275degF) |
| Environmental Impact | Safer for the environment, reduced BPA pollution | Environmental concerns due to BPA leaching |
| Common Uses | Food containers, baby bottles, medical devices | Electronics, automotive parts, consumer goods |
Understanding Polycarbonate: Composition and Uses
Polycarbonate is a durable thermoplastic polymer composed primarily of bisphenol-A (BPA) and phosgene, widely used in automotive parts, electronics, and optical disks. BPA-free polycarbonate substitutes BPA with alternative monomers to reduce potential health risks while maintaining similar mechanical strength and transparency. Understanding the differences in composition aids in selecting the appropriate polycarbonate type for applications requiring safety compliance and environmental considerations.
What is Bisphenol-A (BPA)?
Bisphenol-A (BPA) is an industrial chemical used in manufacturing polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins, known for its durability and clarity. BPA-containing polycarbonate products have raised health concerns due to potential endocrine-disrupting effects when BPA leaches into food or beverages. BPA-free polycarbonate alternatives use safer compounds to eliminate these risks while maintaining similar strength and transparency characteristics.
BPA-Containing Polycarbonate: Characteristics and Applications
BPA-containing polycarbonate is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic widely used in manufacturing optical lenses, electronic components, and automotive parts due to its clarity and strength. This material exhibits excellent heat resistance and dimensional stability, making it suitable for high-performance applications where structural integrity is critical. Despite ongoing health concerns related to BPA leaching, its superior mechanical properties and versatility continue to drive its use in industrial and commercial sectors.
BPA-Free Polycarbonate: Innovation and Evolution
BPA-free polycarbonate represents a significant innovation in the plastics industry, developed to eliminate the health concerns associated with Bisphenol-A, a chemical traditionally used in BPA-containing polycarbonate production. This advanced material maintains the durability, clarity, and impact resistance of conventional polycarbonate while ensuring safety for consumer products such as water bottles, food containers, and medical devices. The evolution toward BPA-free polycarbonate reflects growing regulatory pressure and consumer demand for safer, eco-friendly alternatives in plastic manufacturing.
Health Implications: BPA Exposure Risks
BPA-free polycarbonate products eliminate the risk of bisphenol-A leaching, a chemical linked to hormonal disruptions, reproductive issues, and increased cancer risk. Studies show that BPA exposure, common in BPA-containing polycarbonate, can affect fetal development and contribute to metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes. Choosing BPA-free polycarbonate significantly reduces these health concerns, ensuring safer use in food and beverage containers.
Safety Standards and Regulatory Guidelines for BPA
BPA-free polycarbonate meets stringent safety standards and regulatory guidelines established by agencies such as the FDA and EFSA, ensuring reduced health risks associated with endocrine disruption. Regulatory frameworks mandate clear labeling and limit BPA migration levels in polycarbonate products, emphasizing consumer protection. BPA-containing polycarbonate remains subject to ongoing scrutiny, with many regions enforcing phased restrictions to minimize BPA exposure in food and beverage applications.
Performance Comparison: BPA-Free vs BPA-Containing Polycarbonate
BPA-free polycarbonate offers comparable impact resistance and transparency to BPA-containing variants, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and clarity. BPA-containing polycarbonate typically exhibits slightly higher heat resistance and dimensional stability, which can be critical for high-temperature uses. Both types maintain excellent mechanical properties, but BPA-free formulations prioritize safety and regulatory compliance without significantly compromising performance.
Consumer Demand: Driving the Shift to BPA-Free Products
Consumer demand for safer and environmentally friendly materials has significantly accelerated the shift from BPA-containing polycarbonate to BPA-free alternatives. Studies linking Bisphenol-A to potential health risks have pushed manufacturers to develop BPA-free polycarbonate that maintains durability and clarity without compromising safety. Market trends show a growing preference for BPA-free products in sectors such as baby bottles, food containers, and water bottles, reflecting heightened awareness and regulatory pressures.
Environmental Impact of BPA-Free and BPA Polycarbonates
BPA-free polycarbonate reduces the release of bisphenol-A, a chemical linked to environmental pollution and endocrine disruption in wildlife, making it a safer alternative for ecosystems. BPA-containing polycarbonates contribute to hazardous waste accumulation and can leach BPA into soil and water during disposal or degradation, posing risks to aquatic and terrestrial organisms. Selecting BPA-free polycarbonate lowers the ecological footprint by minimizing toxic chemical exposure and supporting sustainable waste management practices.
Future Trends: The Move Toward Safer Polycarbonate Alternatives
The future of polycarbonate focuses heavily on BPA-free alternatives due to increasing health and environmental concerns linked to Bisphenol-A. Innovations in bio-based and non-toxic monomers enable the production of safer polycarbonate materials that maintain durability and transparency without harmful chemical exposure. Growing regulatory pressure and consumer demand drive industry investment in sustainable, BPA-free polycarbonate technologies designed for medical, food packaging, and consumer electronics applications.
Bisphenol-A (BPA) Free vs BPA-Containing Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com