Polycarbonate laminates consist of multiple thin layers bonded together, offering enhanced impact resistance and improved sound insulation compared to polycarbonate monolithic sheets, which are single-layered and provide superior clarity and light transmission. Laminates are ideal for applications requiring higher durability and noise reduction, while monolithic sheets are preferred for projects needing maximum transparency and lightweight construction. Choosing between the two depends on specific performance requirements such as strength, acoustic properties, and optical clarity.
Table of Comparison
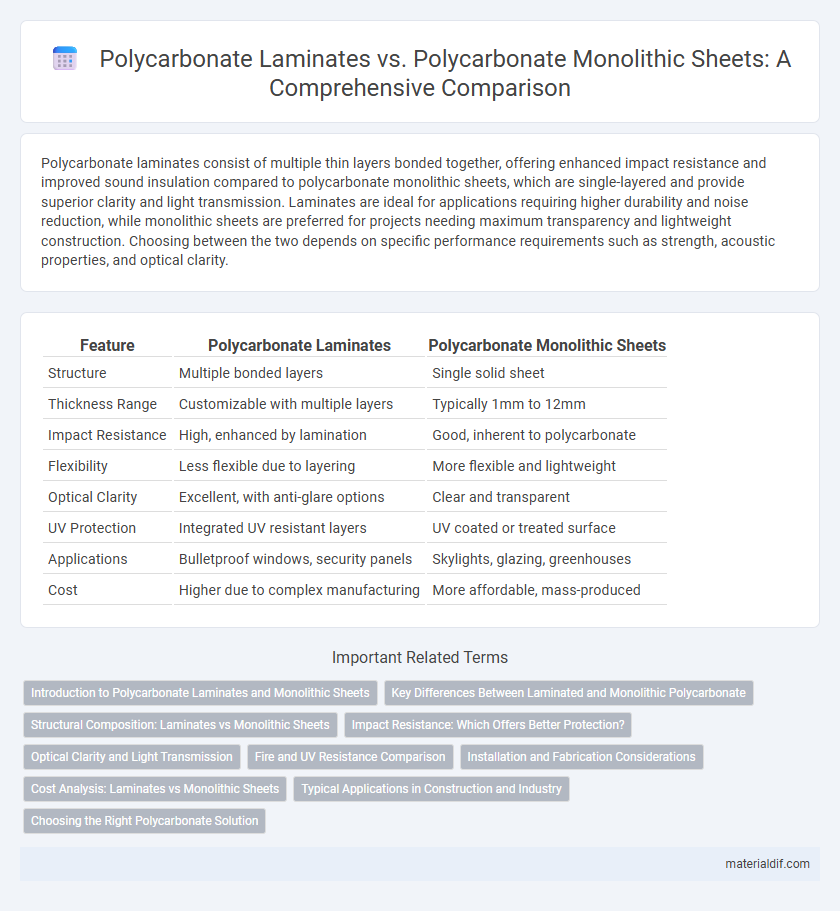
| Feature | Polycarbonate Laminates | Polycarbonate Monolithic Sheets |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Multiple bonded layers | Single solid sheet |
| Thickness Range | Customizable with multiple layers | Typically 1mm to 12mm |
| Impact Resistance | High, enhanced by lamination | Good, inherent to polycarbonate |
| Flexibility | Less flexible due to layering | More flexible and lightweight |
| Optical Clarity | Excellent, with anti-glare options | Clear and transparent |
| UV Protection | Integrated UV resistant layers | UV coated or treated surface |
| Applications | Bulletproof windows, security panels | Skylights, glazing, greenhouses |
| Cost | Higher due to complex manufacturing | More affordable, mass-produced |
Introduction to Polycarbonate Laminates and Monolithic Sheets
Polycarbonate laminates consist of multiple layers of polycarbonate sheets bonded together to enhance strength, impact resistance, and thermal insulation compared to monolithic sheets. Monolithic polycarbonate sheets are single, solid layers known for their excellent clarity, high impact resistance, and lightweight properties, making them ideal for glazing and security applications. The choice between polycarbonate laminates and monolithic sheets depends on specific requirements for durability, optical clarity, and application environment.
Key Differences Between Laminated and Monolithic Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate laminates consist of multiple layers bonded together, enhancing impact resistance and sound insulation compared to single-layer monolithic polycarbonate sheets. Monolithic polycarbonate sheets offer higher transparency and lighter weight, making them suitable for applications requiring clear visibility and ease of installation. Laminates provide superior thermal insulation and UV protection due to their layered structure, while monolithic sheets excel in flexibility and cost-effectiveness for less demanding environments.
Structural Composition: Laminates vs Monolithic Sheets
Polycarbonate laminates consist of multiple polycarbonate layers bonded together, enhancing impact resistance and structural integrity compared to monolithic sheets. In contrast, polycarbonate monolithic sheets are single, solid pieces offering uniform strength but lower resistance to crack propagation and impact stress. The layered composition of laminates provides improved durability and flexibility, making them ideal for applications demanding superior mechanical performance.
Impact Resistance: Which Offers Better Protection?
Polycarbonate laminates consist of multiple layers bonded together, enhancing their ability to absorb and distribute impact forces more effectively than monolithic sheets. Monolithic polycarbonate sheets, although inherently strong and resistant to impact, are more prone to cracking under severe stress compared to laminated versions. For applications requiring superior impact resistance, polycarbonate laminates provide better protection by combining flexibility and toughness through their layered structure.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Polycarbonate laminates offer enhanced optical clarity and superior light transmission by combining multiple layers with specialized coatings that reduce glare and improve UV resistance. In contrast, polycarbonate monolithic sheets provide consistent transparency but may exhibit slight haze or reduced clarity due to inherent material thickness. Selecting laminates is ideal for applications requiring maximum visual clarity and light diffusion, such as architectural glazing and display cases.
Fire and UV Resistance Comparison
Polycarbonate laminates offer enhanced fire resistance compared to polycarbonate monolithic sheets due to their multi-layer structure that slows flame propagation and reduces smoke emission. UV resistance is superior in laminated polycarbonate as interlayers can contain UV inhibitors, providing longer-lasting protection against yellowing and degradation under prolonged sunlight exposure. Monolithic sheets, while durable, tend to be more vulnerable to UV damage and may ignite more rapidly without the additional layers found in laminates.
Installation and Fabrication Considerations
Polycarbonate laminates offer enhanced flexibility in installation due to their layered structure, allowing for easier cutting and shaping compared to monolithic sheets which require more precise handling to prevent cracking. Fabrication of polycarbonate laminates accommodates multi-layer bonding techniques, improving impact resistance and thermal insulation, whereas monolithic sheets prioritize single-layer uniformity and straightforward processing. Installation of laminates demands attention to adhesive compatibility and layering alignment, while monolithic sheets focus on proper thermal expansion allowance and fastening to maintain structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: Laminates vs Monolithic Sheets
Polycarbonate laminates typically incur higher upfront costs compared to polycarbonate monolithic sheets due to additional manufacturing steps involving layering and bonding processes. However, laminates offer enhanced durability, impact resistance, and UV protection, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Monolithic sheets present a cost-effective solution for applications prioritizing affordability and ease of installation over enhanced performance features.
Typical Applications in Construction and Industry
Polycarbonate laminates are widely used in construction for roofing, skylights, and sound barriers due to their enhanced impact resistance, UV protection, and thermal insulation, making them ideal for outdoor and high-traffic environments. Polycarbonate monolithic sheets find applications in industrial settings such as machine guards, safety glazing, and greenhouses, where their transparency, lightweight properties, and high durability provide effective protection and visibility. Both materials offer excellent strength and weather resistance, but laminates excel in multi-layer protection while monolithic sheets are preferred for straightforward, cost-effective installations.
Choosing the Right Polycarbonate Solution
Polycarbonate laminates offer enhanced impact resistance and superior UV protection compared to polycarbonate monolithic sheets, making them ideal for outdoor and high-stress applications. Monolithic sheets provide excellent clarity and are more cost-effective for indoor uses where less durability is required. Selecting the right polycarbonate solution depends on factors like environmental exposure, structural demands, and budget constraints.
Polycarbonate Laminates vs Polycarbonate Monolithic Sheets Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com