Polycarbonate molding involves shaping polycarbonate material using heat and pressure, allowing for precise and durable finished products with excellent impact resistance and clarity. Injection molding, a specific type of polycarbonate molding, injects molten polycarbonate into molds under high pressure, enabling high-volume production with consistent quality and intricate design details. Choosing between polycarbonate molding methods depends on production scale, design complexity, and desired material properties.
Table of Comparison
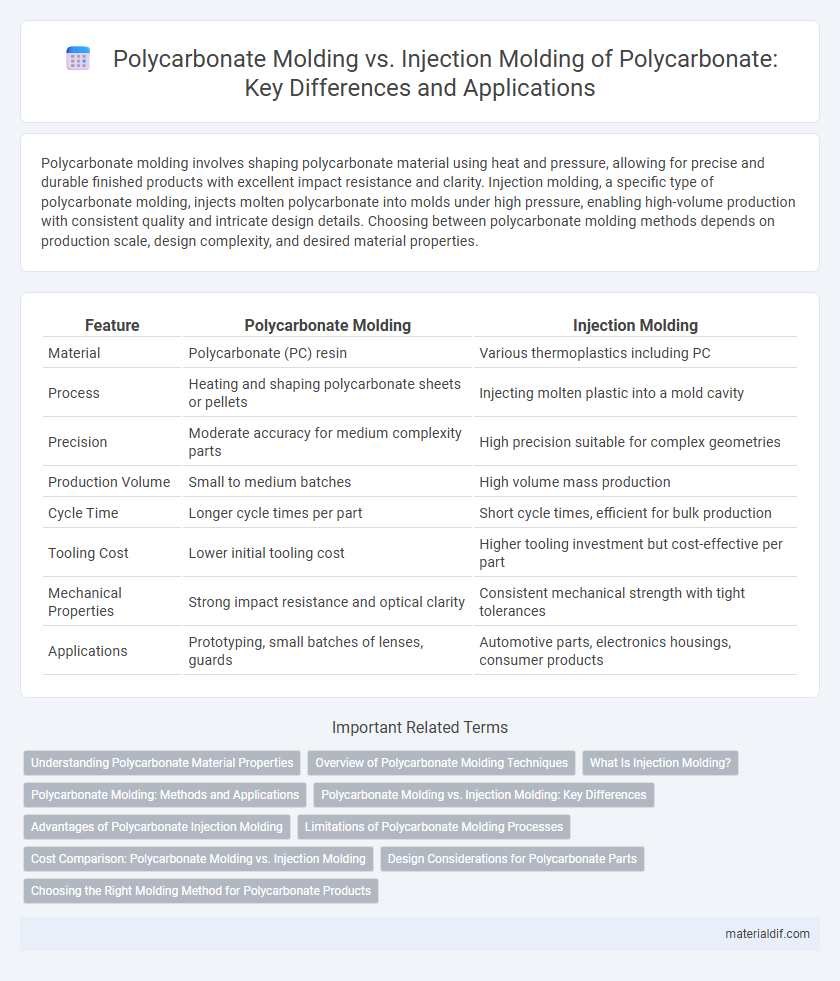
| Feature | Polycarbonate Molding | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polycarbonate (PC) resin | Various thermoplastics including PC |
| Process | Heating and shaping polycarbonate sheets or pellets | Injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity |
| Precision | Moderate accuracy for medium complexity parts | High precision suitable for complex geometries |
| Production Volume | Small to medium batches | High volume mass production |
| Cycle Time | Longer cycle times per part | Short cycle times, efficient for bulk production |
| Tooling Cost | Lower initial tooling cost | Higher tooling investment but cost-effective per part |
| Mechanical Properties | Strong impact resistance and optical clarity | Consistent mechanical strength with tight tolerances |
| Applications | Prototyping, small batches of lenses, guards | Automotive parts, electronics housings, consumer products |
Understanding Polycarbonate Material Properties
Polycarbonate molding leverages the material's high impact resistance, thermal stability, and optical clarity to produce durable, precise components ideal for engineering applications. Understanding polycarbonate's properties, such as its ability to withstand temperatures up to 145degC and its excellent dimensional stability, is crucial for selecting the appropriate molding technique. Injection molding offers fast production and complex geometries but requires careful control of melt temperature and cooling rates to prevent material degradation and ensure optimal mechanical performance.
Overview of Polycarbonate Molding Techniques
Polycarbonate molding techniques primarily include injection molding and compression molding, each suited for specific applications and design requirements. Injection molding of polycarbonate involves melting pellets and injecting the material into a mold cavity, offering high precision and complex geometries with excellent surface finish. Compression molding, while less common for polycarbonate, applies heat and pressure to shape the material in a mold, typically used for larger or less detailed parts requiring strong mechanical properties.
What Is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten polycarbonate is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure to form precise and complex shapes. This method offers high production efficiency, excellent surface finish, and consistent dimensions, making it ideal for mass-producing polycarbonate components. Injection molding allows for intricate designs with tight tolerances, enhancing the functionality and durability of polycarbonate products.
Polycarbonate Molding: Methods and Applications
Polycarbonate molding primarily involves methods such as injection molding, extrusion, and compression molding, each tailored to enhance the material's durability and clarity. Injection molding of polycarbonate enables the production of complex geometries with high precision, making it ideal for automotive parts, electronic housings, and medical devices. The material's excellent impact resistance and thermal stability ensure optimal performance in demanding applications requiring robust and transparent components.
Polycarbonate Molding vs. Injection Molding: Key Differences
Polycarbonate molding involves shaping polycarbonate material through processes like extrusion or compression, emphasizing thermal resistance and impact strength. Injection molding uses molten polycarbonate injected into molds, enabling high precision and complex geometries with rapid production cycles. Key differences include material viscosity handling, mold design complexity, and production volume efficiency specific to polycarbonate properties.
Advantages of Polycarbonate Injection Molding
Polycarbonate injection molding offers superior precision and faster production cycles compared to traditional polycarbonate molding techniques, enabling complex and detailed part geometries. This process enhances material strength and impact resistance by ensuring uniform polymer flow and minimizing defects such as voids or sink marks. High scalability and automation compatibility make polycarbonate injection molding ideal for mass production with consistent quality and reduced labor costs.
Limitations of Polycarbonate Molding Processes
Polycarbonate molding encounters limitations such as high processing temperatures that can cause material degradation and reduce mechanical properties. The complexity of mold designs is constrained to prevent residual stresses and warping during cooling phases. Moreover, polycarbonate's sensitivity to moisture necessitates precise drying procedures to avoid defects like bubbles and surface imperfections.
Cost Comparison: Polycarbonate Molding vs. Injection Molding
Polycarbonate molding generally incurs higher upfront costs due to specialized tooling and material handling requirements, while injection molding offers lower per-unit costs for large production runs because of efficient cycle times and automation. Polycarbonate molding is cost-effective for low to medium volumes where customization and precision are critical, whereas injection molding economies of scale make it more suitable for mass production. Evaluating total cost of ownership should consider tooling amortization, cycle time, and material waste specific to polycarbonate's thermal and mechanical properties.
Design Considerations for Polycarbonate Parts
Polycarbonate molding requires precise temperature control and mold design to prevent material degradation and ensure dimensional stability. Injection molding of polycarbonate mandates careful gate placement and optimized cooling channels to minimize warpage and internal stresses. Design considerations must account for polycarbonate's high impact resistance and thermal expansion properties to achieve durable, high-quality parts.
Choosing the Right Molding Method for Polycarbonate Products
Polycarbonate molding methods include injection molding and compression molding, each offering distinct advantages depending on product specifications. Injection molding provides high precision, fast production cycles, and is ideal for complex shapes with excellent surface finishes. Compression molding is suited for simpler, larger parts requiring enhanced mechanical strength and reduced material waste, helping manufacturers optimize performance and cost-efficiency for polycarbonate products.
Polycarbonate Molding vs Injection Molding Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com