Food grade polycarbonate is specifically manufactured to meet strict safety standards, ensuring it is free from harmful chemicals and safe for direct contact with food and beverages. Industrial grade polycarbonate, while highly durable and impact-resistant, may contain additives or impurities unsuitable for food use and should be reserved for non-food contact applications. Choosing food grade polycarbonate for containers and utensils guarantees compliance with health regulations and prevents contamination risks.
Table of Comparison
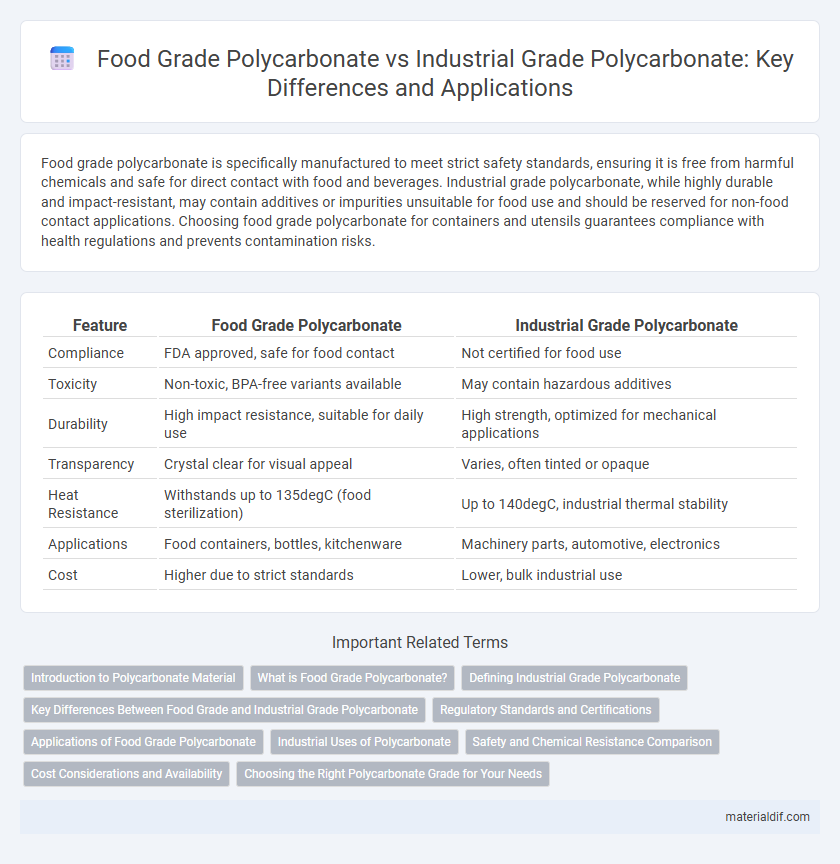
| Feature | Food Grade Polycarbonate | Industrial Grade Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Compliance | FDA approved, safe for food contact | Not certified for food use |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, BPA-free variants available | May contain hazardous additives |
| Durability | High impact resistance, suitable for daily use | High strength, optimized for mechanical applications |
| Transparency | Crystal clear for visual appeal | Varies, often tinted or opaque |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands up to 135degC (food sterilization) | Up to 140degC, industrial thermal stability |
| Applications | Food containers, bottles, kitchenware | Machinery parts, automotive, electronics |
| Cost | Higher due to strict standards | Lower, bulk industrial use |
Introduction to Polycarbonate Material
Polycarbonate is a durable, lightweight thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and optical clarity, widely used in various applications including food storage and industrial components. Food grade polycarbonate meets strict FDA and EU regulations ensuring it is safe for contact with consumables, free from harmful chemicals like BPA. Industrial grade polycarbonate, while offering similar mechanical properties, is typically untreated for food safety and suited for structural or mechanical purposes where direct food contact is not required.
What is Food Grade Polycarbonate?
Food grade polycarbonate is a high-quality plastic material specifically engineered to meet strict safety standards for direct contact with food and beverages, ensuring it is free from harmful chemicals like BPA. It exhibits excellent heat resistance, durability, and transparency, making it ideal for reusable food containers, water bottles, and kitchenware. Unlike industrial grade polycarbonate, food grade variants undergo rigorous testing and certification by regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EFSA to guarantee consumer safety.
Defining Industrial Grade Polycarbonate
Industrial grade polycarbonate is a high-performance thermoplastic designed for heavy-duty applications, featuring enhanced impact resistance and heat tolerance compared to food grade polycarbonate. Unlike food grade polycarbonate, which complies with FDA regulations for safe contact with consumables, industrial grade polycarbonate is optimized for structural, automotive, and electronic components where durability and thermal stability are critical. This type of polycarbonate often contains additives for UV protection and flame retardance, making it suitable for demanding industrial environments.
Key Differences Between Food Grade and Industrial Grade Polycarbonate
Food grade polycarbonate is formulated to meet strict safety standards, ensuring it is BPA-free, non-toxic, and suitable for direct contact with consumables without leaching harmful substances. Industrial grade polycarbonate prioritizes mechanical strength and thermal resistance, making it ideal for manufacturing components, electronics, and automotive parts but not certified for food contact. The key differences lie in regulatory compliance, chemical composition, and intended application, with food grade emphasizing health safety and industrial grade focusing on durability and performance under harsh conditions.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Food grade polycarbonate complies with stringent regulatory standards such as FDA 21 CFR 177.1580 and EU Regulation No. 10/2011, ensuring it is safe for direct contact with food and beverages. Industrial grade polycarbonate lacks these certifications and may contain additives or impurities unsuitable for food applications, limiting its use to non-food environments. Both grades differ significantly in material composition, with food grade necessitating rigorous testing to meet global safety and certification requirements.
Applications of Food Grade Polycarbonate
Food grade polycarbonate is extensively used in applications requiring high safety and durability standards, such as reusable water bottles, food storage containers, and medical-grade equipment. It meets stringent FDA and EU regulations for non-toxicity and resistance to high temperatures, ensuring no harmful chemical leaching into consumables. The material's transparency and impact resistance also make it ideal for packaging and kitchenware that demand clear visibility and long-lasting strength.
Industrial Uses of Polycarbonate
Industrial grade polycarbonate is engineered for superior durability, impact resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for manufacturing automotive components, electrical housings, and safety helmets. Unlike food grade polycarbonate, which meets strict FDA standards for direct food contact, industrial grade variants prioritize mechanical strength and chemical resistance to withstand harsh environments. This material's versatility enables its widespread application in construction, electronics, and industrial machinery where high performance and reliability are critical.
Safety and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Food grade polycarbonate meets stringent FDA and EFSA regulations ensuring it is free from harmful chemicals like BPA, making it safe for direct food contact and resistant to leaching under normal use. Industrial grade polycarbonate lacks such certifications and may contain additives or impurities that reduce its safety for food applications and lower its chemical resistance against aggressive solvents. The enhanced chemical resistance of food grade polycarbonate allows it to withstand repeated cleaning and exposure to mild acids or alkalis without degrading, unlike industrial grade variants prone to surface damage and contamination.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Food grade polycarbonate typically incurs higher costs due to stringent safety standards and certifications required for direct food contact applications, resulting in more rigorous production processes. Industrial grade polycarbonate is generally more affordable and widely available, as it caters to non-food applications with less stringent regulatory requirements. Availability of food grade polycarbonate can be limited compared to industrial grade, impacting lead times and procurement costs in manufacturing or packaging industries.
Choosing the Right Polycarbonate Grade for Your Needs
Food grade polycarbonate is manufactured to meet strict safety standards, ensuring it is BPA-free and suitable for contact with consumables, making it ideal for food containers, water bottles, and kitchenware. Industrial grade polycarbonate offers enhanced impact resistance, UV protection, and thermal stability, tailored for construction, automotive, and electronic applications where durability and mechanical performance are critical. Selecting the appropriate polycarbonate grade depends on regulatory compliance, chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and the specific environmental conditions of the intended use.
Food Grade Polycarbonate vs Industrial Grade Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com